|
KI Polyomavirus
KI polyomavirus (also known as KI virus, KIPyV, or Human polyomavirus 3) is a virus of the family Polyomaviridae. It was discovered in 2007 in stored samples of human respiratory secretions collected by the Karolinska Institute, after which the virus is named. Discovery KI virus was discovered in 2007 in samples of human respiratory secretions being systematically searched as part of a program for identifying novel human viruses. It was identified by sequence homology to known human polyomaviruses BK virus and JC virus, and simian polyomavirus SV40. KI virus was the third human polyomavirus described and the first to be discovered since BK and JC in 1971. A very similar respiratory virus, WU virus, was also reported later in 2007. Genome The complete genome of the KI virus has been sequenced and found to be a circular double-stranded DNA genome of 5040 base pairs containing genetic material characteristic of polyomaviruses, encoding five viral proteins: three capsid components, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The capsid and inner genome is called the nucleocapsid. Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while the helical shape resembles the shape of a spring, taking the space of a cylinder but not being a cylinder itself. The capsid faces may consist of one or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APMIS ".
It was formed by the 1988 union of the three sections of ''Acta Pathologica, Microbiologica, et Immunologica Scandinavica'': ''Section A, Pathology'', ''Section B, Microbiology'', and ''Section C, Immunology''. The original journals dated from 1924, originally published as ''Acta Pathologica et Microbiologica Scandinavica''. ...
''APMIS'', formerly known as ''Acta Pathologica, Microbiologica, et Immunologica Scandinavica'', is a monthly medical journal published on behalf of the Scandinavian Societies for Medical Microbiology and Pathology by Wiley Munksgaard. Its stated aim is to "publish original research in the fields of pathology, microbiology and immunology, and from related developing areas of modern biomedicine Biomedicine (also referred to as Western medicine, mainstream medicine or conventional medicine) [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that affect the patient's immune system. Examples of these extrinsic factors include HIV infection and environmental factors, such as nutrition. Immunocompromisation may also be due to genetic diseases/flaws such as SCID. In clinical settings, immunosuppression by some drugs, such as steroids, can either be an adverse effect or the intended purpose of the treatment. Examples of such use is in organ transplant surgery as an anti- rejection measure and in patients with an overactive immune system, as in autoimmune diseases. Some people are born with intrinsic defects in their immune system, or primary immunodeficiency. A person who has an immunodeficiency of any kind is said to be immunocompromised. An immunocompromised individual may particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merkel Cell Polyomavirus
Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCV or MCPyV) was first described in January 2008 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It was the first example of a human viral pathogen discovered using unbiased metagenomic next-generation sequencing with a technique called digital transcriptome subtraction. MCV is one of seven currently known human oncoviruses. It is suspected to cause the majority of cases of Merkel cell carcinoma, a rare but aggressive form of skin cancer. Approximately 80% of Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) tumors have been found to be infected with MCV. MCV appears to be a common—if not universal—infection of older children and adults. It is found in respiratory secretions suggesting that it may be transmitted by a respiratory route. But it also can be found shedding from healthy skin, and in gastrointestinal tract tissues and elsewhere, and so its precise mode of transmission remains unknown. In addition, recent studies suggest that this virus may latently infect the human sera and per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carcinogenic
A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substances are considered carcinogens, but their carcinogenic activity is attributed to the radiation, for example gamma rays and alpha particles, which they emit. Common examples of non-radioactive carcinogens are inhaled asbestos, certain dioxins, and tobacco smoke. Although the public generally associates carcinogenicity with synthetic chemicals, it is equally likely to arise from both natural and synthetic substances. Carcinogens are not necessarily immediately toxic; thus, their effect can be insidious. Carcinogens, as mentioned, are agents in the environment capable of contributing to cancer growth. Carcinogens can be categorized into two different types: activation-dependent and activation-independent, and each nature impacts their level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maternal Antibodies
Passive immunity is the transfer of active humoral immunity of ready-made antibodies. Passive immunity can occur naturally, when maternal antibodies are transferred to the fetus through the placenta, and it can also be induced artificially, when high levels of antibodies specific to a pathogen or toxin (obtained from humans, horses, or other animals) are transferred to non-immune persons through blood products that contain antibodies, such as in immunoglobulin therapy or antiserum therapy. Passive immunization is used when there is a high risk of infection and insufficient time for the body to develop its own immune response, or to reduce the symptoms of ongoing or immunosuppressive diseases.Microbiology and Immunology On-Line Textbook : USC School of Medicine Passive immunization can be provided when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibodies
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seroprevalence
Seroprevalence is the number of persons in a population who test positive for a specific disease based on serology (blood serum) specimens; often presented as a percent of the total specimens tested or as a proportion per 100,000 persons tested. As positively identifying the occurrence of disease is usually based upon the presence of Antibody, antibodies for that disease (especially with viral infections such as herpes simplex, HIV, and SARS-CoV-2), this number is not significant if the Sensitivity and specificity, specificity of the antibody is low. References External links HIV Portland Glossary definition of seroprevalence Epidemiology Serology {{med-diagnostic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small Tumor Antigen
The small tumor antigen (also called the small T-antigen and abbreviated STag or ST) is a protein encoded in the genomes of polyomaviruses, which are small double-stranded DNA viruses. STag is expressed early in the infectious cycle and is usually not essential for viral proliferation, though in most polyomaviruses it does improve replication efficiency. The STag protein is expressed from a gene that overlaps the large tumor antigen (LTag) such that the two proteins share an N-terminal DnaJ-like domain but have distinct C-terminal regions. STag is known to interact with host cell proteins, most notably protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), and may activate the expression of cellular proteins associated with the cell cycle transition to S phase. In some polyomaviruses - such as the well-studied SV40, which natively infects monkeys - STag is unable to induce neoplastic transformation in the host cell on its own, but its presence may increase the transforming efficiency of LTag. In other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Tumor Antigen
The large tumor antigen (also called the large T-antigen and abbreviated LTag or LT) is a protein encoded in the genomes of polyomaviruses, which are small double-stranded DNA viruses. LTag is expressed early in the infectious cycle and is essential for viral proliferation. Containing four well-conserved protein domains as well as several intrinsically disordered regions, LTag is a fairly large multifunctional protein; in most polyomaviruses, it ranges from around 600-800 amino acids in length. LTag has two primary functions, both related to replication of the viral genome: it unwinds the virus's DNA to prepare it for replication, and it interacts with proteins in the host cell to dysregulate the cell cycle so that the host's DNA replication machinery can be used to replicate the virus's genome. Some polyomavirus LTag proteins - most notably the well-studied SV40 large tumor antigen from the SV40 virus - are oncoproteins that can induce neoplastic transformation in the host cell. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
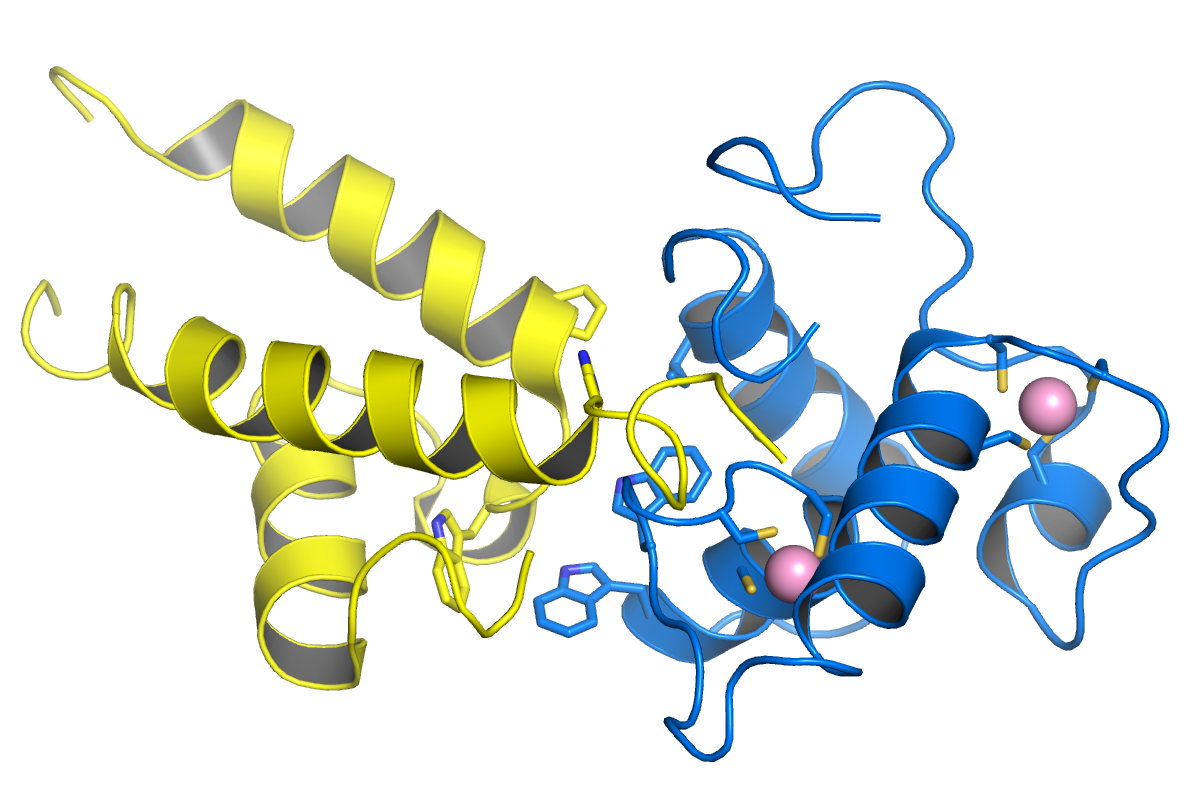
Major Capsid Protein VP1
Major capsid protein VP1 is a viral protein that is the main component of the polyomavirus capsid. VP1 monomers are generally around 350 amino acids long and are capable of self-assembly into an icosahedral structure consisting of 360 VP1 molecules organized into 72 pentamers. VP1 molecules possess a surface binding site that interacts with sialic acids attached to glycans, including some gangliosides, on the surfaces of cells to initiate the process of viral infection. The VP1 protein, along with capsid components VP2 and VP3, is expressed from the "late region" of the circular viral genome. Structure VP1 is the major structural component of the polyomavirus icosahedral capsid, which has T=7 symmetry and a diameter of 40-45 nm. The capsid contains three proteins; VP1 is the primary component and forms a 360-unit outer capsid layer composed of 72 pentamers. The other two components, VP2 and VP3, have high sequence similarity to each other, with VP3 truncated at the N- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.gif)