|
Karnataka Public Service Commission
Karnataka Public Service Commission, chiefly known as KPSC is a government agency of Karnataka state, aimed to make recruitments to various civil services through competitive and departmental examinations in its jurisdiction under the area of 191,791 km2 (74,051 sq mi). History Karnataka state was initially serving without having any recruitment agency. But on 16 May 1921, the government laid the foundation of the ''Central Recruitment Board''. It was headed by a commissioner secretary on 19 January 1940 when the country was under British rule. After 5 years of the independence, the Public Service Commission was constituted on 18 May 1951 under the provisions of the Constitution of India and ''Public Service Commission Regulations 1950''. H.B. Gundappa Gowda, was appointed as the first Chairman and Sri George Matthan, and Sri H.M. Mallikarjunappa, as Members of the Commission in May 1951. Starting with Sri H.B. Gundappa Gowda, 13 Chairmen and 67 Members have been appointed to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
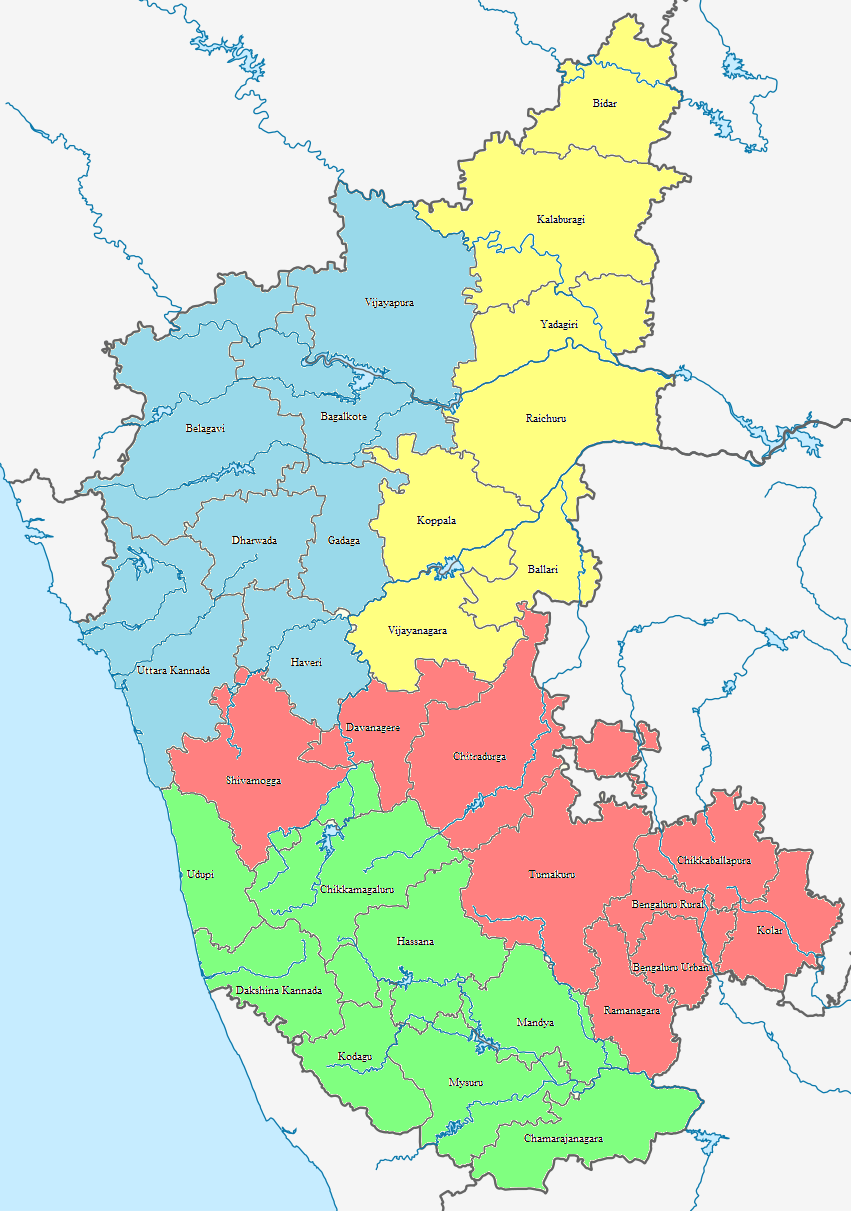
Karnataka
Karnataka (; ISO: , , also known as Karunāḍu) is a state in the southwestern region of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, with the passage of the States Reorganisation Act. Originally known as Mysore State , it was renamed ''Karnataka'' in 1973. The state corresponds to the Carnatic region. Its capital and largest city is Bengaluru. Karnataka is bordered by the Lakshadweep Sea to the west, Goa to the northwest, Maharashtra to the north, Telangana to the northeast, Andhra Pradesh to the east, Tamil Nadu to the southeast, and Kerala to the southwest. It is the only southern state to have land borders with all of the other four southern Indian sister states. The state covers an area of , or 5.83 percent of the total geographical area of India. It is the sixth-largest Indian state by area. With 61,130,704 inhabitants at the 2011 census, Karnataka is the eighth-largest state by population, comprising 31 districts. Kannada, one of the classical languages of India, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengaluru
Bangalore (), officially Bengaluru (), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Karnataka. It has a population of more than and a metropolitan population of around , making it the third most populous city and fifth most populous urban agglomeration in India, as well as the largest city in South India, and the 27th largest city in the world. Located on the Deccan Plateau, at a height of over above sea level, Bangalore has a pleasant climate throughout the year, with its parks and green spaces earning it the reputation as the "Garden City" of India. Its elevation is the highest among the major cities of India. An aerospace, heavy engineering and electronics hub since the 1960s, Bangalore is widely regarded as the "Silicon Valley of India" because of its role as the nation's leading information technology (IT) exporter.——— In the Ease of Living Index 2020 (published by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs), it was ranked the most livable Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Public Service Commission
The Union Public Service Commission (ISO: ), commonly abbreviated as UPSC, is India's premier central recruitment agency for recruitment of all the Group 'A' officers under Government of India. It is responsible for appointments to and examinations for all of the Group 'A' posts of all the central government establishments which also includes all of the central public sector undertakings and all of the central autonomous bodies. While Department of Personnel and Training is the central personnel agency in India. The agency's charter is granted by Part XIV of the Constitution of India, titled as ''Services Under the Union and the States.'' The commission is mandated by the Constitution for appointments to the services of the Union and All India Services. It is also required to be consulted by the Government in matters relating to the appointment, transfer, promotion and disciplinary matters. The commission reports directly to the President and can advise the Government thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Service Of India
The Civil Services refer to the career government civil servants who are the permanent executive branch of the Republic of India. Elected cabinet ministers determine policy, and civil servants carry it out. Central Civil Servants are employees of the Government of India or of the states, but not all employees of the Government are civil servants. As of 2010, there were 6.4 million government employees in India but fewer than 50,000 civil servants to administer them. The agencies with the most personnel are with the Central Secretariat Service and Indian Revenue Service (IT and C&CE). The Government of India approved the formation of Indian Skill Development Service in 2015, and the Indian Enterprise Development Service in 2016. Further, the Cabinet of India approved merging all the central civil services under Indian Railways which are Indian Railway Accounts Service, Indian Railway Traffic Service, Indian Railway Personnel Service and Railway Protection Force Service int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Competitive Examination
An examination (exam or evaluation) or test is an educational assessment intended to measure a test-taker's knowledge, skill, aptitude, physical fitness, or classification in many other topics (e.g., beliefs). A test may be administered verbally, on paper, on a computer, or in a predetermined area that requires a test taker to demonstrate or perform a set of skills. Tests vary in style, rigor and requirements. There is no general consensus or invariable standard for test formats and difficulty. Often, the format and difficulty of the test is dependent upon the educational philosophy of the instructor, subject matter, class size, policy of the educational institution, and requirements of accreditation or governing bodies. A test may be administered formally or informally. An example of an informal test is a reading test administered by a parent to a child. A formal test might be a final examination administered by a teacher in a classroom or an IQ test administered by a psycho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in San F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independence Day (India)
Independence Day is celebrated annually on 15 August as a public holiday in India commemorating the nation's independence from the United Kingdom on 15 August 1947, the day when the provisions of the Indian Independence Act, which transferred legislative sovereignty to the Indian Constituent Assembly, came into effect. India retained King George VI as head of state until its transition to a republic, when the Constitution of India came into effect on 26 January 1950 (celebrated as Indian Republic Day) and replaced the dominion prefix, Dominion of India, with the enactment of the sovereign law Constitution of India. India attained independence following the independence movement noted for largely non-violent resistance and civil disobedience. Independence coincided with the partition of India, in which British India was divided along religious lines into the Dominions of India and Pakistan; the partition was accompanied by violent riots and mass casualties, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitution Of India
The Constitution of India (IAST: ) is the supreme law of India. The document lays down the framework that demarcates fundamental political code, structure, procedures, powers, and duties of government institutions and sets out fundamental rights, directive principles, and the duties of citizens. It is the longest written national constitution in the world. It imparts constitutional supremacy (not parliamentary supremacy, since it was created by a constituent assembly rather than Parliament) and was adopted by its people with a declaration in its preamble. Parliament cannot override the constitution. It was adopted by the Constituent Assembly of India on 26 November 1949 and became effective on 26 January 1950. The constitution replaced the Government of India Act 1935 as the country's fundamental governing document, and the Dominion of India became the Republic of India. To ensure constitutional autochthony, its framers repealed prior acts of the British parliament in A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of India
The Government of India (ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, consisting of 28 union states and eight union territories. Under the Constitution, there are three primary branches of government: the legislative, the executive and the judiciary, whose powers are vested in a bicameral Parliament, President, aided by the Council of Ministers, and the Supreme Court respectively. Through judicial evolution, the Parliament has lost its sovereignty as its amendments to the Constitution are subject to judicial intervention. Judicial appointments in India are unique in that the executive or legislature have negligible say. Etymology and history The Government of India Act 1833, passed by the British parliament, is the first such act of law with the epithet "Government of India". Basic structure The gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arbitrariness
Arbitrariness is the quality of being "determined by chance, whim, or impulse, and not by necessity, reason, or principle". It is also used to refer to a choice made without any specific criterion or restraint. Arbitrary decisions are not necessarily the same as random decisions. For example, during the 1973 oil crisis, Americans were allowed to purchase gasoline only on odd-numbered days if their license plate was odd, and on even-numbered days if their license plate was even. The system was well-defined and not random in its restrictions; however, since license plate numbers are completely unrelated to a person's fitness to purchase gasoline, it was still an arbitrary division of people. Similarly, schoolchildren are often organized by their surname in alphabetical order, a non-random yet an arbitrary method—at least in cases where surnames are irrelevant. Philosophy Arbitrary actions are closely related to teleology, the study of purpose. Actions lacking a ''telos'', a go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Service Commissions In India
Articles 315 to 323 in Part XIV of the Constitution of India provides for the establishment of Public Service Commission for the Union of India and a Public Service Commission for each State. The same set of Articles (i.e., 315 to 323 in Part XIV) of the Constitution also deal with the composition, appointment and removal of members, power and functions and independence of a Public Service Commission. Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) to conduct examinations for recruitment to the ''"All India Services"'' (AIS) and the ''"Higher Central Services"'' (HCS) and to advise the President on disciplinary matters. State Public Service Commission in every state to conduct examinations for recruitment to state services and to advise the governor on disciplinary matters. Public service commissions exams Union Public Services Commission exams Gazetted Group A and B jobs exams * Union Public Service Commission, for Gazetted Group A and B jobs ** Civil Services Examination ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Karnataka
The Government of Karnataka, abbreviated as, GoK, or simply Karnataka Government, is a democratically-elected state body with the governor as the ceremonial head to govern the Southwest Indian state of Karnataka. The governor who is appointed for five years appoints the chief minister and on the advice of the chief minister appoints his council of ministers. Even though the governor remains the ceremonial head of the state, the day-to-day running of the government is taken care of by the chief minister and his council of ministers in whom a great amount of legislative powers are vested. Administrative divisions Karnataka State has been divided into 4 revenue divisions, 49 sub-divisions, 31 districts, 237 taluks, 747 hoblies/ revenue circles and 6,022 gram panchayats for administrative purposes. The state has 281 towns and 7 municipal corporations. Bangalore is the largest urban agglomeration. It is among the fastest growing cities in the world. Political and administrative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |