|
Kanalites
Kanalites ( grc-x-medieval, Καναλῖται, sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Konavljani, Конављани) were a medieval Slavic tribe settled in the today's region of Konavle, within Dalmatia, Croatia, mentioned in the chapter titled "Of the Terbounians and Kanalites and of the country they now dwell in" of the 10th century '' De Administrando Imperio'' by Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII. The country, located in near proximity to Travunia, reportedly became desolated during the Pannonian Avars invasion, and its inhabitants are descendants from the unbaptized Serbs, from the time of the Unknown Archon who came from Boiki and claimed the protection of the Emperor Heraclius in the 7th century. However, a closer reading suggests that the Constantine consideration about the population's ethnic identity, like in regard to other near polities, is based on Serbian political rule during the time of Časlav in 10th century and does not indicate ethnic origin. They were mentio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narentines
The Narentines were a South Slavic tribe that occupied an area of southern Dalmatia centered at the river Neretva (), active in the 9th and 10th centuries, noted as pirates on the Adriatic. Named ''Narentani'' in Venetian sources, Greek sources call them ''Paganoi'', "pagans", as they were for long pagan, in a time when neighbouring tribes were Christianized. The tribe were fierce enemies of the Republic of Venice, having attacked Venetian merchants and clergy passing on the Adriatic, and even raided close to Venice itself, as well as defeated the doge several times. Venetian–Narentine peace treaties did not last long, as the Narentines quickly returned to piracy. They were finally defeated in a Venetian crackdown at the turn of the 10th century and disappeared from sources by the 11th century. Terminology The word ''Narentine'' is a demonym derived from the local Neretva River ( lat, Narenta). The terms "Narentines", "Pagania" or "Pagans" are found in two contemporary source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zachumlians
Zachlumia or Zachumlia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Zahumlje, Захумље, ), also Hum, was a medieval principality located in the modern-day regions of Herzegovina and southern Dalmatia (today parts of Bosnia and Herzegovina and Croatia, respectively). In some periods it was a fully independent or semi-independent South Slavic principality. It maintained relations with various foreign and neighbouring powers (Byzantine Empire, First Bulgarian Empire, Kingdom of Croatia, Principality of Serbia) and later was subjected (temporarily or for a longer period) to Kingdom of Hungary, Kingdom of Serbia, Kingdom of Bosnia, Duchy of Saint Sava and at the end to the Ottoman Empire. Etymology Zachlumia is a derivative of ''Hum'', from Proto-Slavic '' *xŭlmŭ'', borrowed from a Germanic language (cf. Proto-Germanic '' *hulma-''), meaning ''"Hill"''. South Slavic ''Zahumlje'' is named after the mountain of Hum (za + Hum "behind the Hum"), above Bona, at the mouth of the Buna. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
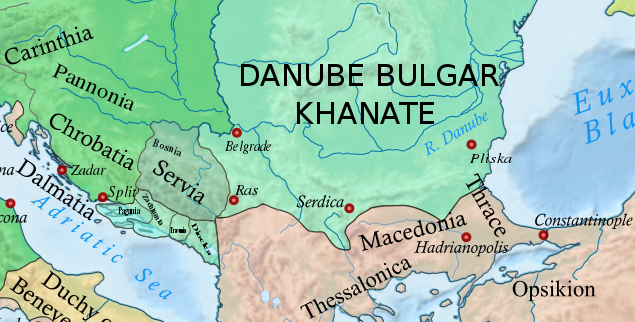
Travunia
Travunia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Travunija, Травунија; el, Τερβουνία, Tervounía; grc, Τερβουνία, Terbounía; la, Tribunia) was a South Slavic medieval principality that was part of Medieval Serbia (850–1371), and later the Medieval Bosnia (1373–1482). The principality became hereditary in a number of noble houses, often kin to the ruling dynasty. The region came under Ottoman rule in 1482. Its seat was in the city of Trebinje. In the 9th and 10th centuries, the ''Župa'' of Travunia was held by the Belojević noble family, who were entitled the rule during the reign of Prince Vlastimir (r. 830–850), of the Vlastimirović dynasty. After the death of Časlav, the last dynastic member, the principality disintegrated, and the provinces were annexed by the Bulgars and Byzantines. In 1034, Stefan Vojislav (the founder of the Vojislavljević dynasty) incited a rebellion and renounced Byzantine rule, becoming the ''Prince of Serbs'', rul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unknown Archon
The term Unnamed Prince of Serbia ( sr, неименовани српски архонт / ''neimenovani srpski arhont''), or the Unknown Prince ( sr, непознати кнез / ''nepoznati knez''), refers to the Serbian prince from the first half of the 7th century, who according to the ''De Administrando Imperio'' (10th century CE) supposedly led his people from their original homeland in White Serbia, to settle in the Balkans during the reign of Byzantine Emperor Heraclius (610–641), as mentioned in Emperor Constantine VII's work ''De Administrando Imperio'' (written in 950s). The work does not record his name, but states that he was the progenitor of the first Serbian dynasty (known in historiography as the Vlastimirović dynasty), and that he died before the arrival of the Bulgars (680), succeeded by his son, and then grandson. ''De Administrando Imperio'' Studies According to the accounts in DAI the first Christianization of the Serbs should be dated to 632–638; this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael II
Michael II ( gr, Μιχαὴλ, , translit=Michaēl; 770–829), called the Amorian ( gr, ὁ ἐξ Ἀμορίου, ho ex Amoríou) and the Stammerer (, ''ho Travlós'' or , ''ho Psellós''), reigned as Byzantine Emperor from 25 December 820 to his death on 2 October 829, the first ruler of the Amorian dynasty. Born in Amorium, Michael was a soldier, rising to high rank along with his colleague Leo V the Armenian ( 813–820). He helped Leo overthrow and take the place of Emperor Michael I Rangabe. However, after they fell out Leo sentenced Michael to death. Michael then masterminded a conspiracy which resulted in Leo's assassination at Christmas in 820. Immediately he faced the long revolt of Thomas the Slav, which almost cost him his throne and was not completely quelled until spring 824. The later years of his reign were marked by two major military disasters that had long-term effects: the beginning of the Muslim conquest of Sicily, and the loss of Crete to the Saracens. Do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th Century In Croatia
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube. As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has greatly symbolic associations in religion, mythology, superstition and philosophy. The seven Classical planets resulted in seven being the number of days in a week. It is often considered lucky in Western culture and is often seen as highly symbolic. Unlike Western culture, in Vietnamese culture, the number seven is sometimes considered unlucky. It is the first natural number whose pronunciation contains more than one syllable. Evolution of the Arabic digit In the beginning, Indians wrote 7 more or less in one stroke as a curve that looks like an uppercase vertically inverted. The western Ghubar Arabs' main contribution was to make the longer line diagonal rather than straight, though they showed some tendencies to making the digit more rectilinear. The eastern Arabs developed the digit fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibor Živković
Tibor Živković ( sr-cyr, Тибор Живковић; 11 March 1966 – 26 March 2013) was a reputable Serbian academic, historian and Byzantinist who specialised in the period of the Early Middle Ages. Biography Živković was born in Mostar, and history studied at the Faculty of Philosophy at the University of Belgrade between 1985–90, when he graduated at the Department of Antiquity. He received his MA in 1996 with a thesis ''slavizacija na teritoriju Srbije VII-XI stoljeća'' (Slavicization on the territory of Serbia 7th–11th centuries). He received his PhD in 2000 with a dissertation ''Slavs under Byzantine rule from the 7th to 11th Centuries (until 1025''). As of 1997, he worked at The Institute of History of the Serbian Academy of Sciences and Arts (SANU), and was the director of the Historical Institute from 2002–10, as well as editor in chief of the Drafting Committee editions of the Historical Institute. During the doctoral studies he was a scholar of the Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Serbia (early Medieval)
The Principality of Serbia ( sr, Кнежевина Србија, Kneževina Srbija) was one of the early medieval states of the Serbs, located in the western regions of Southeastern Europe. It existed from the 8th century up to c. 969–971 and was ruled by the Vlastimirović dynasty. Its first ruler known by name was Višeslav who started ruling around 780. While by that time, starting from the year 680–681, the Bulgarian state had taken the lands to the east. Vlastimir resisted and defeated the Bulgarian army in a three-year-war (839–842), and the two powers lived in peace for some decades. Vlastimir's three sons succeeded in ruling Serbia together, although not for long; Serbia became a key part in the power struggle between the Byzantines and Bulgarians, predominantly allied with the Byzantines, which also resulted in major dynastic wars for a period of three decades. The principality was annexed in 924 by Simeon I and subjected to Bulgarian rule until 927 when Serbian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Ceremoniis
The ''De Ceremoniis'' (fully ''De cerimoniis aulae Byzantinae'') is the conventional Latin name for a Greek book of ceremonial protocol at the court of the Byzantine emperors in Constantinople. Its Greek title is often cited as ("Explanation of the Order of the Palace"), taken from the work's preface, or ("On the Order of the Palace"). In non-specialist English sources, it tends to be called the ''Book of Ceremonies of Constantine VII Porphyrogennetos'' (variably spelt), a formula used by writers including David Talbot Rice and the modern English translation. History and Sources It was written or at least commissioned by Emperor Constantine VII (reigned 913-959), probably around 956-959. The compilation of Rep. I 17 (Leipzig, Universitätsbibliothek) was partially revised later under Nikephoros II (963-969), perhaps under the supervision of Basil Lekapenos, the imperial ''parakoimomenos'', and it also contains earlier descriptions of the 6th century."De Ceremoniis" in ''The Ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basil I
Basil I, called the Macedonian ( el, Βασίλειος ὁ Μακεδών, ''Basíleios ō Makedṓn'', 811 – 29 August 886), was a Byzantine Emperor who reigned from 867 to 886. Born a lowly peasant in the theme of Macedonia, he rose in the Imperial court. He entered into the service of Theophilitzes, a relative of Emperor Michael III (r. 842–867), and was given a fortune by the wealthy Danielis. He gained the favour of Michael III, whose mistress he married on the emperor's orders, and was proclaimed co-emperor in 866. He ordered the assassination of Michael the next year. Despite his humble origins, he showed great ability in running the affairs of state. He was the founder of the Macedonian dynasty. He was succeeded upon his death by his son (perhaps actually Michael III's son) Leo VI. From peasant to emperor Basil was born to peasant parents in late 811 (or sometime in the 830s in the estimation of some scholars) at Chariopolis in the Byzantine theme of Macedonia (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis II's Campaign Against Bari (866–871)
The Frankish emperor Louis II campaigned against the Emirate of Bari continuously from 866 until 871. Louis was allied with the Lombard principalities of southern Italy from the start, but an attempt at joint action with the Byzantine Empire failed in 869. In the final siege of the city of Bari in 871, Louis was assisted by a Slavic fleet from across the Adriatic. The city fell and the emir was taken captive, bringing the emirate to an end, but a Saracen presence remained at Taranto. Louis himself was betrayed by his Lombard allies six months after his victory and had to leave southern Italy. Military actions of 866–867 Louis II was sent by his father, Lothair I, to southern Italy to counteract Saracen raids in 848–849. He launched an unsuccessful attack on Bari in 852, and again in 855 and 857. In 865, he began planning a campaign to completely oust the Saracens from southern Italy. In that year he issued a capitulary in northern Italy summoning an army to gather at Lucera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |