|
Kuźnica, Podlaskie Voivodeship
Kuźnica (; formerly Kuźnica Białostocka) is a village in Sokółka County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland, close to the border with Belarus. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Kuźnica. It lies approximately north-east of Sokółka and north-east of the regional capital Białystok. In 2019, the village had a population of 1,717. History The beginning of the village was an ore plant - a plant for smelting iron from bog ores - founded on the Łosośna River around 1504. Soon, a princely manor was established. In 1536, on the orders of Queen Bona Sforza, Jerzy Zielepucha founded the town of Kuźnica, which in 1546 received Magdeburg rights. In 1545, Sigismund II Augustus founded a Catholic church. In 1679, the city had a market square and four streets. There was a royal pheasantry here. After the Partitions of Poland, Kuźnica was initially part of the Prussian Partition (1795-1807), and then, from 1807, within the borders of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divine Providence
In theology, divine providence, or simply providence, is God's intervention in the universe. The term ''Divine Providence'' (usually capitalized) is also used as a names of God, title of God. A distinction is usually made between "general providence", which refers to God's God the Sustainer, continuous upholding of the existence and natural law, natural order of the universe, and "special providence", which refers to God's extraordinary intervention in the life of people. Miracles and even divine retribution, retribution generally fall in the latter category. Etymology "Divine" evolved in the late 14th century to mean "pertaining to, in the nature of or proceeding from God or a god". This came from the Old French , with a similar meaning, and that from the Latin , meaning "of a god", in turn from , with similar meaning, which was related the Latin , meaning god or deity. The word "providence" comes from Latin meaning foresight or prudence, and that in turn from "ahead" and " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg Rights
Magdeburg rights (, , ; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages granted by the local ruler. Named after the city of Magdeburg, these town charters were perhaps the most important set of Middle Ages, medieval laws in Central Europe. They became the basis for the German town laws developed during many centuries in the Holy Roman Empire. The Magdeburg rights were adopted and adapted by numerous monarchs, including the rulers of Crown of Bohemia, Bohemia, Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, Crown of Poland, Poland, and Grand Duchy of Lithuania, Lithuania, a milestone in the urbanization of the region which prompted the development of thousands of villages and cities. Provisions Being a member of the Hanseatic League, Magdeburg was one of the most important trade cities, maintaining commerce with the Low Countries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treblinka Extermination Camp
Treblinka () was the second-deadliest extermination camp to be built and operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland during World War II. It was in a forest north-east of Warsaw, south of the village of Treblinka in what is now the Masovian Voivodeship. The camp operated between 23 July 1942 and 19 October 1943 as part of Operation Reinhard, the deadliest phase of the Final Solution. During this time, it is estimated that between 700,000 and 900,000 Jews were murdered in its gas chambers, along with 2,000 Romani people. More Jews were murdered at Treblinka than at any other Nazi extermination camp apart from Auschwitz-Birkenau. Managed by the German SS with assistance from Trawniki guards – recruited from among Soviet POWs to serve with the Germans – the camp consisted of two separate units. Treblinka I was a forced-labour camp ('' Arbeitslager'') whose prisoners worked in the gravel pit or irrigation area and in the forest, where they cut wood to fuel the crema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghetto
A ghetto is a part of a city in which members of a minority group are concentrated, especially as a result of political, social, legal, religious, environmental or economic pressure. Ghettos are often known for being more impoverished than other areas of the city. Versions of such restricted areas have been found across the world, each with their own names, classifications, and groupings of people. The term was originally used for the Venetian Ghetto in Venice, Italy, as early as 1516, to describe the part of the city where Jewish people were restricted to live and thus segregated from other people. However, other early societies may have formed their own versions of the same structure; words resembling ''ghetto'' in meaning appear in Hebrew, Yiddish, Italian, Germanic, Polish, Corsican, Old French, and -4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ..., and Latin. During the Holocaust">Latin"> ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
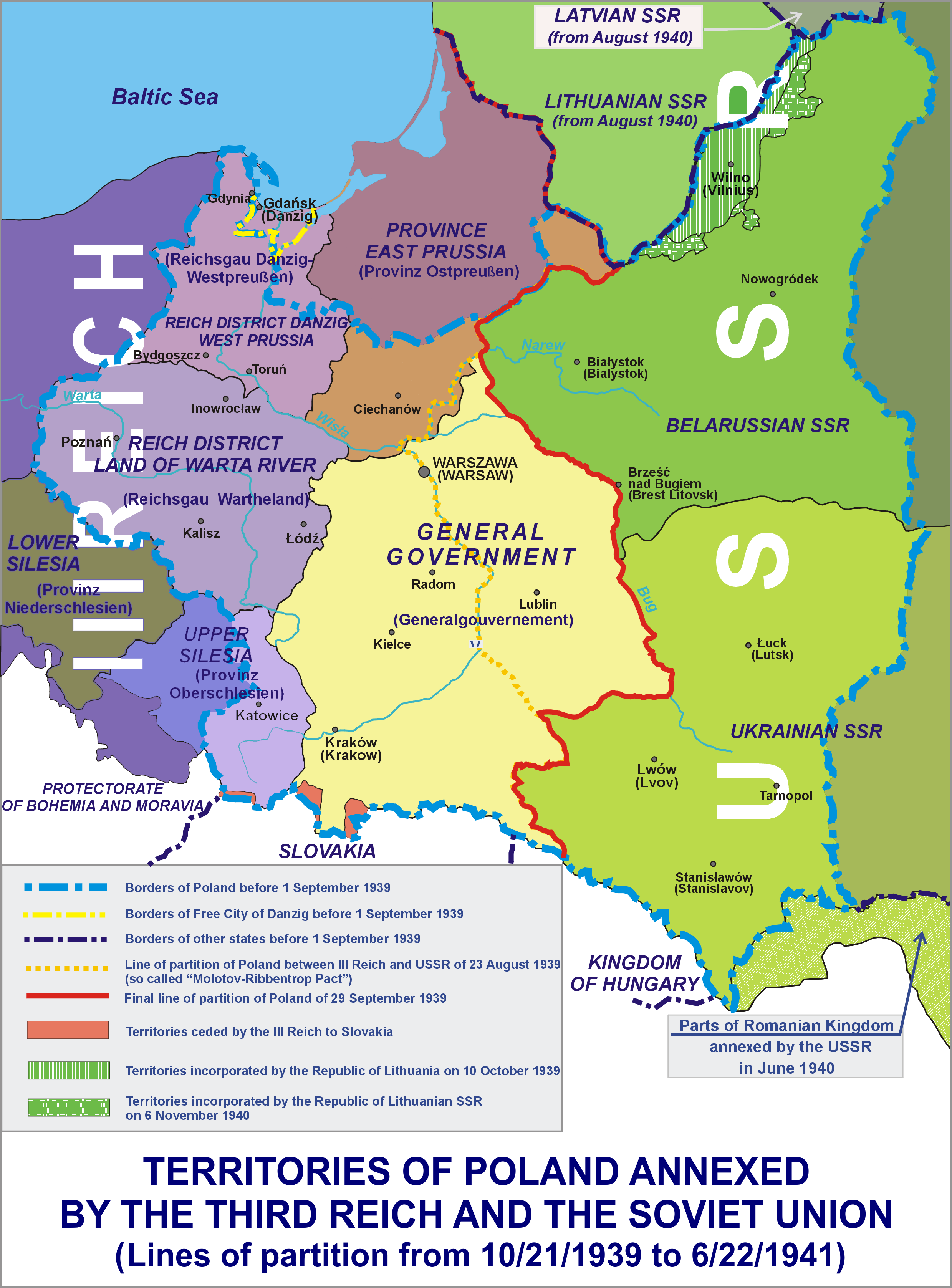
Occupation Of Poland (1939–1945)
During World War II, Poland was occupied by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union following the invasion in September 1939, and it was formally concluded with the defeat of Germany by the Allies in May 1945. Throughout the entire course of the occupation, the territory of Poland was divided between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union (USSR), both of which intended to eradicate Poland's culture and subjugate its people. In the summer-autumn of 1941, the lands which were annexed by the Soviets were overrun by Germany in the course of the initially successful German attack on the USSR. After a few years of fighting, the Red Army drove the German forces out of the USSR and crossed into Poland from the rest of Central and Eastern Europe. Sociologist Tadeusz Piotrowski argues that both occupying powers were hostile to the existence of Poland's sovereignty, people, and the culture and aimed to destroy them. Before Operation Barbarossa, Germany and the Soviet Union coordinated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town Privileges
Town privileges or borough rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium. The city law customary in Central Europe probably dates back to Italian models, which in turn were oriented towards the traditions of the self-administration of Roman cities. Judicially, a borough (or burgh) was distinguished from the countryside by means of a charter from the ruling monarch that defined its privileges and laws. Common privileges involved trade (marketplace, the storing of goods, etc.) and the establishment of guilds. Some of these privileges were permanent and could imply that the town obtained the right to be called a borough, hence the term "borough rights" (; ). Some degree of self-government, representation by diet, and tax-relief could also be granted. Multiple tiers existed; for example, in Sweden, the basic royal charter establishing a borough enabled trade, but not foreign trade, which required a higher-tier charter granting staple ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Armed Forces (Second Polish Republic)
Polish Armed Forces () were the armed forces of the Second Polish Republic from 1919 until the demise of independent Poland at the onset of Second World War in September 1939. History The outbreak of First World War meant that a huge number of Poles from the lands of the Polish partitions were forced to stand as soldiers in the ranks of German, Russian and Austro-Hungarian armies.In addition to these troops, Polish volunteer units were formed to fight either on the side of the coalition or central states. A branch of 'Bajonians' was established in France and in Poland by Witold Ostoja-Gorczyński ( Legion of Puławy). However, these were small units. The first ceased to exist due to losses, and the second could not grow due to political considerations. The Polish Legions were the greater union of the Polish Army of the independent Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. They were created in 1914 by brigadier Józef Piłsudski. The members of these formations were members of underg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish–Soviet War
The Polish–Soviet War (14 February 1919 – 18 March 1921) was fought primarily between the Second Polish Republic and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, following World War I and the Russian Revolution. After the collapse of the Central Powers and the Armistice of 11 November 1918, Vladimir Lenin's Soviet Russia annulled the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk and moved forces westward to reclaim the ''Ober Ost'' regions abandoned by the Germans. Lenin viewed the newly independent Poland as a critical route for spreading communist revolutions into Europe. Meanwhile, Polish leaders, including Józef Piłsudski, aimed to restore Poland's First Partition of Poland, pre-1772 borders and secure the country's position in the region. Throughout 1919, Polish forces occupied much of present-day Lithuania and Belarus, emerging victorious in the Polish–Ukrainian War. However, Soviet forces regained strength after their victories in the Russian Civil War, and Symon Petliura, lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg–Warsaw Railway
In Christian belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but a selected few are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. In many Protestant denominations, and following from Pauline usage, ''saint'' refers broadly to any holy Christian, without special recognition or selection. While the English word ''saint'' (deriving from the Latin ) originated in Christianity, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Independence Day (Poland)
Independence Day () is a national day in Poland celebrated on to commemorate the anniversary of the restoration of Poland's sovereignty as the Second Polish Republic in 1918 from the German, Austro-Hungarian and Russian Empires. Following the partitions in the late 18th century, Poland ceased to exist for 123 years until the end of World War I, when the destruction of the neighbouring powers allowed the country to reemerge. It is a non-working day and a flag flying day in Poland. Historical background The restoration of Poland's independence was gradual. On 1916 the Act of 5th November was released in order to create the Regency Kingdom of Poland. On 1917 the Provisional Council of State had started its activity. On 12 November 1917 the Regency Council took over the head of state duties. Following the defeat of the occupying forces, the Poles seized military and civil power, building the foundations of their future state. On 7 October 1918 the Regency Council annou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Partition
The Russian Partition (), sometimes called Russian Poland, constituted the former territories of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that were annexed by the Russian Empire in the course of late-18th-century Partitions of Poland. The Russian acquisition encompassed the largest share of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth's population, living on 463,200 km2 (178,800 sq mi) of land constituting the eastern and central territory of the former Commonwealth. The three partitions, which took place in 1772, 1793 and 1795, resulted in the complete loss of Poland's and Lithuania's sovereignty, with their territories split between Russia, Prussia and Austria. The majority of Lithuania's former territory was annexed by the Russian Empire, except for (a geographical area on the left bank of the River Neman) which was annexed by Prussia. The Napoleonic Wars saw significant parts of Prussia's and Austria's partitions reconstituted as the Duchy of Warsaw (a French client state in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughly one-sixth of the world's landmass, making it the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, behind only the British Empire, British and Mongol Empire, Mongol empires. It also Russian colonization of North America, colonized Alaska between 1799 and 1867. The empire's 1897 census, the only one it conducted, found a population of 125.6 million with considerable ethnic, linguistic, religious, and socioeconomic diversity. From the 10th to 17th centuries, the Russians had been ruled by a noble class known as the boyars, above whom was the tsar, an absolute monarch. The groundwork of the Russian Empire was laid by Ivan III (), who greatly expanded his domain, established a centralized Russian national state, and secured inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |