|
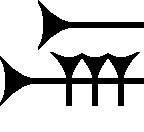
KÁ (gate Sumerogram)
The cuneiform sign KÁ, for ''gate'' is the Sumerogram-(logogram) used in the Amarna letters and the Epic of Gilgamesh; as just ''KÁ'' it means "gate" or "doorway", Akkadian language, "bābu"; as "Gate-Great", KÁ.GAL for City gate, City-Gate, it is from Akkadian "abullu", ("(city) gate"). Both uses are in the Epic of Gilgamesh. In the Epic, it is only used as the sumerogram, a total of 19 times, (7 times for 'abullu', city gate). In the Epic, all spellings for city gate use KÁ.GAL; for gate ('bābu') only one spelling uses the alphabetic letters for b-a-b-u; the rest use KÁ along with other added cuneiform signs (KÁ-x-x, or KÁ-x, etc.). Amarna letters In the Amarna letters, the topic of Amarna letter EA 296, ''Under the Yoke,'' is the guarding of two cities, at the city gate; also the man authoring the letter, Yabitiri-(Yahtiru)-(governor?) of City? is called a "gatekeeper", lines 24 and 31: LÚ (man Sumerogram), LÚ.Pa (cuneiform), PA.KÁ.ŠU, Man-Gate-"hand". Šu (cuneifor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B222ellst
B, or b, is the second letter of the Latin-script alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''bee'' (pronounced ), plural ''bees''. It represents the voiced bilabial stop in many languages, including English. In some other languages, it is used to represent other bilabial consonants. History Old English was originally written in runes, whose equivalent letter was beorc , meaning " birch". Beorc dates to at least the 2nd-century Elder Futhark, which is now thought to have derived from the Old Italic alphabets' either directly or via Latin . The uncial and half-uncial introduced by the Gregorian and Irish missions gradually developed into the Insular scripts' . These Old English Latin alphabets supplanted the earlier runes, whose use was fully banned under King Canute in the early 11th century. The Norman Conquest popularised the Carolingian half-uncial forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šu (cuneiform)
The cuneiform šu sign is a common, multi-use syllabic and alphabetic sign for ''šu'', ''š'', and ''u''; it has a subsidiary usage for syllabic ''qat''; it also has a majuscule-(capital letter) Sumerogram usage for ŠU, for Akkadian language "qātu", the word for "hand". The human hand is the shape of cuneiform character ''šu'', and thus the origin of its creation (late 4th millennium BC, or early 3rd millennium BC). The scribal usage of a sign allows for any of the 4 vowels (no vowel 'o' in Akkadian), ''a, e, i, u'' to be interchangeable; thus a usage for syllabic ''qat'' could conceivably be used for the following (k can replace 'q', and d can replace 't'): ''q, a,'' or ''t''; also ''ka, qa, ad, at''. (The "š" (shibilant s) is also interchangeable with the other two esses, "s", and "ṣ", for "''šu''"!) The ''šu'' sign has a common usage in the Amarna letters and the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. Its usage numbers in the Epic are as follows:Parpola, 1971. ''The Standard Babylo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumerian Words And Phrases
Sumerian or Sumerians may refer to: *Sumer, an ancient civilization **Sumerian language **Sumerian art **Sumerian architecture **Sumerian literature **Cuneiform script, used in Sumerian writing *Sumerian Records, an American record label based in Washington, D.C. and Los Angeles See also *Sumeria (other) *Sumer (other) *Sumarian (other) Sumarian is a misspelling and may refer to: * Sumerian *Samaria or Samaritans Samaritans (; ; he, שומרונים, translit=Šōmrōnīm, lit=; ar, السامريون, translit=as-Sāmiriyyūn) are an ethnoreligious group who originate fr ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GAL (great Sumerogram)
Gal may refer to: People Surname * Gál, a Hungarian surname * Andreas Gal (born 1976), German programmer * Dani Gal (born 1975), Israeli video artist * Dean Gal (born 1995), Israeli footballer * Edward Gal (born 1970), Dutch dressage rider * Gedalia Gal (born 1933), Israeli farmer and former politician * Igor Gal (born 1983), Croatian footballer * Jenny Gal (born 1969), Dutch-Italian judoka * Lidia Gal, Israel chess master * Naomi Gal (born 1944), Israeli writer * Nora Gal (1912–1991), Soviet translator and literary critic * Riki Gal (born 1950), Israeli singer * Reuven Gal (born 1942), Israeli psychologist * Sandra Gal (born 1985), German LPGA golfer * Șandor Gal (born 1955), Romanian former ice hockey player * Sharon Gal (born 1974), Israeli journalist and politician * Shmuel Gal, Israeli mathematician and professor * Susan Gal (born 1949), American academic * Udi Gal (born 1979), Israeli Olympic sailor * Uziel Gal (1923–2002), German-born Israeli gun designer * Yeho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma (cuneiform)
The cuneiform ma sign, is found in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. In the Epic it is also used as the Sumerogram MA, (for Akkadian language "mina", ''manû'', a weight measure, as MA.NA, or MA.NA.ÀM). The ''ma'' sign is often used at the end of words, besides its alphabetic usage inside words as syllabic ''ma'', elsewhere for ''m'', or ''a''. The usage of cuneiform ''ma'' in the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'', is only exceeded by the usage of a (cuneiform) (1369 times, and 58, A (Sumerogram), versus 1047 times for ''ma'', 6 for MA (Sumerogram)). The high usage for ''a'' is partially a result of the prepositional use for ''a-na''-(Akkadian "ana", ''to, for'', etc.); "''i''", also has an increased prepositional use of i (cuneiform), for Akkadian ''ina'', ( i- na), for ''in, into, etc.'' References * Moran, William L. 1987, 1992. ''The Amarna Letters.'' Johns Hopkins University Press, 1987, 1992. 393 pages.(softcover, ) * Parpola, 1971. ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anson Rainey
Anson Frank Rainey (January 11, 1930 – February 19, 2011) was professor emeritus of ancient Near Eastern cultures and Semitic linguistics at Tel Aviv University. He is known in particular for contributions to the study of the Amarna tablets, the noted administrative letters from the period of Pharaoh Akhenaten's rule during the 18th Dynasty of Egypt.Rollston, C. (2011)Among the last of the titans: Aspects of Professor Anson Rainey's life and legacy (1930–2011)(February 20, 2011); retrieved May 22, 2017 He authored and edited books and articles on the cultures, languages and geography of the Biblical lands. Early life Anson Rainey was born in Dallas, Texas, in 1930. Upon the death of his father that same year, he was left with his maternal grandparents. He attended Brown Military Academy in San Diego, California, from 1943 to 1946. After one semester of study there – as a cadet battalion commander – he served as assistant commandant at Southern California Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project
The Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project is an international scholarly project aimed at collecting and publishing ancient Assyrian texts and studies based on them. Its headquarters are in Helsinki in Finland. State Archives of Assyria State Archives of Assyria Cuneiform Texts State Archives of Assyria Studies See also *Epic of Gilgamesh *Text corpus References *Cole, S. '' Nippur in Late Assyrian Times, c. 755-612 BC,'' by Steven W. Cole, (The Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project, University of Helsinki, by Vammalan Kirjapaino Oy, Finland), c 1996. *Novotny, J. ''The Standard Babylonian'' ''Etana Etana (, ''E.TA.NA'') was the probably fictional thirteenth king of the first dynasty of Kish. He is listed in the ''Sumerian King List'' as the successor of Arwium, the son of Mashda, as king of Kish. The list also calls Etana "the shepherd ... Epic,'' by Jamie R. Novotny, (University of Helsinki, Ibid.), c 2001. External links Official page, University of Helsinki {{Corpus lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simo Parpola
Simo Kaarlo Antero Parpola (born 4 July 1943) is a Finnish Assyriologist specializing in the Neo-Assyrian Empire and Professor emeritus of Assyriology at the University of Helsinki (retired fall 2009). Career Simo Parpola studied Assyriology, Classics and Semitic Philology at the University of Helsinki, the Pontifical Biblical Institute and the British Museum in 1961–1968. He completed his PhD in Helsinki and began his academic career as wissenschaftlicher Assistant of Karlheinz Deller at the Seminar für Sprachen und Kulturen des Vorderen Orients of the University of Heidelberg in 1969. Between 1973 and 1976 he was Docent of Assyriology and Research Fellow at the University of Helsinki, and from 1977 to 1979 Associate Professor of Assyriology with tenure at the Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago. He was appointed Extraordinary Professor of Assyriology at the University of Helsinki in 1978 and has directed the University's Neo-Assyrian Text Corpus Project since 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William L
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tjaru
Tjaru ( egy, ṯꜣrw) was an ancient Egyptian fortress on the ''Way of Horus'' or ''Horus military road'', the major road leading out of Egypt into Canaan. It was known in Greek as Selē ( grc, Σελη), in Latin as Sile or Sele, and in Coptic as Selē or Slē ( cop, Ⲥⲉⲗⲏ or Ⲥⲗⲏ). It has been suggested that its remains form the Tel Habuwa, Tel el-Habua near El-Qantarah el-Sharqiyya, Qantarah.Ian Shaw, ''The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt'', Oxford University Press 2000, , p.200Barry J. Kemp, ''Ancient Egypt: Anatomy of a Civilization'', Routledge 2005, , p.25 History The Horus of Mesen was worshipped at Tjaru in the form of a lion, and because of its close theological connections to Edfu, it is sometimes referred to as the Edfu of Lower Egypt. Tjaru, being a frontier town in an inhospitable desert region, was a place of banishment for criminals. Horemheb in his Great Edict threatens as punishment for various crimes by officials disfigurement and banishment to Tja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pa (cuneiform)
The cuneiform pa sign, (as Sumerogram, PA), has many uses in both the 14th century BC Amarna letters and the ''Epic of Gilgamesh''. It is routinely and commonly used to spell the Akkadian language word "pānu", ''face, presence'', and with a preposition (ex. a na pā nu), ''before''. In the photo of the obverse of EA 364, it is used to spell Akkadian "eperu", 'dust', (EA 364, lines 7,8: "...and ( ù dust (IŠ (Sumerogram)=dust)) and ( u)\ dust "-( a-pa- ru). (The two ''"and"''-s are u-(no. 3), then u-(no. 1)-(u (cuneiform))(the bottom half).) The alphabetic/syllabic uses and Sumerograms of the 'pa' sign from the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'': :hat :pa :PA (Sumerogram)s :SÀG Its usage numbers from the ''Epic of Gilgamesh'' are as follows: ''hat''-(21), ''pa''-(209), ''PA''-(11), ''SÀG''-(1). In the Amarna letters the start of "messenger Xxxxx" is often spelled in cuneiform characters: "LÚ.PA.X.y.z" (etc.), (LÚ the beginning determinative for ''Man''). References * Moran, W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-shaped impressions (Latin: ) which form its signs. Cuneiform was originally developed to write the Sumerian language of southern Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). Cuneiform is the earliest known writing system. Over the course of its history, cuneiform was adapted to write a number of languages in addition to Sumerian. Akkadian texts are attested from the 24th century BC onward and make up the bulk of the cuneiform record. Akkadian cuneiform was itself adapted to write the Hittite language in the early second millennium BC. The other languages with significant cuneiform corpora are Eblaite, Elamite, Hurrian, Luwian, and Urartian. The Old Persian and Ugaritic alphabets feature cuneiform-style signs; however, they are unrelated to the cuneiform lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |