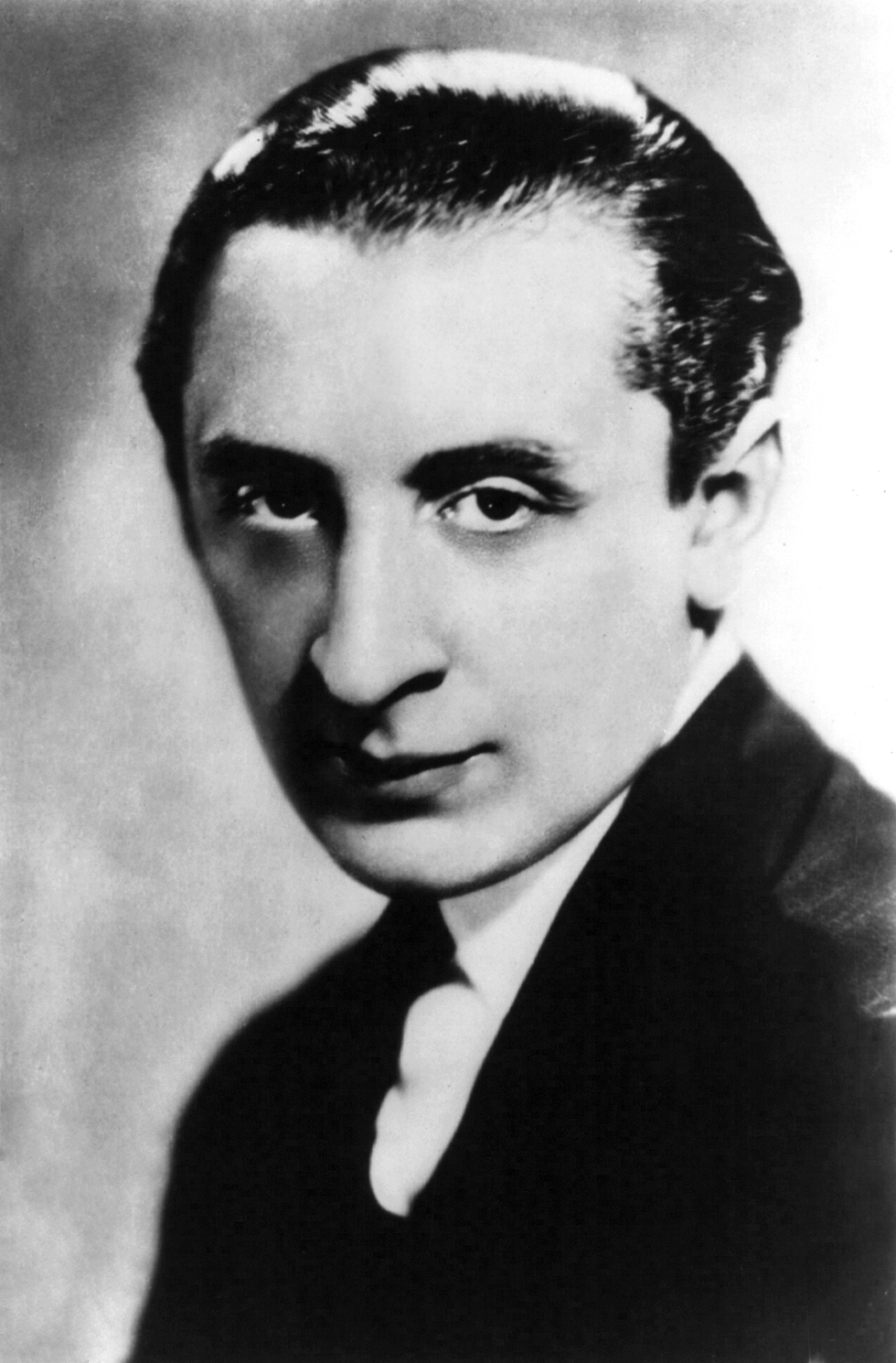|
Kabalevsky
Dmitry Borisovich Kabalevsky (russian: Дми́трий Бори́сович Кабале́вский ; 14 February 1987) was a Soviet composer, conductor, pianist and pedagogue of Russian gentry descent. He helped set up the Union of Soviet Composers in Moscow and remained one of its leading figures during his lifetime. He was a prolific composer of piano music and chamber music; many of his piano works were performed by Vladimir Horowitz. He is best known in Western Europe for his Second Symphony, the "Comedians' Galop" from '' The Comedians'' Suite, Op. 26 and his Third Piano Concerto. Life Kabalevsky was born in Saint Petersburg in 1904, but moved to Moscow at a young age. His father was a mathematician and encouraged him to study mathematics, but he showed a fascination for the arts from a young age. He studied at the Academic Music College in Moscow and graduated in 1922. He then continued his studies with Vasily Selivanov. In 1925, he then went on to study at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Comedians (Kabalevsky)
''The Comedians'', Op. 26, is an orchestral suite of ten numbers by Dmitry Kabalevsky. It is one of his best-known and best-loved works. In particular, the "Comedians' Galop" (No. 2) is the single most famous piece of music he ever wrote. It is popular as a piece played on sports days in Japan. (1942). Background In 1938 or 1939, Kabalevsky wrote incidental music for a children's play called ''The Inventor and the Comedians'', by the Soviet Jewish writer Mark Daniel. The play was staged at the Central Children's Theatre in Moscow, and it was about the German inventor Johannes Gutenberg and a group of travelling buffoons. Mark Daniel died young the following year. Concert suite In 1940, Kabalevsky chose ten short numbers from the incidental music and arranged them into a concert suite. The movements are: * Prologue: ''Allegro vivace'' * Comedians' Galop: ''Presto'' * March: ''Moderato'' * Waltz: ''Moderato'' * Pantomime: ''Sostenuto e pesante'' * Intermezzo: ''Allegro sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nikolai Myaskovsky
Nikolai Yakovlevich Myaskovsky or Miaskovsky or Miaskowsky (russian: Никола́й Я́ковлевич Мяско́вский; pl, Mikołaj Miąskowski, syn Jakóbowy; 20 April 18818 August 1950), was a Russian and Soviet composer. He is sometimes referred to as the "Father of the Soviet Symphony". Myaskovsky was awarded the Stalin Prize five times. Early years Myaskovsky was born in Nowogieorgiewsk, near Warsaw, Congress Poland, Russian Empire, the son of an engineer officer in the Russian army. After the death of his mother the family was brought up by his father's sister, Yelikonida Konstantinovna Myaskovskaya, who had been a singer at the Saint Petersburg Opera. The family moved to Saint Petersburg in his teens. Though he learned piano and violin, he was discouraged from pursuing a musical career, and entered the military. However, a performance of Tchaikovsky's ''Pathétique'' Symphony conducted by Arthur Nikisch in 1896 inspired him to become a composer. In 1902 he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Horowitz
Vladimir Samoylovich Horowitz; yi, וולאַדימיר סאַמוילאָוויטש האָראָוויץ, group=n (November 5, 1989)Schonberg, 1992 was a Russian-born American classical pianist. Considered one of the greatest pianists of all time, he was known for his virtuoso technique, tone color, and the public excitement engendered by his playing. Life and early career Horowitz was born on October 1, 1903, in Kiev, then in the Russian Empire (now Ukraine). There are unsubstantiated claims that he was born in Berdichev (a city near Zhitomir in Volhynian Governorate), but his birth certificate unequivocally states that Kiev was his birthplace. He was the youngest of four children of Samuil Horowitz and Sophia Bodik, who were assimilated Jews. His father was a well-to-do electrical engineer and a distributor of electric motors for German manufacturers. His grandfather Joachim was a merchant (and an arts-supporter), belonging to the 1st Guild, which exempted him from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Academy (journal)
''Music Academy'' (russian: Музыкальная Академия, translit=Muzykalʹnaja Akademija, italic=yes; before 1992 – ''Soviet Music'') is the oldest Russian peer-reviewed academic journal about music. History ''Soviet Music'' (russian: Советская музыка, translit=Sovetskaya muzika, italic=yes) was established in February 1933 by the Union of Soviet Composers and the Soviet Ministry of Culture. In the first year, the journal was a bimonthly publication 200 pages in length, but after that until World War II the journal was published once a month and was on average 110 pages long. In 1979, the circulation of the magazine was 21,000 copies. In Soviet times, the journal published articles devoted to the works of domestic and foreign composers, the problems of music science, the development of national and ethnic musical cultures, heritage and education, and questions of the performer skills. The journal also contained various discussion materials, reviews ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Goldenweiser (composer)
Alexander Borisovich Goldenweiser (or ''Goldenveyzer''; russian: Алекса́ндр Бори́сович Гольденве́йзер; 26 November 1961), was a Soviet and Russian pianist, teacher and composer. Goldenweiser was born in Kishinev, Bessarabia, Russia. In 1889 he was admitted to the Moscow Conservatory in the class of Alexander Siloti (also Ziloti). He graduated from the Moscow Conservatory in 1895 in the piano class of Pavel Pabst (previously with A.I.Siloti), winning the Gold Medal for Piano, in 1897 – in the composition class of Mikhail Ippolitov-Ivanov. He also studied composition with Anton Arensky and counterpoint with Sergei Taneyev (1892–1893). He joined the faculty of the Conservatory shortly afterward, and during his tenure there, his pupils included Grigory Ginzburg, Lazar Berman, Samuil Feinberg, Rosa Tamarkina, Dmitry Kabalevsky, Galina Eguiazarova, Nikolai Kapustin, Alexander Braginsky, Sulamita Aronovsky, Tatiana Nikolayeva, Dmitry Paperno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
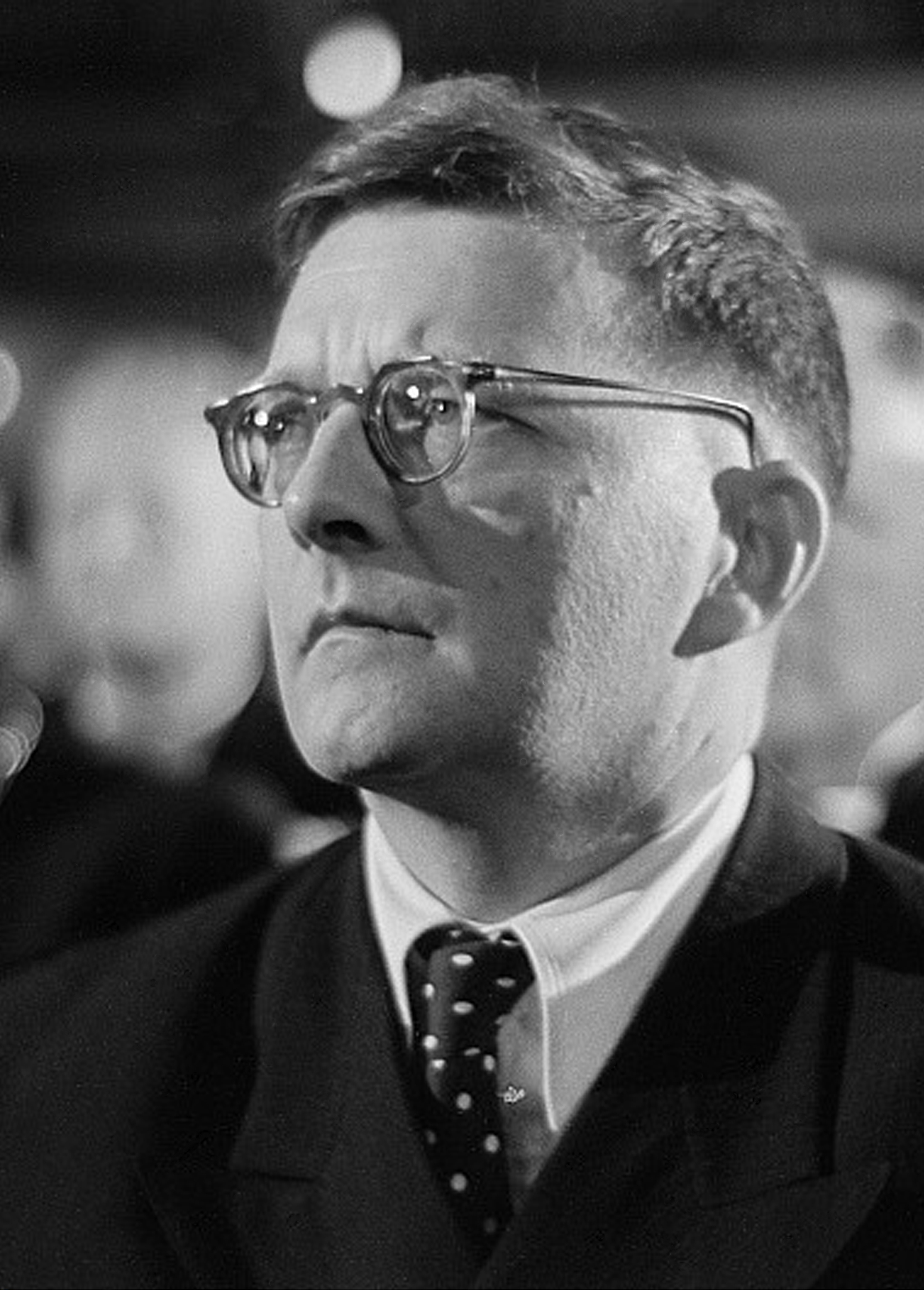
Dmitri Shostakovich
Dmitri Dmitriyevich Shostakovich, , group=n (9 August 1975) was a Soviet-era Russian composer and pianist who became internationally known after the premiere of his First Symphony in 1926 and was regarded throughout his life as a major composer. Shostakovich achieved early fame in the Soviet Union, but had a complex relationship with its government. His 1934 opera '' Lady Macbeth of Mtsensk'' was initially a success, but eventually was condemned by the Soviet government, putting his career at risk. In 1948 his work was denounced under the Zhdanov Doctrine, with professional consequences lasting several years. Even after his censure was rescinded in 1956, performances of his music were occasionally subject to state interventions, as with his Thirteenth Symphony (1962). Shostakovich was a member of the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR (1947) and the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union (from 1962 until his death), as well as chairman of the RSFSR Union of Composers (1960–196 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Conservatory
The Moscow Conservatory, also officially Moscow State Tchaikovsky Conservatory (russian: Московская государственная консерватория им. П. И. Чайковского, link=no) is a musical educational institution located in Moscow, Russia. It grants undergraduate and graduate degrees in musical performance and musical research. The conservatory offers various degrees including Bachelor of Music Performance, Master of Music and PhD in research. History It was co-founded in 1866 as the Moscow Imperial Conservatory by Nikolai Rubinstein and Prince Nikolai Troubetzkoy. It is the second oldest conservatory in Russia after the Saint Petersburg Conservatory. Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky was appointed professor of theory and harmony at its opening. Since 1940, the conservatory has borne his name. Choral faculty Prior to the October Revolution, the choral faculty of the conservatory was second to the Moscow Synodal School and Moscow Synodal Choir, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Music College
Academic Music College, fully Tchaikovsky Academic Music College at the Moscow State Conservatory (russian: Академическое музыкальное училище при Московской государственной консерватории им. П. И. Чайковского) is an educational institution located in Moscow, Russia. History Founded in 1891 as ''Public Music College'' by pianist , the college was given the name of and an official attachment to the Moscow Conservatory in 1936. Overview Academic Music College's full graduate program lasts four years. Entry exams are normally held for students age 15, although students from the vocal department are usually older. Its diploma gives graduates the right to work professionally as teachers, orchestra players, conductors, operatic and choir soloists. The Academic Music College can also be considered a preparatory stage for further advancement in higher education institutions such as conservatories and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sergei Prokofiev
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev; alternative transliterations of his name include ''Sergey'' or ''Serge'', and ''Prokofief'', ''Prokofieff'', or ''Prokofyev''., group=n (27 April .S. 15 April1891 – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, pianist, and conductor who later worked in the Soviet Union. As the creator of acknowledged masterpieces across numerous music genres, he is regarded as one of the major composers of the 20th century. His works include such widely heard pieces as the March from '' The Love for Three Oranges,'' the suite ''Lieutenant Kijé'', the ballet ''Romeo and Juliet''—from which "Dance of the Knights" is taken—and '' Peter and the Wolf.'' Of the established forms and genres in which he worked, he created—excluding juvenilia—seven completed operas, seven symphonies, eight ballets, five piano concertos, two violin concertos, a cello concerto, a symphony-concerto for cello and orchestra, and nine completed piano sonatas. A graduate of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Association Of Proletarian Musicians
The Russian Association of Proletarian Musicians or RAPM (russian: Российская Ассоциация Пролетарских Музыкантов, РАПМ ) was a musicians' creative union of the early Soviet period. It was founded in June 1923, by Lev Shul'gin, Aleksei Sergeev, and David Chernomoridikov. RAPM's members advocated "mass songs" for choirs , easily accessible melodies that were often inspired by folk tunes, and which songs were often collectively composed. The RAPM initially had the task of liaising with composers, critics, educators and administrators sympathetic with the regime. However, it soon became clear to the founders of RAPM that the organization was outgrowing its role as an advisory body, and tensions grew between members. By 1924, Shul'gin and Sergeev left the organization, believing the content being produced was either too simplistic, or too inaccessible to actual workers. Sergeev and Shul'gin, along with most of the composers from RAPM would go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Zhdanov
Andrei Aleksandrovich Zhdanov ( rus, Андре́й Алекса́ндрович Жда́нов, p=ɐnˈdrej ɐlʲɪˈksandrəvʲɪtɕ ˈʐdanəf, links=yes; – 31 August 1948) was a Soviet politician and cultural ideologist. After World War II, Zhdanov was thought to be the successor-in-waiting to Joseph Stalin but died before him. He has been described as the "propagandist-in-chief" of the Soviet Union from 1945 to 1948.V. M. Zubok and Konstantin Pleshakov. Inside the Kremlin's Cold War: from Stalin to Khrushchev. Harvard: Harvard UP, 1996, p.119 Early life Zhdanov was born in Mariupol (now Ukraine), where his father was a school inspector. His maternal grandfather was the former rector of the Moscow Theological Academy. He studied at the Moscow Commercial Institute. In 1914, he was drafted into the Russian army, graduated from an officers' school and served in the reserves. He joined the Bolsheviks in 1915. In 1917, he was chairman of the Shadrinsk committee of the Bol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Film
A sound film is a motion picture with synchronized sound, or sound technologically coupled to image, as opposed to a silent film. The first known public exhibition of projected sound films took place in Paris in 1900, but decades passed before sound motion pictures became commercially practical. Reliable synchronization was difficult to achieve with the early sound-on-disc systems, and amplification and recording quality were also inadequate. Innovations in sound-on-film led to the first commercial screening of short motion pictures using the technology, which took place in 1923. The primary steps in the commercialization of sound cinema were taken in the mid-to-late 1920s. At first, the sound films which included synchronized dialogue, known as "talking pictures", or "talkies", were exclusively shorts. The earliest feature-length movies with recorded sound included only music and effects. The first feature film originally presented as a talkie (although it had only limited so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |