|
Kahrizi Syndrome
Kahrizi syndrome (KHRZ) is an autosomal-recessive disease that is identified by mental retardation, cataracts, coloboma, kyphosis, and coarse facial features caused by a homozygous mutation in the SRD5A3 gene. Signs and symptoms Human traits related to Kahrizi syndrome are cataracts, wide nasal bridge, severe intellectual disability, motor delay, thick lower lip vermilion, capillary hemangioma, iris coloboma, bulbous nose, knee and elbow flexion contracture, and thoracic kyphosis. Symptoms of Kahrizi Syndrome * Head and Neck eyes: ** Iris Coloboma ** Cataracts * Skeletal Spine: ** Thoracic Kyphosis * Head and Neck Mouth: ** Thick Lips * Skeletal: ** Joint Contractures * Head and Neck Nose: ** Bulbous Nose ** Broad Nasal Bridge * Neurological Central Nervous System: ** Delayed Motor Development ** Severe Mental Retardation ** Speech Never Acquired * Skeletal Limbs: ** Knee Contractures * Skin Nails Hair Skin: ** Capillary hemangioma A capillary is a small bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal-recessive Disease
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development (a ''de novo'' mutation), or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene ( autosomal recessive inheritance) or from a parent with the disorder ( autosomal dominant inheritance). When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA (due to their size). There are well over 6,000 known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SRD5A3
Steroid 5-alpha-reductase 3, also known as 3-oxo-5-alpha-steroid 4-dehydrogenase 3, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SRD5A3'' gene. It is one of three forms of 5α-reductase. See also * SRD5A3-CDG * Congenital disorder of glycosylation A congenital disorder of glycosylation (previously called carbohydrate-deficient glycoprotein syndrome) is one of several rare inborn errors of metabolism in which glycosylation of a variety of tissue proteins and/or lipids is deficient or defecti ... * Kahrizi syndrome, a syndrome caused by a mutation in this gene References Further reading * * * * EC 1.3.99 {{gene-4-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
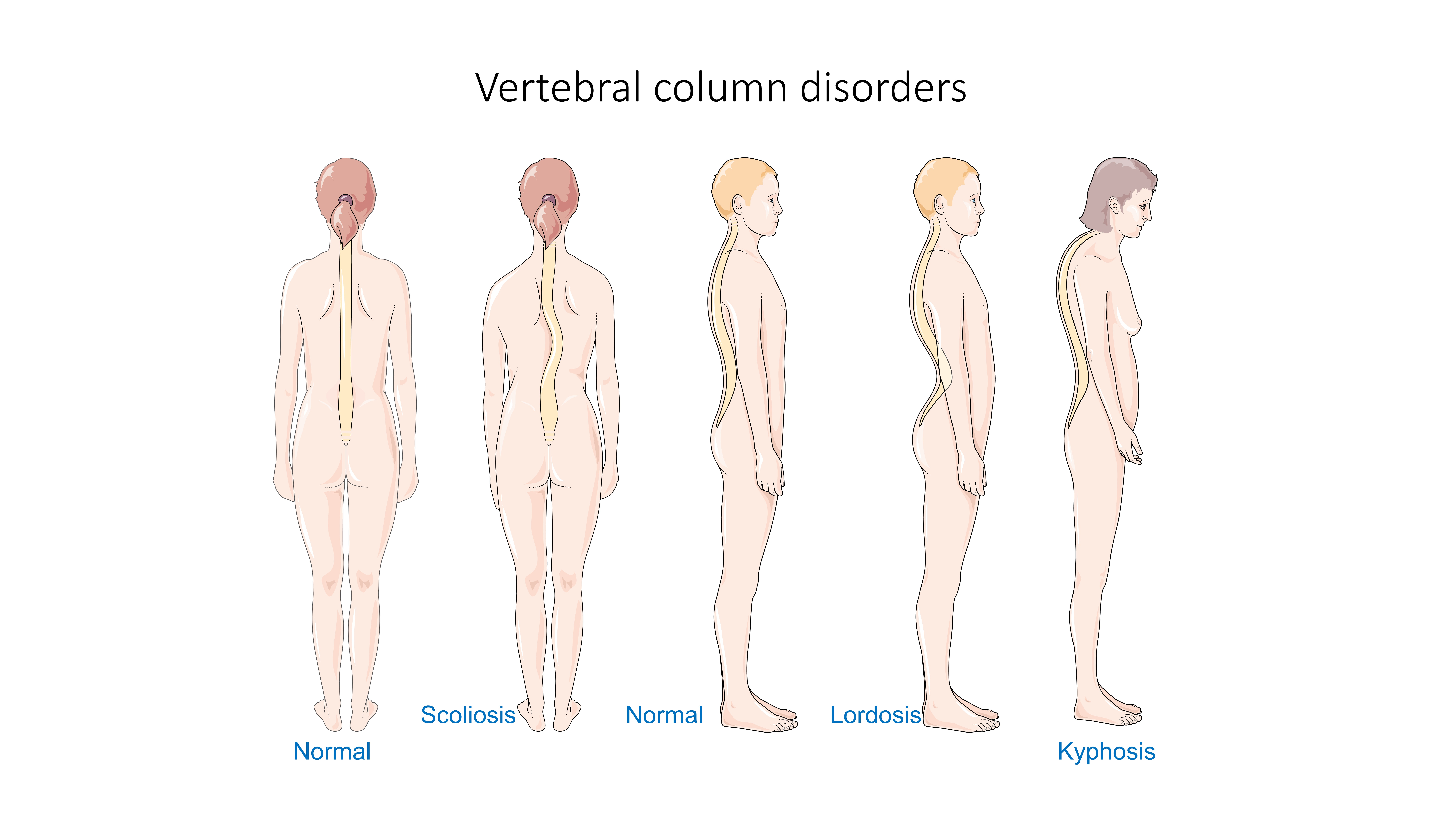
Kyphosis
Kyphosis is an abnormally excessive convex curvature of the spine as it occurs in the thoracic and sacral regions. Abnormal inward concave ''lordotic'' curving of the cervical and lumbar regions of the spine is called lordosis. It can result from degenerative disc disease; developmental abnormalities, most commonly Scheuermann's disease; Copenhagen disease, osteoporosis with compression fractures of the vertebra; multiple myeloma; or trauma. A normal thoracic spine extends from the 1st thoracic to the 12th thoracic vertebra and should have a slight kyphotic angle, ranging from 20° to 45°. When the "roundness" of the upper spine increases past 45° it is called kyphosis or "hyperkyphosis". Scheuermann's kyphosis is the most classic form of hyperkyphosis and is the result of wedged vertebrae that develop during adolescence. The cause is not currently known and the condition appears to be multifactorial and is seen more frequently in males than females. In the sense of a deformit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary Hemangioma
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: they convey blood between the arterioles and venules. These microvessels are the site of exchange of many substances with the interstitial fluid surrounding them. Substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in the microcirculation. During early embryonic development, new capillaries are formed through vasculogenesis, the process of blood vessel formation that occurs through a '' de novo'' production of endothelial cells that then form vascular tubes. The term '' angiogenesis'' denotes the formation of new capillaries from pre-existing blood vessels and already present ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |