|
Karl Gustav Sanio
Karl Gustav Sanio (5 December 1832 – 3 February 1891) was a Prussian botanist and served as a professor of botany at the University of Königsberg. He observed patterns in the growth of plant vasculature and wrote several articles on the organization of wood and cambium. He examined patterns in the size distribution of the xylem vessels in five statements known as Sanio's laws was also among the first to describe the formation of compression wood by conifers. Life Sanio was born in Lyck in a wealthy family and became interested in nature in the vast family estate. He studied botany under Ernst Meyer at the University of Königsberg and then moved to study medicine. He published his first note at the age of 24 on the spores of ''Equisetum''. Unhappy with medical studies, he moved back to study botany at Berlin under Nathaniel Braun and Alexander Pringsheim. He received a doctorate in 1858 and then taught botany after moving back to Königsberg. He suffered from a stroke on Janu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Sanio
Karl Gustav Sanio (5 December 1832 – 3 February 1891) was a Prussian botanist and served as a professor of botany at the University of Königsberg. He observed patterns in the growth of plant vasculature and wrote several articles on the organization of wood and cambium. He examined patterns in the size distribution of the xylem vessels in five statements known as Sanio's laws was also among the first to describe the formation of compression wood by conifers. Life Sanio was born in Lyck in a wealthy family and became interested in nature in the vast family estate. He studied botany under Ernst Meyer at the University of Königsberg and then moved to study medicine. He published his first note at the age of 24 on the spores of ''Equisetum''. Unhappy with medical studies, he moved back to study botany at Berlin under Nathaniel Braun and Alexander Pringsheim. He received a doctorate in 1858 and then taught botany after moving back to Königsberg. He suffered from a stroke on Jan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Königsberg
The University of Königsberg (german: Albertus-Universität Königsberg) was the university of Königsberg in East Prussia. It was founded in 1544 as the world's second Protestant academy (after the University of Marburg) by Duke Albert of Prussia, and was commonly known as the Albertina. Following World War II, the city of Königsberg was transferred to the Soviet Union according to the 1945 Potsdam Agreement, and renamed Kaliningrad in 1946. The Albertina was closed and the remaining non-Lithuanian population either executed or expelled, by the terms of the Potsdam Agreement. Today, the Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University in Kaliningrad claims to maintain the traditions of the Albertina. History Albert, former Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights and first Duke of Prussia since 1525, had purchased a piece of land behind Königsberg Cathedral on the Kneiphof island of the Pregel River from the Samland chapter, where he had an academic gymnasium (school) erected in 154 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
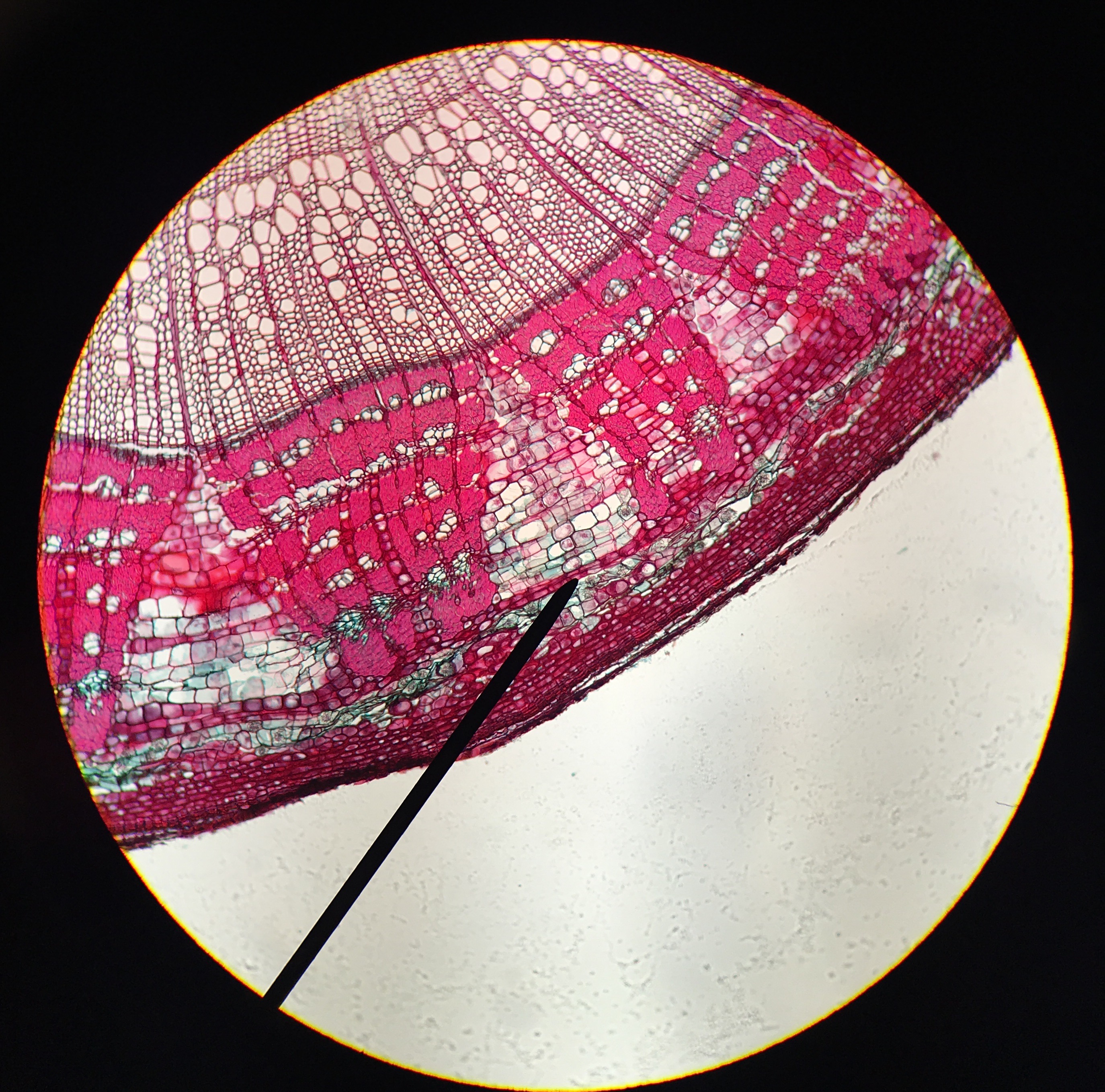
Cambium
A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. There are several distinct kinds of cambium found in plant stems and roots: * Cork cambium, a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. * Unifacial cambium, which ultimately produces cells to the interior of its cylinder. * Vascular cambium, a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants. Uses The cambium of many species of woody plants are edible; however, due to its vital role in the homeostasis and growth of woody plants, this may result in death of the plant if enough cambium is removed at once. The cambium can generally be eaten raw or cooke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ełk
Ełk (; former pl, Łek; german: Lyck; Old Prussian: ''Luks''; lt, Lukas), also spelled Elk in English, is a small city in northeastern Poland with 61,677 inhabitants as of December 2021. It was assigned to Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship in 1999, after belonging to Suwałki Voivodeship from 1975 to 1998. Ełk is the seat of Ełk County. It lies on the shore of Ełk Lake, which was formed by a glacier, and is surrounded by extensive forests. It is the largest city and unofficial capital of historical Masuria. One of the principal attractions in the area is legal hunting. History Middle Ages The area where the town of Ełk is located was originally inhabited by Jatvingians, a Baltic peoples, during the early middle ages. By 1281, Skomand (Lithuanian: ''Skalmantas'') the last leader of the pagan Jatvingians, capitulated to the crusading Teutonic Knights, who initially were invited in 1226 by Konrad I of Masovia from the Polish Piast dynasty to put an end to the constant pagan rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Heinrich Friedrich Meyer
Ernst Heinrich Friedrich Meyer (1 January 1791 – 7 August 1858) was a German botanist and botanical historian. Born in Hanover, he lectured in Göttingen and in 1826 became a professor of botany at the University of Königsberg, as well as Director of the Botanical Garden. His botanical specialty was the Juncaceae, or family of rushes. His major work was the four-volume ''Geschichte der Botanik'' (“History of Botany,” 1854–57). His history covered ancient authorities such as Aristotle and Theophrastus, explored the beginnings of modern botany in the context of 15th- and 16th-century intellectual practice, and offered a wealth of biographical data on early modern botanists. Julius von Sachs pronounced him “no great botanist” but admitted that he “possessed a clever and cultivated intellect.” He died in Königsberg, East Prussia. In 1828, he was honoured by Swiss botanist Augustin Pyramus de Candolle who named a genus of plants from tropical South America after hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equisetum
''Equisetum'' (; horsetail, snake grass, puzzlegrass) is the only living genus in Equisetaceae, a family of ferns, which reproduce by spores rather than seeds. ''Equisetum'' is a "living fossil", the only living genus of the entire subclass Equisetidae, which for over 100 million years was much more diverse and dominated the understorey of late Paleozoic forests. Some equisetids were large trees reaching to tall. The genus ''Calamites'' of the family Calamitaceae, for example, is abundant in coal deposits from the Carboniferous period. The pattern of spacing of nodes in horsetails, wherein those toward the apex of the shoot are increasingly close together, is said to have inspired John Napier to invent logarithms. Modern horsetails first appeared during the Jurassic period. A superficially similar but entirely unrelated flowering plant genus, mare's tail (''Hippuris''), is occasionally referred to as "horsetail", and adding to confusion, the name "mare's tail" is sometimes ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheid
A tracheid is a long and tapered lignified cell in the xylem of vascular plants. It is a type of conductive cell called a tracheary element. Angiosperms use another type of tracheary element, called vessel elements, to transport water through the xylem. The main functions of tracheid cells are to transport water and inorganic salts, and to provide structural support for trees. There are often pits on the cell walls of tracheids, which allows for water flow between cells. Tracheids are dead at functional maturity and do not have a protoplast. The wood (softwood) of gymnosperms such as pines and other conifers is mainly composed of tracheids. Tracheids are also the main conductive cells in the primary xylem of ferns. The tracheid was first named after the German botanist Carl Gustav Sanio in 1863, from the German ''Tracheide''. Evolution Tracheids were the main conductive cells found in early vascular plants. In the first 140-150 million years of vascular plant evolution, tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanionia
''Sanionia'' is a genus of mosses belonging to the family Amblystegiaceae. The genus has cosmopolitan distribution, and was circumscribed In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a polygon is a circle that passes through all the vertices of the polygon. The center of this circle is called the circumcenter and its radius is called the circumradius. Not every polyg ... by Leopold Loeske in Verh. Bot. Vereins. Prov. Brandenburg vol.49 on page 63 in 1907. The genus is named after Karl Gustav Sanio (1832–1891). Species * '' Sanionia fertilis'' * '' Sanionia georgicouncinata'' * '' Sanionia nivalis'' * '' Sanionia uncinata'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q12334533 Amblystegiaceae Moss genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1832 Births
Year 183 ( CLXXXIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Victorinus (or, less frequently, year 936 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 183 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * An assassination attempt on Emperor Commodus by members of the Senate fails. Births * January 26 – Lady Zhen, wife of the Cao Wei state Emperor Cao Pi (d. 221) * Hu Zong, Chinese general, official and poet of the Eastern Wu state (d. 242) * Liu Zan (Zhengming), Chinese general of the Eastern Wu state (d. 255) * Lu Xun Zhou Shuren (25 September 1881 – 19 October 1936), better known by his pen name Lu Xun (or Lu Sun; ; Wade–Giles: Lu Hsün), was a Chinese writer, essayist, poet, and literary criti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1891 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 ** Paying of old age pensions begins in Germany. ** A strike of 500 Hungarian steel workers occurs; 3,000 men are out of work as a consequence. **Germany takes formal possession of its new African territories. * January 2 – A. L. Drummond of New York is appointed Chief of the Treasury Secret Service. * January 4 – The Earl of Zetland issues a declaration regarding the famine in the western counties of Ireland. * January 5 **The Australian shearers' strike, that leads indirectly to the foundation of the Australian Labor Party, begins. **A fight between the United States and Indians breaks out near Pine Ridge agency. ** Henry B. Brown, of Michigan, is sworn in as an Associate Justice of the Supreme Court. **A fight between railway strikers and police breaks out at Motherwell, Scotland. * January 6 – Encounters continue, between strikers and the authorities at Glasgow. * January 7 ** General Miles' force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century German Botanists
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the large S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The University Of Königsberg
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulation, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)


