|
Kaman K-MAX
The Kaman K-MAX (company designation K-1200) is an American helicopter with intermeshing rotors (synchropter) by Kaman Aircraft. It is optimized for external cargo load operations, and is able to lift a payload of over , which is more than the helicopter's empty weight. An unmanned aerial vehicle version with optional remote control has been developed and evaluated in extended practical service in the war in Afghanistan. After being out of production for more than a decade, in June 2015 Kaman announced it was restarting production of the K-MAX due to it receiving ten commercial orders.Kaman restarts K-Max production on new commercial orders Flightglobal The first flight of a K-MAX from the restarted production took place in May ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
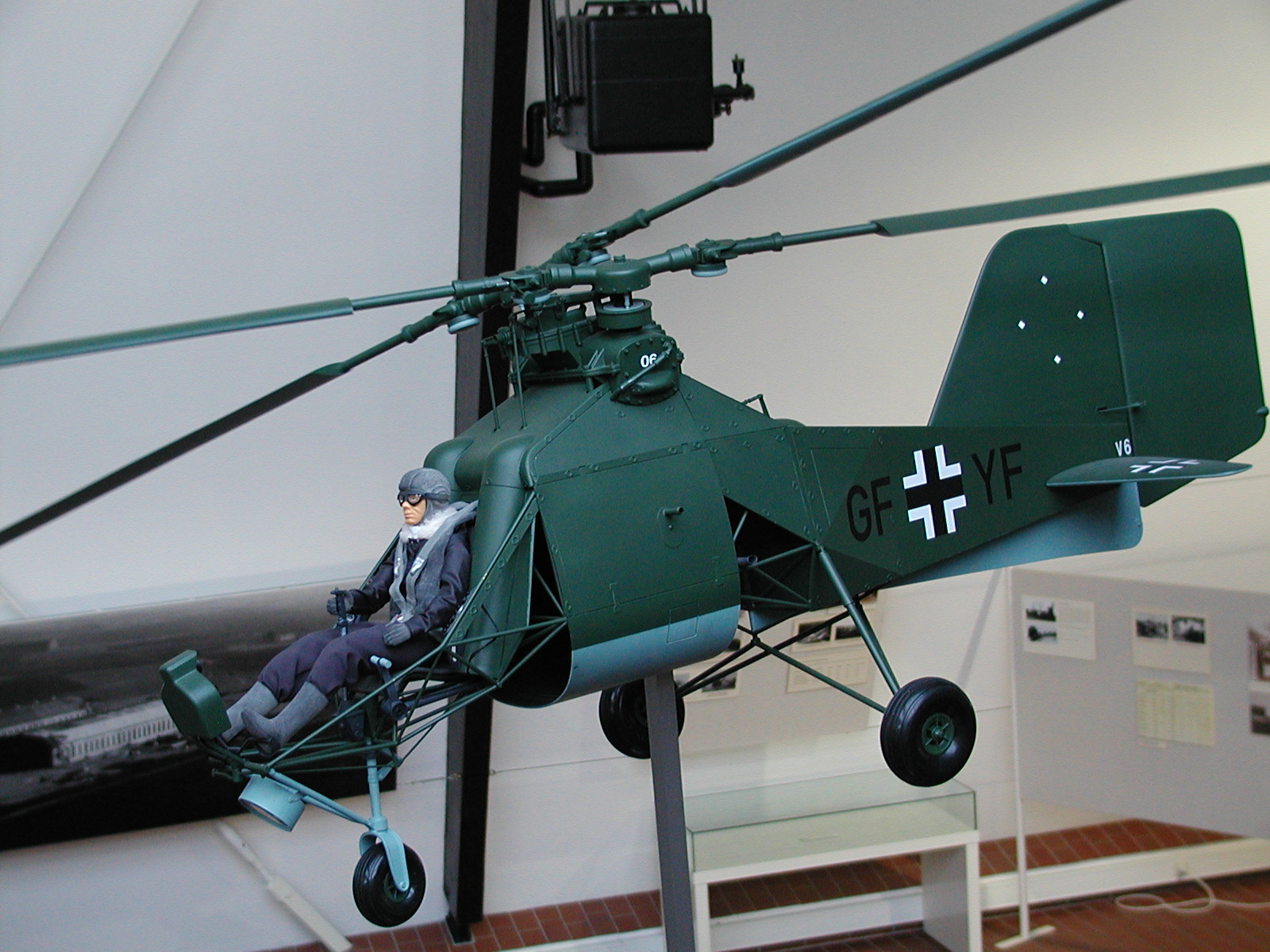
Flettner Fl 282
The Flettner Fl 282 ''Kolibri'' ("Hummingbird") is a single-seat intermeshing rotor helicopter, or ''synchropter'', produced by Anton Flettner of Germany. According to Yves Le Bec, the Flettner Fl 282 was the world's first series production helicopter. Design and development The Fl 282 ''Kolibri'' was an improved version of the Flettner Fl 265 announced in July 1940, which pioneered the same intermeshing rotor configuration that the ''Kolibri'' used. It had a 7.7 litre displacement, seven-cylinder Siemens-Halske Sh 14 radial engine of mounted in the center of the fuselage, with a transmission mounted on the front of the engine from which a drive shaft ran to an upper gearbox, which then split the power to a pair of opposite-rotation drive shafts to turn the rotors. The Sh 14 engine was a venerable, tried-and-true design with low specific power output and low power/weight ratio (20.28 hp/L, 0.54 hp/lb) which could (anecdotally) run for up to 400 hours without major ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Martin
The Lockheed Martin Corporation is an American aerospace, arms, defense, information security, and technology corporation with worldwide interests. It was formed by the merger of Lockheed Corporation with Martin Marietta in March 1995. It is headquartered in North Bethesda, Maryland, in the Washington, D.C. area. Lockheed Martin employs approximately 115,000 employees worldwide, including about 60,000 engineers and scientists as of January 2022. Lockheed Martin is one of the largest companies in the aerospace, military support, security, and technologies industry. It is the world's largest defense contractor by revenue for fiscal year 2014.POC Top 20 Defence Contractors of 2014 . Retrieved: July 2015 In 2013, 78% of Lockheed Martin's revenues came from military sales; [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
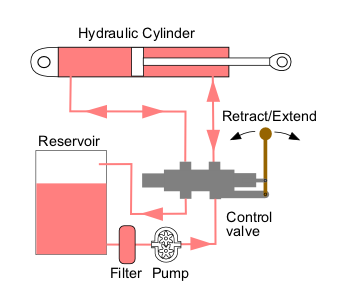
Hydraulic Machinery
Hydraulic machines use liquid fluid power to perform work. Heavy construction vehicles are a common example. In this type of machine, hydraulic fluid is pumped to various hydraulic motors and hydraulic cylinders throughout the machine and becomes pressurized according to the resistance present. The fluid is controlled directly or automatically by control valves and distributed through hoses, tubes, or pipes. Hydraulic systems, like pneumatic systems, are based on Pascal's law which states that any pressure applied to a fluid inside a closed system will transmit that pressure equally everywhere and in all directions. A hydraulic system uses an incompressible liquid as its fluid, rather than a compressible gas. The popularity of hydraulic machinery is due to the very large amount of power that can be transferred through small tubes and flexible hoses, the high power density and a wide array of actuators that can make use of this power, and the huge multiplication of forces t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Servo Tab
__NOTOC__ A servo tab is a small hinged device installed on an aircraft control surface to assist the movement of the control surfaces. Introduced by the German firm Flettner, servo tabs were formerly known as Flettner tabs. Servo tabs are not true servomechanisms, as they do not employ negative feedback to keep the control surfaces in a desired position; they only provide a mechanical advantage to the pilot. Servo tabs A servo tab, or balance tab, moves in the direction opposite to the desired movement of the control surface. It deflects airflow, generating force on the whole control surface in the desired direction. The tab has a leverage advantage, being located well aft of the control surface hinge line, and thus its airflow deflection moves the control surface in the opposite direction, overcoming the resistance generated by the airflow deflection of the control surface. This has the effect of reducing the control force required from the pilot to move the controls. In som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spar (aviation)
In a fixed-wing aircraft, the spar is often the main structural member of the wing, running spanwise at right angles (or thereabouts depending on wing sweep) to the fuselage. The spar carries flight loads and the weight of the wings while on the ground. Other structural and forming members such as ribs may be attached to the spar or spars, with stressed skin construction also sharing the loads where it is used. There may be more than one spar in a wing or none at all. Where a single spar carries most of the force, it is known as the main spar. Spars are also used in other aircraft aerofoil surfaces such as the tailplane and fin and serve a similar function, although the loads transmitted may be different from those of a wing spar. Spar loads The wing spar provides the majority of the weight support and dynamic load integrity of cantilever monoplanes, often coupled with the strength of the wing 'D' box itself. Together, these two structural components collectively provide the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flightglobal
FlightGlobal is an online news and information website which covers the aviation and aerospace industries. The website was established in February 2006 as the website of ''Flight International'' magazine, ''Airline Business'', ''ACAS'', ''Air Transport Intelligence'' (ATI), ''The Flight Collection'' and other services and directories. FlightGlobal is a resource for aviation history with a picture library of over 1 million images starting with the foundation of ''Flight'' in 1909. Thousands of images and back copies of ''Flight'' are searchable online. FlightGlobal won the prize for of "Business Website of the Year" at the Association of Online Publishers' Digital Publishing Awards 2010. According to the contest judges, "The site uses the full spectrum of digital tools, with a special focus on engagement and effective use of social media in a B2B usiness-to-businessenvironment". In August 2019, FlightGlobal and its associated divisions (except analytics and consulting divisio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell 204/205
The Bell 204 and 205 are the civilian versions of the UH-1 Iroquois single-engine military helicopter of the Huey family of helicopters. They are type-certificated in the transport category and are used in a wide variety of applications, including crop dusting, cargo lifting and aerial firefighting. Development Bell designed its ''Model 204'' in response to a 1955 United States Army requirement for a utility helicopter. The 204 was a giant step forward in helicopter design, being one of the first to be powered by a turboshaft. The turboshaft engine radically improved the practicality of the helicopter due to its light weight and high power-to-weight ratio, lower fuel consumption, and lower maintenance and operating costs. The use of a turboshaft in the 204 allowed it to carry a useful payload over respectable ranges and at reasonable speeds, which resulted in the 204 and subsequent 205 becoming the most successful western helicopter series in terms of numbers built.Frawley, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IFR Certification
In aviation, instrument flight rules (IFR) is one of two sets of regulations governing all aspects of civil aviation aircraft operations; the other is visual flight rules (VFR). The U.S. Federal Aviation Administration's (FAA) ''Instrument Flying Handbook'' defines IFR as: "Rules and regulations established by the FAA to govern flight under conditions in which flight by outside visual reference is not safe. IFR flight depends upon flying by reference to instruments in the flight deck, and navigation is accomplished by reference to electronic signals." It is also a term used by pilots and controllers to indicate the type of flight plan an aircraft is flying, such as an IFR or VFR flight plan. Basic information Comparison to visual flight rules It is possible and fairly straightforward, in relatively clear weather conditions, to fly an aircraft solely by reference to outside visual cues, such as the horizon to maintain orientation, nearby buildings and terrain features for n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Popular Mechanics
''Popular Mechanics'' (sometimes PM or PopMech) is a magazine of popular science and technology, featuring automotive, home, outdoor, electronics, science, do-it-yourself, and technology topics. Military topics, aviation and transportation of all types, space, tools and gadgets are commonly featured. It was founded in 1902 by Henry Haven Windsor, who was the editor and—as owner of the Popular Mechanics Company—the publisher. For decades, the tagline of the monthly magazine was "Written so you can understand it." In 1958, PM was purchased by the Hearst Corporation, now Hearst Communications. In 2013, the US edition changed from twelve to ten issues per year, and in 2014 the tagline was changed to "How your world works." The magazine added a podcast in recent years, including regular features ''Most Useful Podcast Ever'' and ''How Your World Works''. History ''Popular Mechanics'' was founded in Chicago by Henry Haven Windsor, with the first issue dated January 11, 1902. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
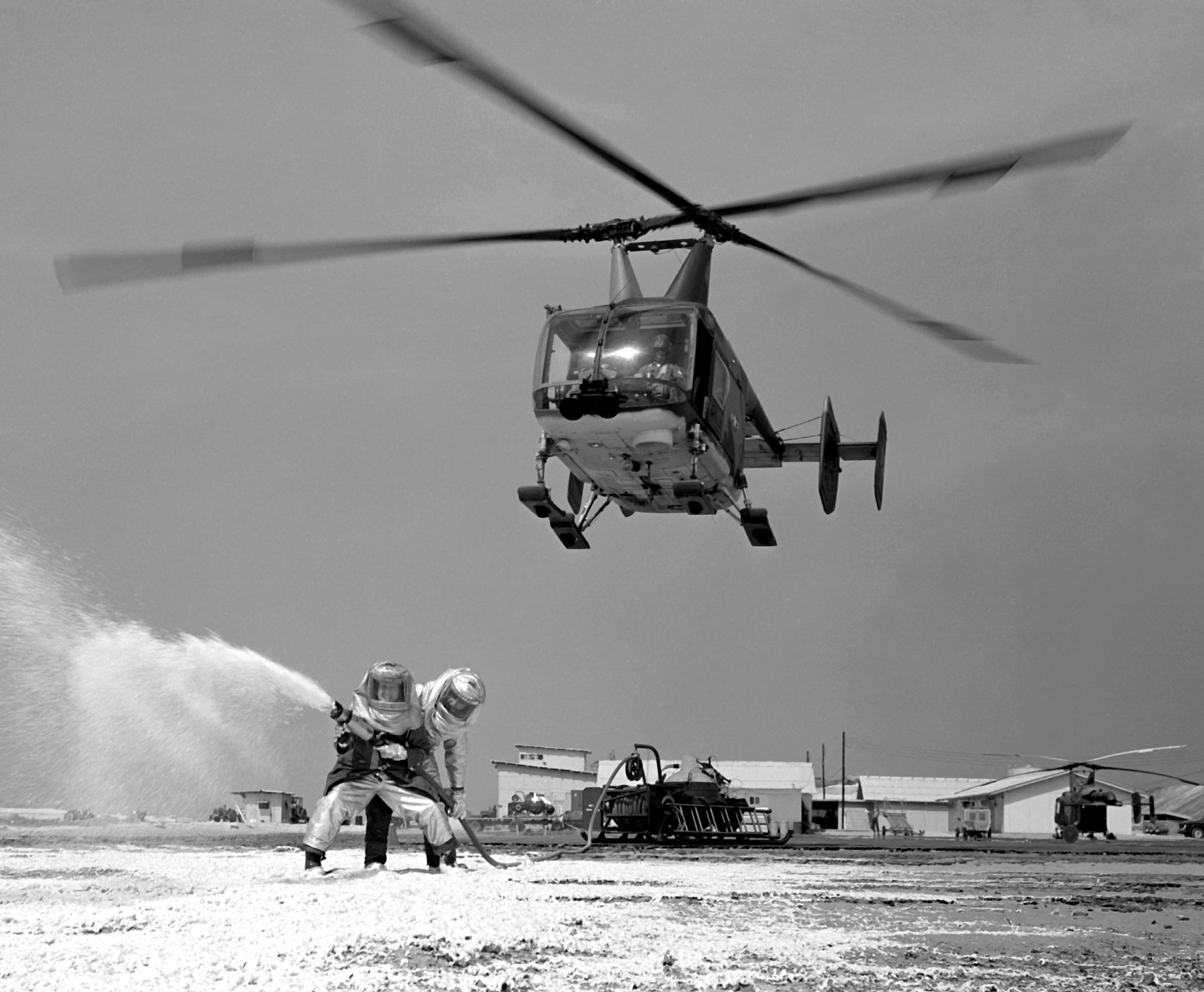
Kaman HH-43 Huskie
The Kaman HH-43 Huskie is a helicopter with intermeshing rotors used by the United States Air Force, the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps from the 1950s until the 1970s. It was primarily used for aircraft firefighting and rescue in the close vicinity of air bases, but was later used as a short-range overland search and rescue aircraft during the Vietnam War. Under the aircraft designation system used by the U.S. Navy pre-1962, Navy and U.S. Marine Corps versions were originally designated as the HTK, HOK or HUK, for their use as training, observation or utility aircraft, respectively. Design and development In 1947 Anton Flettner, a German aviation engineer, was brought to New York in the United States as part of Operation Paperclip. He was the developer of Germany's Flettner Fl 282 "Kolibri" (Hummingbird), a helicopter employing the "synchropter" principle of intermeshing rotors, a unique design principle that dispenses with the need for a tail rotor. Flet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchropter
Intermeshing rotors on a helicopter are a set of two rotors turning in opposite directions, with each rotor mast mounted with a slight angle to the other, in a transversely symmetrical manner, so that the blades intermesh without colliding. The arrangement allows the helicopter to function without a tail rotor, which saves power. However, neither rotor lifts directly vertically, which reduces efficiency per each rotor. This configuration is sometimes referred to as a synchropter. Yaw is accomplished through varying torque, which is done by increasing collective pitch on one of the blade sets. Most intermeshing designs have two blades per mast, although exceptions such as the Kellett XR-10 with three blades per mast do exist. The arrangement was developed in Germany by Anton Flettner for a small anti-submarine warfare helicopter, the Flettner Fl 265 as the pioneering example, and later the Flettner Fl 282 Kolibri. During the Cold War the American Kaman Aircraft company p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)