|
Kocher–Debre–Semelaigne Syndrome
Kocher–Debré–Semelaigne syndrome (KDSS) is hypothyroidism in infancy or childhood characterised by lower extremity or generalized muscular hypertrophy ( Herculean appearance), myxoedema, short stature, and cognitive impairment. The syndrome is named after Emil Theodor Kocher, Robert Debré and Georges Semelaigne. Also known as Debré–Semelaigne syndrome or cretinism-muscular hypertrophy, hypothyroid myopathy, hypothyroidism-large muscle syndrome, hypothyreotic muscular hypertrophy in children, infantile myxoedema-muscular hypertrophy, myopathy-myxoedema syndrome, myxoedema-muscular hypertrophy syndrome, myxoedema-myotonic dystrophy syndrome. The adult-onset form of this syndrome is Hoffmann syndrome. Some sources claim that two of the differentiating symptoms between KDSS and Hoffmann syndrome is that Hoffmann syndrome lacks painful spasms and pseudomyotonia; however, this claim is in conflict with other sources that list these symptoms as also being present in Hoffmann s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
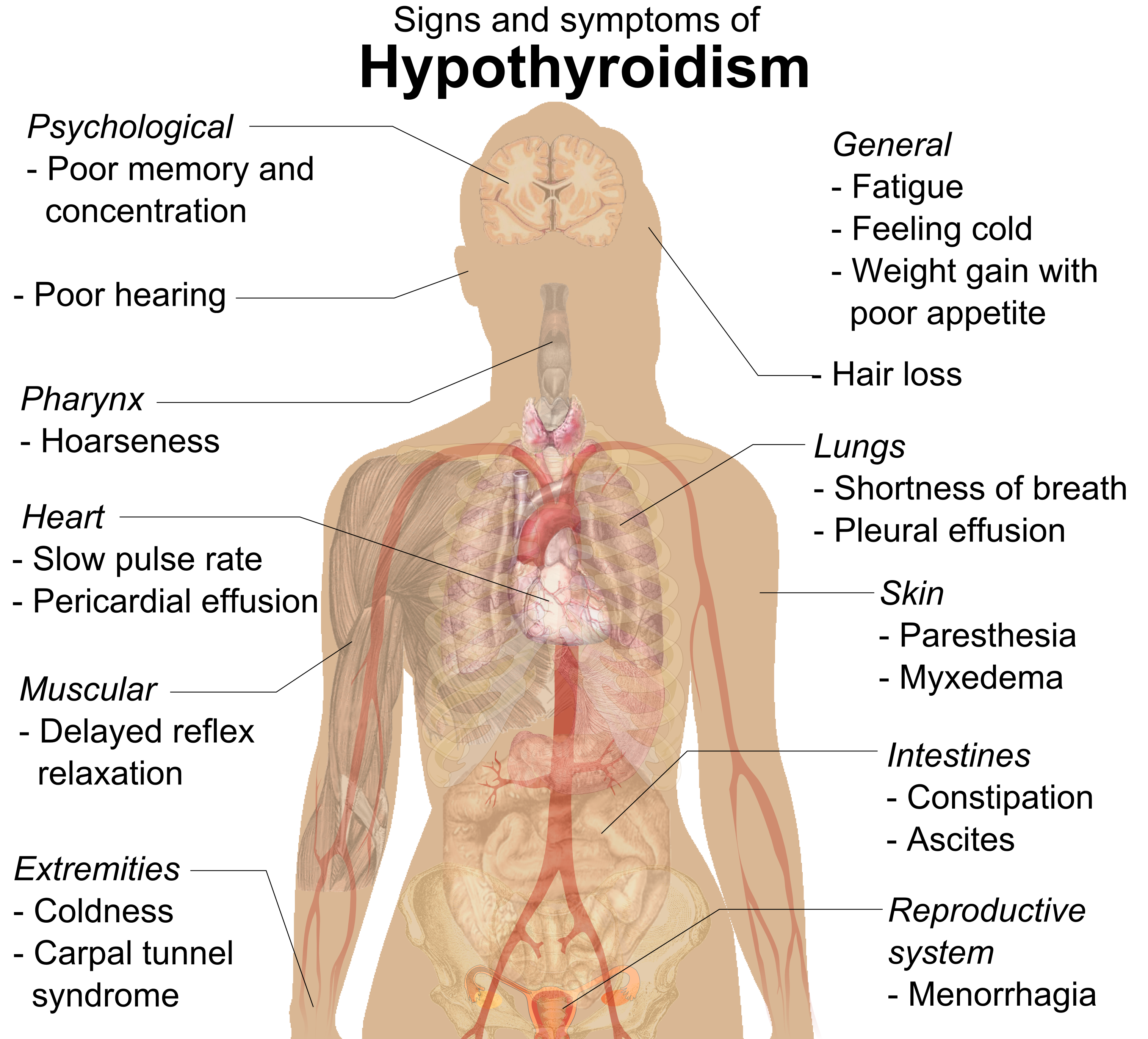
Hypothyroidism
Hypothyroidism is an endocrine disease in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones. It can cause a number of symptoms, such as cold intolerance, poor ability to tolerate cold, fatigue, extreme fatigue, muscle aches, constipation, slow heart rate, Depression (mood), depression, and weight gain. Occasionally there may be swelling of the front part of the neck due to goiter. Untreated cases of hypothyroidism during pregnancy can lead to delays in child development, growth and intellectual development in the baby or congenital iodine deficiency syndrome. Worldwide, iodine deficiency, too little iodine in the diet is the most common cause of hypothyroidism. Hashimoto's thyroiditis, an autoimmune disease where the body's immune system reacts to the thyroid gland, is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in countries with sufficient dietary iodine. Less common causes include previous treatment with iodine-131, radioactive iodine, injury to the hypothalamus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycogen Storage Disease
A glycogen storage disease (GSD, also glycogenosis and dextrinosis) is a metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency of an enzyme or transport protein affecting glycogen synthesis, glycogen breakdown, or glycolysis, glucose breakdown, typically in muscles and/or liver cells. GSD has two classes of cause: genetic and environmental. Genetic GSD is caused by any Inborn errors of carbohydrate metabolism, inborn error of carbohydrate metabolism (genetically defective enzymes or transport proteins) involved in these processes. In livestock, environmental GSD is caused by Substance intoxication, intoxication with the alkaloid castanospermine. However, not every inborn error of carbohydrate metabolism has been assigned a GSD number, even if it is known to affect the muscles or liver. For example, phosphoglycerate kinase deficiency (gene PGK1) has a myopathic form. Also, Fanconi–Bickel syndrome, Fanconi-Bickel syndrome (gene SLC2A2) and Danon disease (gene LAMP2) were declassed as GSDs d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levothyroxine
Levothyroxine, also known as -thyroxine, is a synthetic form of the thyroid hormone thyroxine (T4). It is used to treat thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism), including a severe form known as myxedema coma. It may also be used to treat and prevent certain types of thyroid tumors. It is not indicated for weight loss. Levothyroxine is taken orally (by mouth) or given by intravenous injection. Levothyroxine has a half-life of 7.5 days when taken daily, so about six weeks is required for it to reach a steady level in the blood. Side effects from excessive doses include weight loss, trouble tolerating heat, sweating, anxiety, trouble sleeping, tremor, and fast heart rate. Use is not recommended in people who have had a recent heart attack. Use during pregnancy has been found to be safe. Dosing should be based on regular measurements of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and T4 levels in the blood. Much of the effect of levothyroxine is following its conversion to tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are associated with specific signs and symptoms. A disease may be caused by external factors such as pathogens or by internal dysfunctions. For example, internal dysfunctions of the immune system can produce a variety of different diseases, including various forms of immunodeficiency, hypersensitivity, allergy, allergies, and autoimmune disorders. In humans, ''disease'' is often used more broadly to refer to any condition that causes pain, Abnormality (behavior), dysfunction, distress (medicine), distress, social problems, or death to the person affected, or similar problems for those in contact with the person. In this broader sense, it sometimes includes injury in humans, injuries, disability, disabilities, Disorder (medicine) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolic Myopathy
Metabolic myopathies are myopathies that result from defects in biochemical metabolism that primarily affect muscle. They are generally genetic defects (inborn errors of metabolism) that interfere with the ability to create energy, causing a low ATP reservoir within the muscle cell. Types Metabolic myopathies are generally caused by an inherited genetic mutation, an inborn error of metabolism. (In livestock, an acquired environmental GSD is caused by intoxication with the alkaloid castanospermine.) Metabolic myopathies cause the underproduction of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) within the muscle cell. The genetic mutation typically has an autosomal recessive hereditary pattern making it fairly rare to inherit, and even more rarely it can be caused by a random de novo genetic mutation, or autosomal dominant, X-linked, or mitochondrial. Metabolic myopathies are categorized by the metabolic pathway to which the deficient enzyme or transport protein belongs. The main categories of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comorbidity
In medicine, comorbidity refers to the simultaneous presence of two or more medical conditions in a patient; often co-occurring (that is, concomitant or concurrent) with a primary condition. It originates from the Latin term (meaning "sickness") prefixed with ("together") and suffixed with ''-ity'' (to indicate a state or condition). Comorbidity includes all additional ailments a patient may experience alongside their primary diagnosis, which can be either physiological or psychological in nature. In the context of mental health, comorbidity frequently refers to the concurrent existence of mental disorders, for example, the co-occurrence of depressive and anxiety disorders. The concept of multimorbidity is related to comorbidity but is different in its definition and approach, focusing on the presence of multiple diseases or conditions in a patient without the need to specify one as primary. Definition The term "comorbid" has three definitions: # to indicate a medical con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amyloid
Amyloids are aggregates of proteins characterised by a fibrillar morphology of typically 7–13 nm in diameter, a β-sheet secondary structure (known as cross-β) and ability to be stained by particular dyes, such as Congo red. In the human body, amyloids have been linked to the development of various diseases. Pathogenic amyloids form when previously healthy proteins lose their normal structure and physiological functions ( misfolding) and form fibrous deposits within and around cells. These protein misfolding and deposition processes disrupt the healthy function of tissues and organs. Such amyloids have been associated with (but not necessarily as the cause of) more than 50 human diseases, known as amyloidosis, and may play a role in some neurodegenerative diseases. Some of these diseases are mainly sporadic and only a few cases are familial. Others are only familial. Some result from medical treatment. Prions are an infectious form of amyloids that can act as a templa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
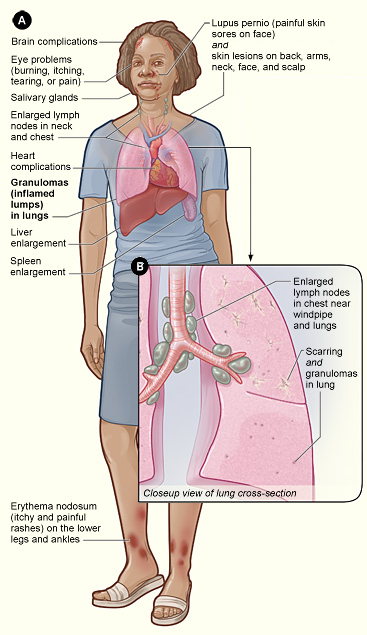
Sarcoid Granuloma
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver, heart, and brain, though any organ can be affected. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no symptoms or only mild symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, enlarged hilar lymph nodes, arthritis, and a rash known as erythema nodosum. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs and symptoms, which may be supported by biopsy. Findings that make it likely i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myositis
Myositis is a rarely-encountered medical condition characterized by inflammation affecting the muscles. The manifestations of this condition may include skin issues, muscle weakness, and the potential involvement of other organs. Additionally, systemic symptoms like weight loss, fatigue, and low-grade fever can manifest in individuals with myositis. Causes Myositis can arise from various causes, including injury, certain medications, infections, inherited muscle disorders, or autoimmune conditions. In some instances, the origins of myositis remain idiopathic, without a discernible cause. * Injury: A mild form of myositis can occur with hard exercise. A more severe form of muscle injury, called rhabdomyolysis, is also associated with myositis. This is a condition where an injury to the patient's muscles causes them to quickly break down. * Medicines: A variety of different medicines can cause myositis. One of the most common types of drugs that can cause myositis are sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Becker Muscular Dystrophy
Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) is an X-linked recessive inherited disorder characterized by slowly progressing muscle weakness of the legs and pelvis. It is a type of dystrophinopathy. The cause is mutations and deletions in any of the 79 exons encoding the large dystrophin protein, essential for maintaining the muscle fiber's cell membrane integrity. Becker muscular dystrophy is related to Duchenne muscular dystrophy in that both result from a mutation in the dystrophin gene, however, the hallmark of Becker is milder in-frame deletions. and hence has a milder course, with patients maintaining ambulation till 50–60 years if detected early. While there is no known cure, management strategies such as physical therapy, braces, and corrective surgery may alleviate symptoms. Assisted ventilation may be required in those with weakness of breathing muscles. Several drugs designed to address the root cause are currently available including gene therapy ( Elevidys). Other medications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a severe type of muscular dystrophy predominantly affecting boys. The onset of muscle weakness typically begins around age four, with rapid progression. Initially, muscle loss occurs in the thighs and pelvis, extending to the arms, which can lead to difficulties in standing up. By the age of 12, most individuals with Duchenne muscular dystrophy are unable to walk. Affected muscles may appear larger due to an increase in fat content, and scoliosis is common. Some individuals may experience intellectual disability, and females carrying a single copy of the mutated gene may show mild symptoms. Duchenne muscular dystrophy is caused by mutations or deletions in any of the 79 exons encoding the large dystrophin protein, which is essential for maintaining the muscle fibers' cell membrane integrity. The disorder follows an X-linked recessive inheritance pattern, with approximately two-thirds of cases inherited from the mother and one-third res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limb–girdle Muscular Dystrophy
Limb–girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) is a genetically heterogeneous group of rare muscular dystrophies that share a set of clinical characteristics. It is characterised by progressive muscle wasting which affects predominantly hip and shoulder muscles. LGMD usually has an autosomal pattern of inheritance. It currently has no known cure or treatment. LGMD may be triggered or worsened in genetically susceptible individuals by statins, because of their effects on HMG-CoA reductase. Signs and symptoms By definition, all limb-girdle muscular dystrophies (LGMD) cause progressive proximal weakness, meaning weakness of the muscles on or close to the torso that worsens over time. Explicitly, LGMD preferentially affects muscles of the hip girdle, thigh, shoulder girdle, and/or upper arm. The muscle weakness is generally symmetric. Usually, the hip girdle is the first area to exhibit weakness, manifesting as difficulty walking, going up and/or downstairs, rising from a chair, bending at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |