|
Kalyan Thaat
Kalyan () is one of the ten basic thaats of Hindustani music from the Indian subcontinent. It is also the name of a raga (more popularly known as Yaman) within this thaat. Description Kalyan thaat consists of an important group of evening ragas. Characterised by the teevra Madhyam, this thaat literally means good luck. Ragas of this thaat are considered to be a blessing-seeking and soothing. As a result, they are performed in the evening at the beginning of a concert. These ragas create a feeling of the unfolding of an evening. The Hindustani Classical Thaats are defined in their relation with the Bilawal Thaat, which has all shuddha(pure) notes. Ragas Ragas in Kalyan Thaat: Yaman, Bhupali, Hindol, Kedar, Shuddha Kalyan, Shyam Kalyan, Yaman Kalyan, Khem Kalyan, Savani Kalyan Chhayanat, Hameer, Gaud Sarang Gaud Sarang is a raga in Hindustani classical music that combines characteristics of Sarang and the now extinct raga named Gaud. Unlike most other members of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindustani Music
Hindustani classical music is the classical music of northern regions of the Indian subcontinent. It may also be called North Indian classical music or, in Hindustani, ''shastriya sangeet'' (). It is played in instruments like the violin, sitar and sarod. Its origins from the 12th century CE, when it diverged from Carnatic music, the classical tradition in South India. Hindustani classical music arose in the Ganga-Jamuni Tehzeeb, a period of great influence of Perso-Arabic arts in the subcontinent, especially the Northern parts. This music combines the Indian classical music tradition with Perso-Arab musical knowledge, resulting in a unique tradition of gharana system of music education. History Around the 12th century, Hindustani classical music diverged from what eventually came to be identified as Carnatic classical music.The central notion in both systems is that of a melodic musical mode or '' raga'', sung to a rhythmic cycle or '' tala''. It is melodic music, with no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhupali
Bhoopali, also known as ''Bhoop'', ''Bhopali,'' or ''Bhupali'', is a Hindustani classical raga. Bhupālī, is a raag in Kalyan Thaat. It is a pentatonic scale (uses 5 notes in ascending and descending scale). Most of the songs in this raga are based on Bhakti rasa. Since it uses 5 notes, belongs to the "Audav jaati" of ragas. The same raga in Carnatic music is known as Mohanam. Raga Bhoopali, Raga Yaman, and Raga Bhairav tend to be the three basic ragas of Hindustani music, learned first by its students. Theory Karhade (2011) explains that raga Bhopali consists of just 5 notes - सा रे ग प ध (sa, re, ga, pa and dha). It does not use Ma (also called Madhyam) and Ni (also called Nishadh). It is said that the absence of Ni (representative of physical pleasure) and Ma (representative of loving) means this raga is about non-attachment. The Introduction consists of two parts – ''Aaroh'' आरोह (where the notes are simply recited on an ascending scale) and A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hameer
Hameer is a nocturnal Hindustani classical nominally placed in Kalyan . All the ( (natural notes) along with ( are used in it. Generally, its (the most used, principal note of a raga on which a pause may be taken) is and the (the second-most used important note assisting the ) is . However, some exponents consider the to be (G natural) as Hameer is mainly sung in the upper half of an octave and is nocturnal. Pancham is not taken in the but is taken in . Its is "Shadav Sampurn". "Vadi Svar" is ''Dhaivat'' (Dh) and ''Samvadi Swar'' is ''Gandhar.'' The Carnatic raaga named Hameer Kalyani is similar to Hindusthani raag Kedar, not to Hindusthani Hamir. Carnatic music also has a separate raaga named Kedaram. As it happens, the Hindusthani raagas Kedar, Kamod and Hameer have fairly strong genetic overlap; in Kedar, madhyama is prominet; in Kamod it is Pancham; and in Hameer it is dhaivat which is most dominant. Ascent and descent In the ascent, all natural notes are used, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chhayanat (raga)
Chhayanat ("shadow or glimpse of ''Nat''") is a raga in Hindustani classical music. It is a relative of Nat Nat or NAT may refer to: Computing * Network address translation (NAT), in computer networking Organizations * National Actors Theatre, New York City, U.S. * National AIDS trust, a British charity * National Archives of Thailand * National As ..., an old raga that is rarely performed. Technical description Chhayanat is a very popular raag whereas its constituent "Chhaya" and "Nat" are rarely sung anymore. Its distinctive phrases P->R and P->S' set it apart from the related Kamod, Kedar, Alhaiya Bilawal and Hameer. Samay Chhayanat is an evening raag, and is sung during the second "prahar" 9PM-12AM. References Hindustani ragas {{India-music-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaman Kalyan
Yaman Kalyan is a Hindustani classical raga, related to Yaman. The movement of this raga is like Yaman, except that in the descent, it gently touches the flat madhyam using the GmG pattern occasionally. Description Ustad Dhyanesh Khan used to say that the flat madhyam in Yaman Kalyan is like the beautiful face of a veiled woman that comes out of the veil occasionally but disappears behind it almost instantaneously. As it is related to Yaman, it is a part of the Kalyan thaat. Compositions * Bhavayami GopalaBalam by Annamacharya Tallapaka Annamacharya (Telugu : తాళ్ళపాక అన్నమాచార్య) ( IAST: taḷḷapāka annamācārya; 22 May 1408 – 4 April 1503), also popularly known as Annamayya, was a 15th-century Hindu saint and the ea ... Film Songs Tamil External links SRA on Samay and Ragas Hindustani ragas {{India-music-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shyam Kalyan
Shyam is a name of Krishna and an Indian masculine given name and surname. Notable people with this name include: ;Shyam *Shyam (actor), Indian Hindi film actor *Shyam (composer), an Indian music composer from Kerala *Shyam Benegal, Indian film director *Shyam Satardekar, Indian politician *Karam Shyam, Indian politician ;Syam * Syam Pushkaran, scriptwriter in the Malayalam cinema * Syam Sudhakar (born 1983), Malayalam-language poet See also * Shyam (film), 2016 Indian Malayalam-language film * Sam (given name) Sam is a given name or nickname, often used by people named "Samuel," "Samson," and "Samantha". A *Sam Abbas (born 1993), Egyptian film producer and director * Sam Adams (other), multiple people *Sam Adekugbe (born 1995), Canadian socce ... * {{given name, type=both Indian given names Indian surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shuddha Kalyan
Suddha can refer to: * ''Suddha'' (film), a 2005 Indian film *Śuddha, a Sanskrit term referring to purity in Buddhism Purity (Pali: ''Vissudhi'') is an important concept within much of Theravada and Mahayana Buddhism, although the implications of the resultant moral purification may be viewed differently in the varying traditions. The aim is to purify the person ... *Śuddha, pure ''tattva''s in Śaivism {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kedar (raga)
Raga Kedar, also known as Kedara, is a Hindustani classical raga. Named after Lord Shiva, the raga occupies a high pedestal in Indian classical music. It is characterised by many melodious turns. This raga is the repetition of the swaras सा and म. It is generally accepted that it displays much thermal energy and is regarded as the Raagini of Raag Deepak. While preceding from Shuddha Madhyam (m) to Pancham (P), a touch of Gandhar (G) or a smooth passage from Gandhar (G) to Pancham (P) expressed as m G P is the more common way of instant raga manifestation. Origin The raga emerges from the Kalyan thaat. This raga is named after Lord Shiva and is loved by Lord Krishna. Lord Krishna played this raga on his flute and everyone in Gokul was mesmerized. Technical description The raga is of ''shaadava-sampurna'' nature, i.e., in its arohana (ascent), only six notes are used, and in avarohana (descent), all seven notes are used. In general, the progression of the raga is hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindol
Hindol is a Hindustani classical ''raga'' from the Kalyan Thaat. According to Indian classical vocalist Pandit Jasraj, Hindol is an ancient raga associated with the spring season and is sung during the first part of the day. Origin The raga emerges from Kalyan Thaat. It is an ancient ''raga'' associated with the spring season. Technical description Arohana The Arohana has five notes. Sa Ga Ma# Dha Ni Dha Sa. Avarohana The Avarohana has five notes. Sa Ni Dha Ma# Ga Sa. Re and Pa are not used. The only ''Teevra'' note used is Ma (henceforth represented by Ma#). All other ''swaras'' are ''shuddha''. Pakad Sa Ga Ma# Dha Ni Dha Ma# Ga Sa. The '' vadi swara'' is Dha, and the ''samvadi'' is Ga. Jati Audhva – Audhav Samay (time) The raga is to be sung or played on an instrument such as ''veena'', ''sitar'', ''sehnai'', flute, etc., during the first part of the day. Further information The raga has Teevra Madhyam at its heart, and revolves around that note, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lydian Mode
The modern Lydian mode is a seven-tone musical scale formed from a rising pattern of pitches comprising three whole tones, a semitone, two more whole tones, and a final semitone. : Because of the importance of the major scale in modern music, the Lydian mode is often described as the scale that begins on the fourth scale degree of the major scale, or alternatively, as the major scale with the fourth scale degree raised half a step. This sequence of pitches roughly describes the scale underlying the fifth of the eight Gregorian (church) modes, known as Mode V or the authentic mode on F, theoretically using B but in practice more commonly featuring B. The use of the B as opposed to B would have made such piece in the modern day F major scale. Ancient Greek Lydian The name Lydian refers to the ancient kingdom of Lydia in Anatolia. In Greek music theory, there was a Lydian scale or "octave species" extending from ''parhypate hypaton'' to ''trite diezeugmenon'', equivalent in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yaman (raga)
Yaman (also known as kalyaan, Iman, Aiman,'Eman', ' Kalyani' in Carnatic classical music) is a heptatonic ( Sampurna) Indian classical raga of Kalyan Thaat. Its signature phrase (Pakad) is ni-Re-Ga-/Re-Ga/ni-Re-Sa/Pa-Ma#-Ga-Re/ni-Re-Sa' (Ma is teevra). Tonal movements of the notes mostly reflect zigzag motion ''with gap of one or several notes'' usually that prefer reverse order very often like DNS' mDN GmD RGm N,GR or MDNS' GmDN RGmD N,RGm D,N,GR etc. Ideally yaman should not use PR combination but can use P~R showing colour of m or G while gliding from P to R, for PR is one of the specific identification of raag kalyaan. Description Yaman emerged from the parent musical scale of Kalyan. Considered to be one of the most fundamental and basic ragas in Hindustani tradition, it is thus often one of the first ragas taught to students. Mechanics Yaman's Jati is a Sampurna raga (ideally, yaman is audav sampoorna raag because of the structure- N,RGmDNR'S' NDPmGRS) and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
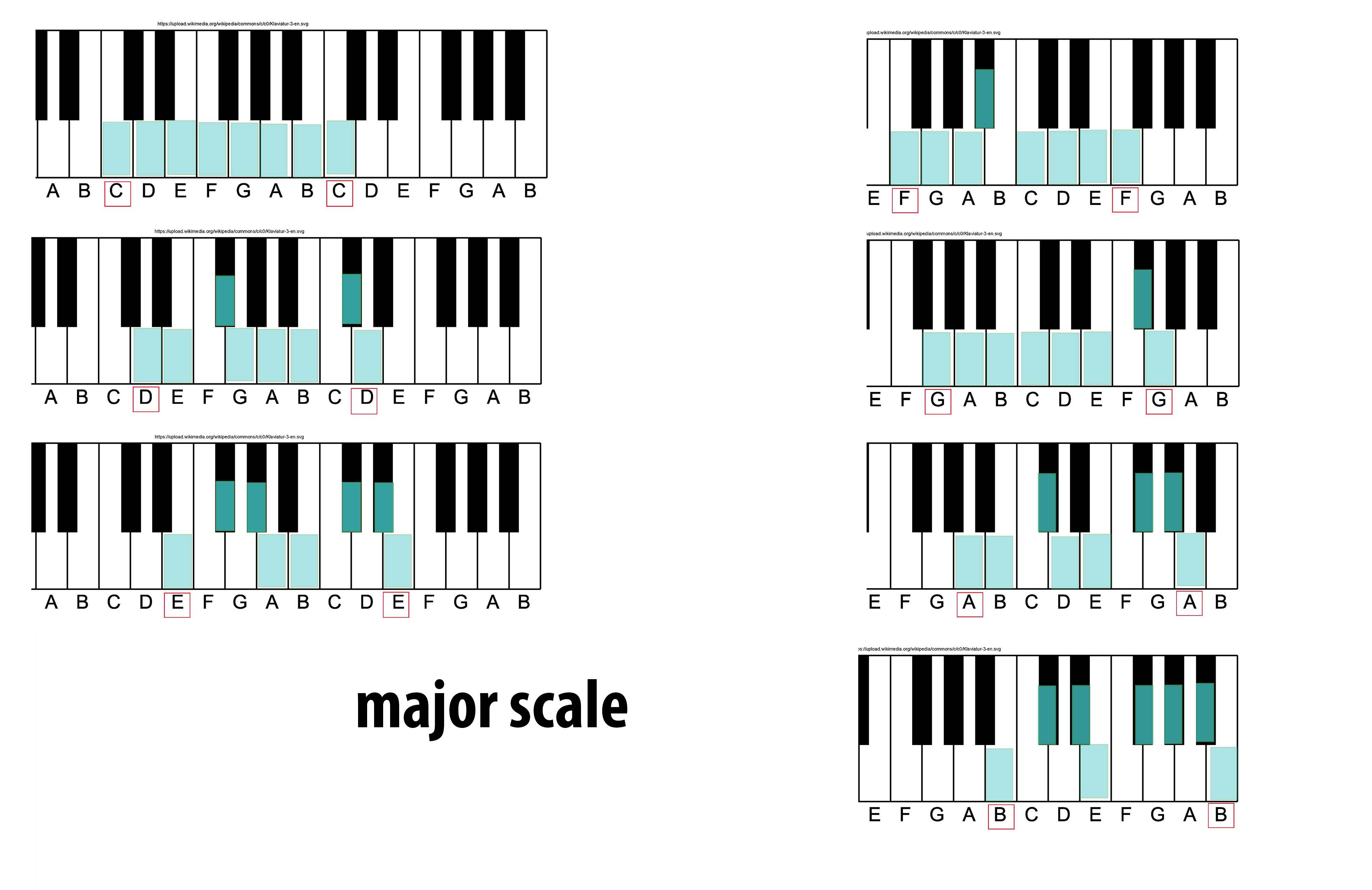
Major Scale
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale had a central importance in Western music, particularly in the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as '' Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as '' Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled line in the figu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
%2C_1660-1670_CE%2C_Golkonda.png)