|
Karamagara Bridge
The Karamagara Bridge ( tr, Karamağara Köprüsü, "Bridge of the Black Cave") is a Byzantine or late Roman bridge in the ancient region of Cappadocia in eastern Turkey, and possibly the earliest known pointed arch bridge. The bridge, along with much of the Arapgir Çayı valley, has been submerged since the completion of the Keban Dam in 1975, as a result of which the water level in the Euphrates valley and some of its upstream tributaries dramatically rose. Location and situation The single arch of 17 m spans between the cliffs of the rocky gorge of the Arapgir Çayı, an affluent of the Euphrates. The structure belonged to the Roman road to Melitene, which was cut into the rock near the bridge at both sides of the river. Its name ''Karamağara'' ("black cave") probably derives from an artificially widened cavern on the southern bank which was carved into the darkish rock 75 m above the structure and served for protection of the crossing point. The bridge was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. They provided efficient means for the overland movement of armies, officials, civilians, inland carriage of official communications, and trade goods. Roman roads were of several kinds, ranging from small local roads to broad, long-distance highways built to connect cities, major towns and military bases. These major roads were often stone-paved and metaled, cambered for drainage, and were flanked by footpaths, bridleways and drainage ditches. They were laid along accurately surveyed courses, and some were cut through hills, or conducted over rivers and ravines on bridgework. Sections could be supported over marshy ground on rafted or piled foundations.Corbishley, Mike: "The Roman World", page 50. Warwick Press, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
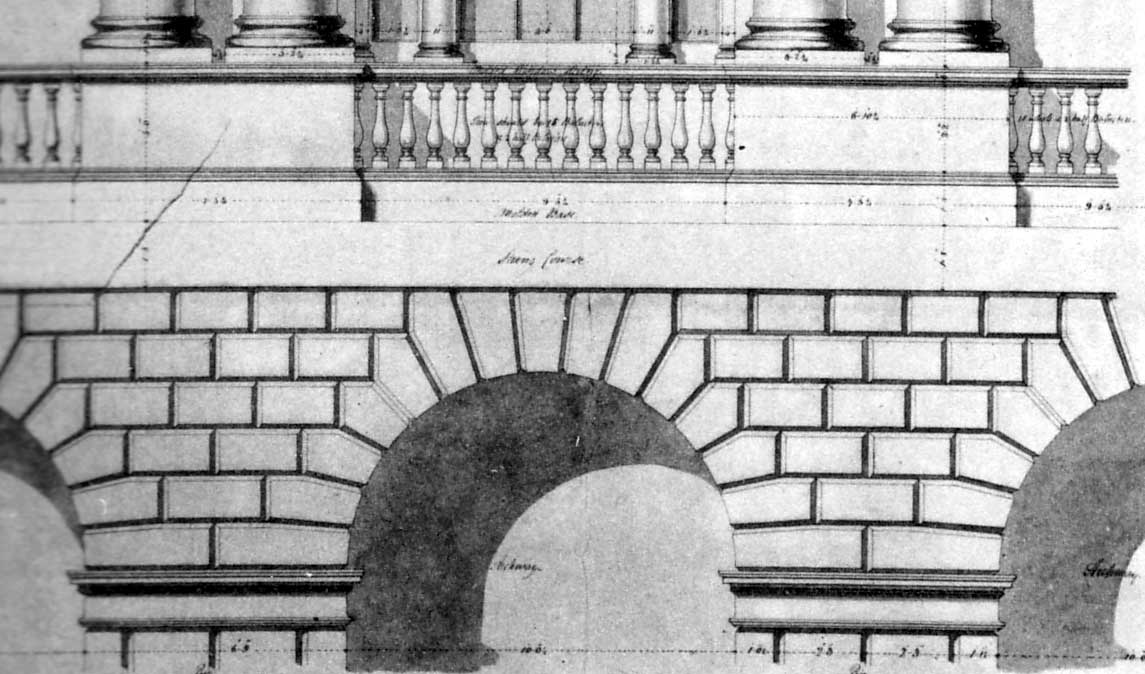
Voussoir
A voussoir () is a wedge-shaped element, typically a stone, which is used in building an arch or vault. Although each unit in an arch or vault is a voussoir, two units are of distinct functional importance: the keystone and the springer. The keystone is the centre stone or masonry unit at the apex of an arch. The springer is the lowest voussoir on each side, located where the curve of the arch springs from the vertical support or abutment of the wall or pier. The keystone is often decorated or enlarged. An enlarged and sometimes slightly dropped keystone is often found in Mannerist arches of the 16th century, beginning with the works of Giulio Romano, who also began the fashion for using voussoirs above rectangular openings, rather than a lintel (Palazzo Stati Maccarani, Rome, circa 1522). The word is a stonemason's term borrowed in Middle English from French verbs connoting a "turn" (''OED''). Each wedge-shaped voussoir ''turns aside'' the thrust of the mass above, transf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia occupies modern Iraq. In the broader sense, the historical region included present-day Iraq and Kuwait and parts of present-day Iran, Syria and Turkey. The Sumerians and Akkadians (including Assyrians and Babylonians) originating from different areas in present-day Iraq, dominated Mesopotamia from the beginning of written history () to the fall of Babylon in 539 BC, when it was conquered by the Achaemenid Empire. It fell to Alexander the Great in 332 BC, and after his death, it became part of the Greek Seleucid Empire. Later the Arameans dominated major parts of Mesopotamia (). Mesopotamia is the site of the earliest developments of the Neolithic Revolution from around 10,000 BC. It has been identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It is a unitary republic that consists of 14 governorates (subdivisions), and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east and southeast, Jordan to the south, and Israel and Lebanon to the southwest. Cyprus lies to the west across the Mediterranean Sea. A country of fertile plains, high mountains, and deserts, Syria is home to diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Syrian Arabs, Kurds, Turkmens, Assyrians, Armenians, Circassians, Albanians, and Greeks. Religious groups include Muslims, Christians, Alawites, Druze, and Yazidis. The capital and largest city of Syria is Damascus. Arabs are the largest ethnic group, and Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Architecture
Church architecture refers to the architecture of buildings of churches, convents, seminaries etc. It has evolved over the two thousand years of the Christian religion, partly by innovation and partly by borrowing other architectural styles as well as responding to changing beliefs, practices and local traditions. From the birth of Christianity to the present, the most significant objects of transformation for Christian architecture and design were the great churches of Byzantium, the Romanesque abbey churches, Gothic cathedrals and Renaissance basilicas with its emphasis on harmony. These large, often ornate and architecturally prestigious buildings were dominant features of the towns and countryside in which they stood. However, far more numerous were the parish churches in Christendom, the focus of Christian devotion in every town and village. While a few are counted as sublime works of architecture to equal the great cathedrals and churches, the majority developed along si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sassanid Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named after the House of Sasan, it endured for over four centuries, from 224 to 651 AD, making it the longest-lived Persian imperial dynasty. The Sasanian Empire succeeded the Parthian Empire, and re-established the Persians as a major power in late antiquity alongside its neighbouring arch-rival, the Roman Empire (after 395 the Byzantine Empire).Norman A. Stillman ''The Jews of Arab Lands'' pp 22 Jewish Publication Society, 1979 International Congress of Byzantine Studies ''Proceedings of the 21st International Congress of Byzantine Studies, London, 21–26 August 2006, Volumes 1–3'' pp 29. Ashgate Pub Co, 2006 The empire was founded by Ardashir I, an Iranian ruler who rose to power as Parthia weakened from internal strife and wars with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English has generally been credited to historian Peter Brown, after the publication of his seminal work '' The World of Late Antiquity'' (1971). Precise boundaries for the period are a continuing matter of debate, but Brown proposes a period between the 3rd and 8th centuries AD. Generally, it can be thought of as from the end of the Roman Empire's Crisis of the Third Century (235–284) to the early Muslim conquests (622–750), or as roughly contemporary with the Sasanian Empire (224–651). In the West its end was earlier, with the start of the Early Middle Ages typically placed in the 6th century, or earlier on the edges of the Western Roman Empire. The Roman Empire underwent considerable social, cultural and organizational changes starting wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it. Arches may be synonymous with vaults, but a vault may be distinguished as a continuous arch forming a roof. Arches appeared as early as the 2nd millennium BC in Mesopotamian brick architecture, and their systematic use started with the ancient Romans, who were the first to apply the technique to a wide range of structures. Basic concepts An arch is a pure compression form. It can span a large area by resolving forces into compressive stresses, and thereby eliminating tensile stresses. This is sometimes denominated "arch action". As the forces in the arch are transferred to its base, the arch pushes outward at its base, denominated "thrust". As the rise, i. e. height, of the arch decreases the outward thrust increases. In order to preserve arch action and prevent collapse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleography
Palaeography ( UK) or paleography ( US; ultimately from grc-gre, , ''palaiós'', "old", and , ''gráphein'', "to write") is the study of historic writing systems and the deciphering and dating of historical manuscripts, including the analysis of historic handwriting. It is concerned with the forms and processes of writing; not the textual content of documents. Included in the discipline is the practice of deciphering, reading, and dating manuscripts, and the cultural context of writing, including the methods with which writing and books were produced, and the history of scriptoria. The discipline is one of the auxiliary sciences of history. It is important for understanding, authenticating, and dating historic texts. However, it generally cannot be used to pinpoint dates with high precision. Application Palaeography can be an essential skill for historians and philologists, as it tackles two main difficulties. First, since the style of a single alphabet in each given langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyrios
''Kyrios'' or ''kurios'' ( grc, κύριος, kū́rios) is a Greek word which is usually translated as "lord" or "master". It is used in the Septuagint translation of the Hebrew scriptures about 7000 times, in particular translating the name God YHWH (the Tetragrammaton), and it appears in the Koine Greek New Testament about 740 times, usually referring to Jesus.''The Christology of the New Testament'' by Oscar Cullmann 1959 pages 234-23/ref> Classical Greece In Classical Athens, the word ''kyrios'' referred to the head of the household, who was responsible for his wife, children, and any unmarried female relatives. It was the responsibility of the ''kyrios'' to arrange the marriages of his female relatives, provide their dowries, represent them in court, if necessary, and deal with any economic transactions they were involved in worth more than a ''medimnos'' of barley. When an Athenian woman married, her husband became her new ''kyrios''. The existence of the system o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalm 120
Psalm 120 is the 120th psalm of the Book of Psalms, beginning in the English of the King James Version: "In my distress I cried unto the LORD, and he heard me". In the slightly different numbering system used in the Greek Septuagint and Latin Vulgate translations of the Bible, this psalm is Psalm 119. In Latin, it is known as "Ad Dominum cum tribularer clamavi". It is one of 15 psalms categorized as Song of Ascents (''Shir Hama'alot''). The psalm forms a regular part of Jewish, Catholic, Lutheran, Anglican and other Protestant liturgies. It has been set to music in several languages. Text King James Version # In my distress I cried unto the LORD, and he heard me. # Deliver my soul, O LORD, from lying lips, and from a deceitful tongue. # What shall be given unto thee? or what shall be done unto thee, thou false tongue? # Sharp arrows of the mighty, with coals of juniper. # Woe is me, that I sojourn in Mesech, that I dwell in the tents of Kedar! # My soul hath long dwelt with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a variety of forms originally written in Hebrew, Aramaic, and Koine Greek. These texts include instructions, stories, poetry, and prophecies, among other genres. The collection of materials that are accepted as part of the Bible by a particular religious tradition or community is called a biblical canon. Believers in the Bible generally consider it to be a product of divine inspiration, but the way they understand what that means and interpret the text can vary. The religious texts were compiled by different religious communities into various official collections. The earliest contained the first five books of the Bible. It is called the Torah in Hebrew and the Pentateuch (meaning ''five books'') in Greek; the second oldest part was a coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)