|
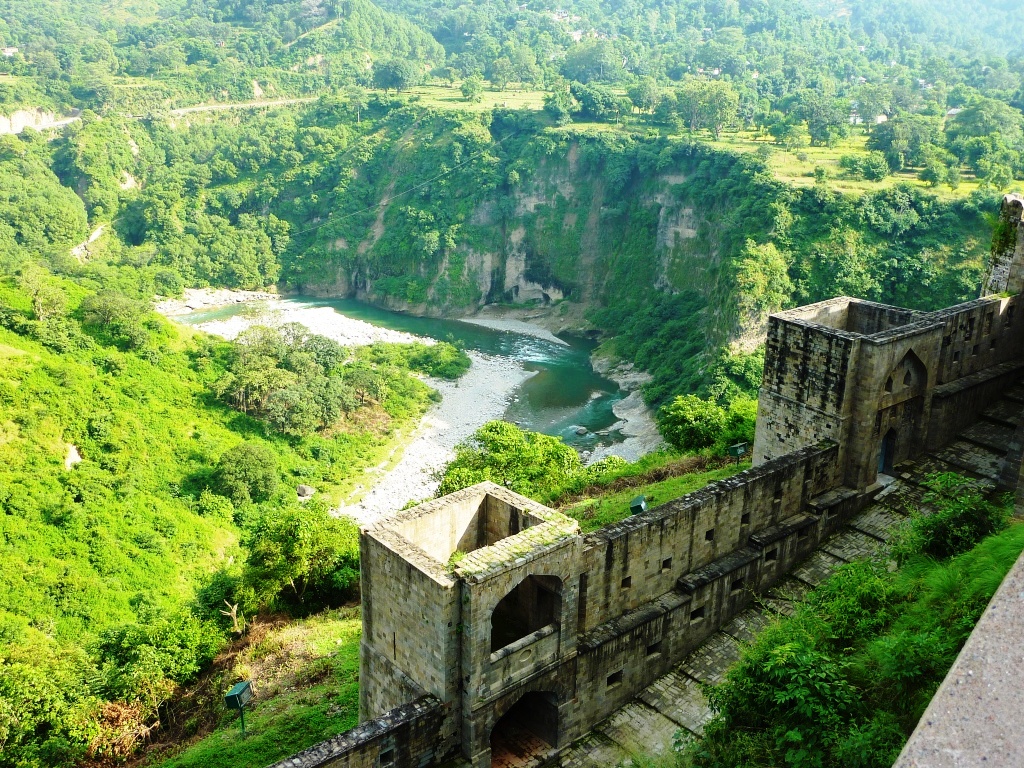
Kuhl Irrigation (Himachal Pradesh)
: Kuhls are traditional systems of community managed, interconnected gravity flow irrigation systems of Kangra Valley in the western Himachal Pradesh region of India.The Kangra Valley is composed of forested alluvial plains sloping away from the base of the Dhauladhar mountain range falling largely within the sub districts of Kangra and Palampur. It is crisscrossed by small streams called ''nalas'' and perennial rivers fed by glacial melts called ''khad'', that originate in the Dhauladhar and eventually join the Beas River. The ''Kuls'' of Spiti and ''Guls'' of Kashmir are similar water management systems. History The kulhs have a history that is 300 years old. They are believed to have started during the rule of the Katoch family who is said to have sponsored the largest kuhl systems. The names of these kuhls often find their origins in 'raja' (king) and 'rani' (queen) after the royalty who sponsored the construction of the kuhls. Since all communities benefited from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangra Valley
Kangra Valley is a river valley situated in the Western Himalayas.Earthquakes '''', v. 1, ''p. 98.'' It lies in the state of in , and is a popular tourist destination. The is spoken there. |
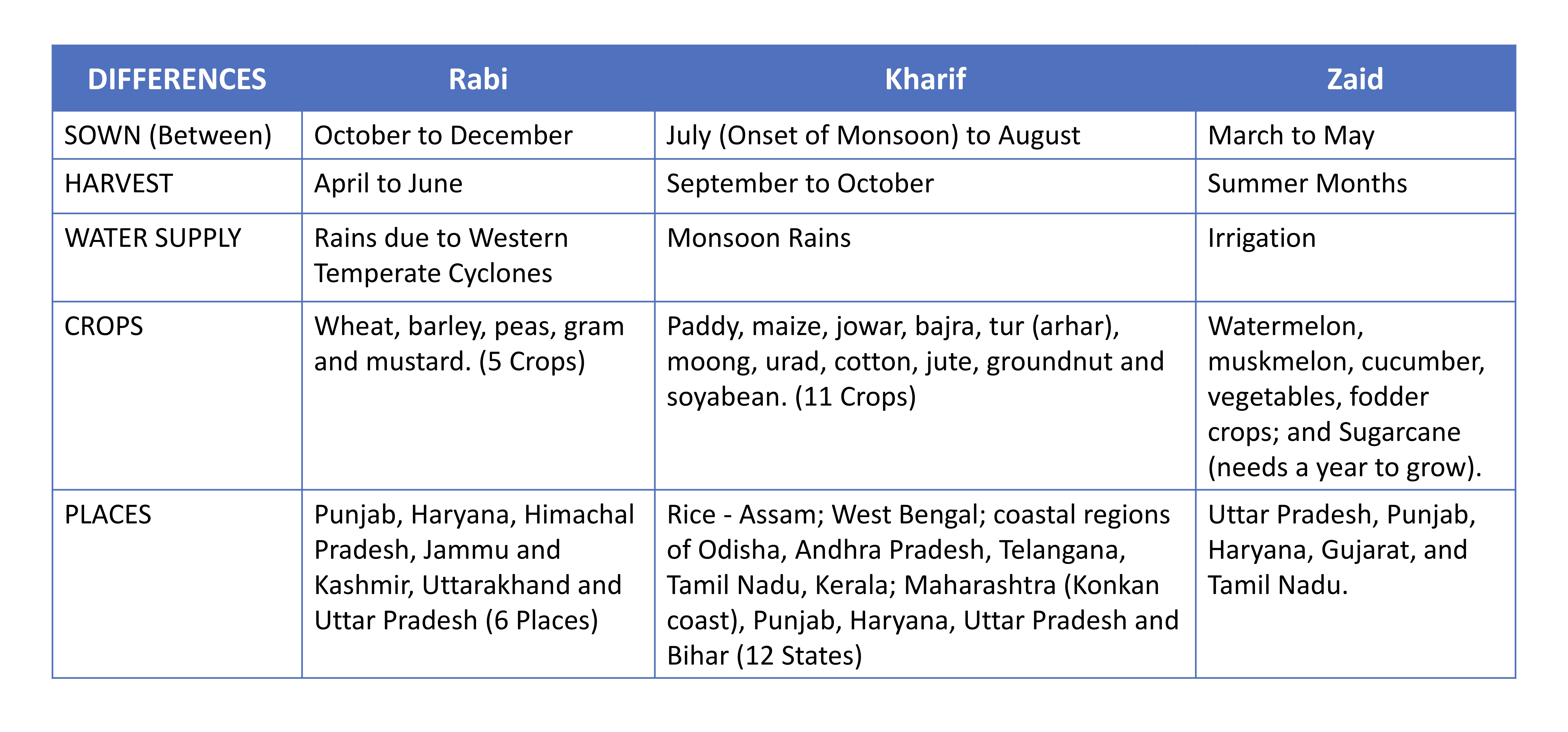
Rabi Crop
Rabi crops or rabi harvest, also known as winter crops, are agricultural crops that are sown in winter and harvested in the spring in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh. The complimentary of the rabi crop is the kharif crop, which is grown after the rabi and zaid (zaa-id) crops are harvested one after another respectively. Etymology The words ''Kharif'' and ''rabi'' have their origins in Arabic. These came to be used in India with the ascent of the Mughal empire in the Indian subcontinent and have been widely used ever since. The term is derived from the Arabic word for "spring", which is used in the Indian subcontinent, where it is the spring harvest (also known as the "winter crop"). Rabi season in India The rabi crops are sown around mid-November, preferably after the monsoon rains are over, and harvesting begins in April / May. The crops are grown either with rainwater that has percolated into the ground or using irrigation. Good rain in winter spoils the rabi crops but is go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irrigation In India
Irrigation in India includes a network of major and minor canals from Indian rivers, groundwater well based systems, tanks, and other rainwater harvesting projects for agricultural activities. Of these groundwater system is the largest. In 2013–14, only about 36.7% of total agricultural land in India was reliably irrigated, and remaining 2/3 cultivated land in India is dependent on monsoons. 65% of the irrigation in India is from groundwater. Currently about 51% of the agricultural area cultivating food grains is covered by irrigation. The rest of the area is dependent on rainfall which is most of the times unreliable and unpredictable. Indian government launched a demand side water management plan costing INR6000 crore or USD854 million across 8,350 water stressed villages of 78 districts in seven states – Gujarat, Haryana, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh – over five years from 2021–2022 to 2026–27, with the view to harvest rainwat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tragedy Of The Commons
Tragedy (from the grc-gre, τραγῳδία, ''tragōidia'', ''tragōidia'') is a genre of drama based on human suffering and, mainly, the terrible or sorrowful events that befall a main character. Traditionally, the intention of tragedy is to invoke an accompanying catharsis, or a "pain hatawakens pleasure", for the audience. While many cultures have developed forms that provoke this paradoxical response, the term ''tragedy'' often refers to a specific tradition of drama that has played a unique and important role historically in the self-definition of Western civilization. That tradition has been multiple and discontinuous, yet the term has often been used to invoke a powerful effect of cultural identity and historical continuity—"the Greeks and the Elizabethans, in one cultural form; Hellenes and Christians, in a common activity," as Raymond Williams puts it. From its origins in the theatre of ancient Greece 2500 years ago, from which there survives only a fraction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garrett Hardin
Garrett James Hardin (April 21, 1915 – September 14, 2003) was an American ecologist. He focused his career on the issue of human overpopulation, and is best known for his exposition of the tragedy of the commons in a 1968 paper of the same title in ''Science'', which called attention to "the damage that innocent actions by individuals can inflict on the environment". He is also known for Hardin's First Law of Human Ecology: "We can never do merely one thing. Any intrusion into nature has numerous effects, many of which are unpredictable." Garrett held hardline anti-immigrant positions as well positions on eugenics and multiethnicism that have led multiple sources to label him a white nationalist. The Southern Poverty Law Center called his publications "frank in their racism and quasi-fascist ethnonationalism". Biography Hardin received a BS in zoology from the University of Chicago in 1936 and a PhD in microbiology from Stanford University in 1941 where his dissertation resea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common-pool Resource
In economics, a common-pool resource (CPR) is a type of good consisting of a natural or human-made resource system (e.g. an irrigation system or fishing grounds), whose size or characteristics makes it costly, but not impossible, to exclude potential beneficiaries from obtaining benefits from its use. Unlike pure public goods, common pool resources face problems of congestion or overuse, because they are subtractable. A common-pool resource typically consists of a core resource (e.g. water or fish), which defines the ''stock variable'', while providing a limited quantity of extractable fringe units, which defines the ''flow variable''. While the core resource is to be protected or nurtured in order to allow for its continuous exploitation, the fringe units can be harvested or consumed. Examples of a Common-Pool Resource Common-pool goods are typically regulated and nurtured in order to prevent demand from overwhelming supply and allow for their continued exploitation. Examples of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elinor Ostrom
Elinor Claire "Lin" Ostrom (née Awan; August 7, 1933 – June 12, 2012) was an American Political science, political scientist and Political economy, political economist whose work was associated with New institutional economics, New Institutional Economics and the resurgence of political economy. In 2009, she was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for her "analysis of economic governance, especially the commons", which she shared with Oliver E. Williamson. She was List of Nobel Memorial Prize laureates in Economics, the first woman to win the Nobel Prize in Economics. After graduating with a B.A. and Ph.D. in political science from UCLA, Ostrom lived in Bloomington, Indiana, Bloomington, Indiana, and served on the faculty of Indiana University Bloomington, Indiana University, with a late-career affiliation with Arizona State University. She was a Distinguished Professor at Indiana University and the Arthur F. Bentley Professor of Political Science and co-dire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, 2005
Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act 2005 or MNREGA, earlier known as the National Rural Employment Guarantee Act or NREGA, is an Indian labour law and social security measure that aims to guarantee the 'right to work'. This act was passed in 23 August 2005 under the UPA government of Prime Minister Manmohan Singh following tabling of the bill in parliament by the Minister for Rural Development Raghuvansh Prasad Singh. It aims to enhance livelihood security in rural areas by providing at least 100 days of wage employment in a financial year to at least one member of every household whose adult members volunteer to do unskilled manual work. Women are guaranteed one third of the jobs made available under the MGNREGA. Another aim of MGNREGA is to create durable assets (such as roads, canals, ponds and wells). Employment is to be provided within 5 km of an applicant's residence, and minimum wages are to be paid. If work is not provided within 15 days of apply ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharif Crop
Kharif crops, also known as monsoon crops or autumn crops, are domesticated plants that are cultivated and harvested in India, Pakistan and Bangladesh during the Indian subcontinent's monsoon season, which lasts from June to November depending on the area. Monsoon rains may begin as early as May in some parts of the Indian subcontinent, and crops are generally harvested from the third week of September to October. Rice, maize, and cotton are some of the major Kharif crops in India. Unlike the Rabi crops, which are grown in the winter, the kharif crops require good rainfall. Etymology The words ''Kharif'' and ''rabi'' both have their origins in the Arabic language. These came to be used in India with the ascent of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent and have been widely used ever since. ''Kharif'' literally means "autumn" in Arabic. The sowing happens during monsoon and reaping happens close to Autumn in the Indian subcontinent ; this proximity to Autumn reap season is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks and extensive river systems. Himachal Pradesh is the northernmost state of India and shares borders with the union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh to the north, and the states of Punjab to the west, Haryana to the southwest, Uttarakhand to the southeast and a very narrow border with Uttar Pradesh to the south. The state also shares an international border to the east with the Tibet Autonomous Region in China. Himachal Pradesh is also known as , meaning 'Land of Gods' and which means 'Land of the Brave'. The predominantly mountainous region comprising the present-day Himachal Pradesh has been inhabited since pre-historic times, having witnessed multiple waves of human migrations from other areas. Through its history, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in San F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katoch
Katoch is a Chandravanshi Rajput clan. Their traditional area of residence was in the Trigarta Kingdom, based at Jalandhar and at Kangra Fort in the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh. They descent from the Trigarta dynasty mentioned in the Mahabharata. Famous subclans came into existence from Katoch Rajputs are Dadwal Dynasty, Guleria Dynasty, Sibaia Dynasty, Chib Dynasty, Jaswal Dynasty. Etymology There are two possible origins for the word ''Katoch''. Members of the clan say it comes from the words ''Kat'' (army) and ''uch'' (upper class) but other sources say that it comes from ''kot'' (fort). The Kangra fort was known as Nagarkot or Kot Kangra, and since the administrators/rulers resided within that particular ''kot'' they were vernacularly called "Kot'ch" or कोटच, which means ''those within the fort''. This over time became Katoch. History The main branch of the Katoch clan were the rulers of the Kangra State, which was, by some accounts, the most prominent kingd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |