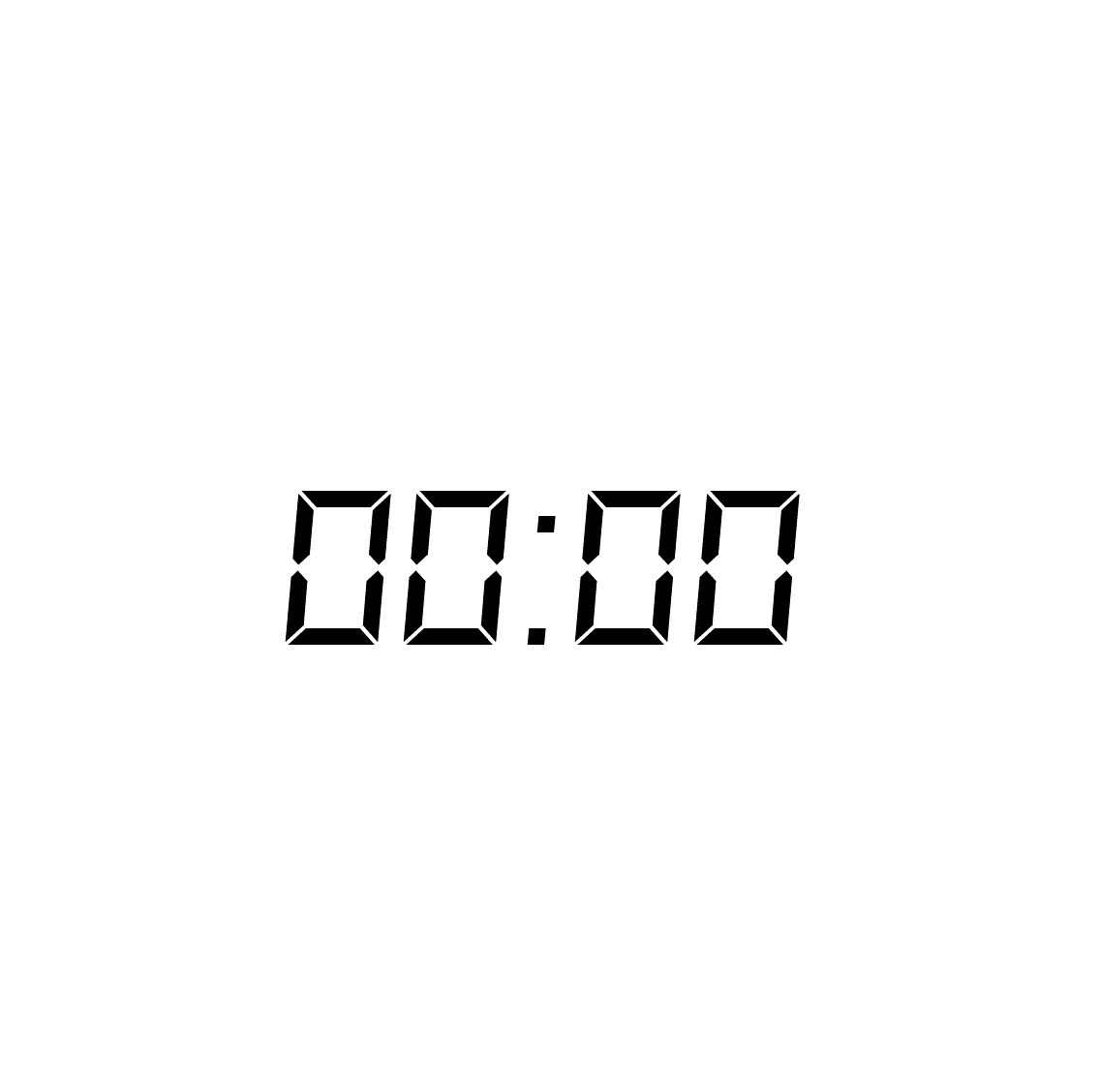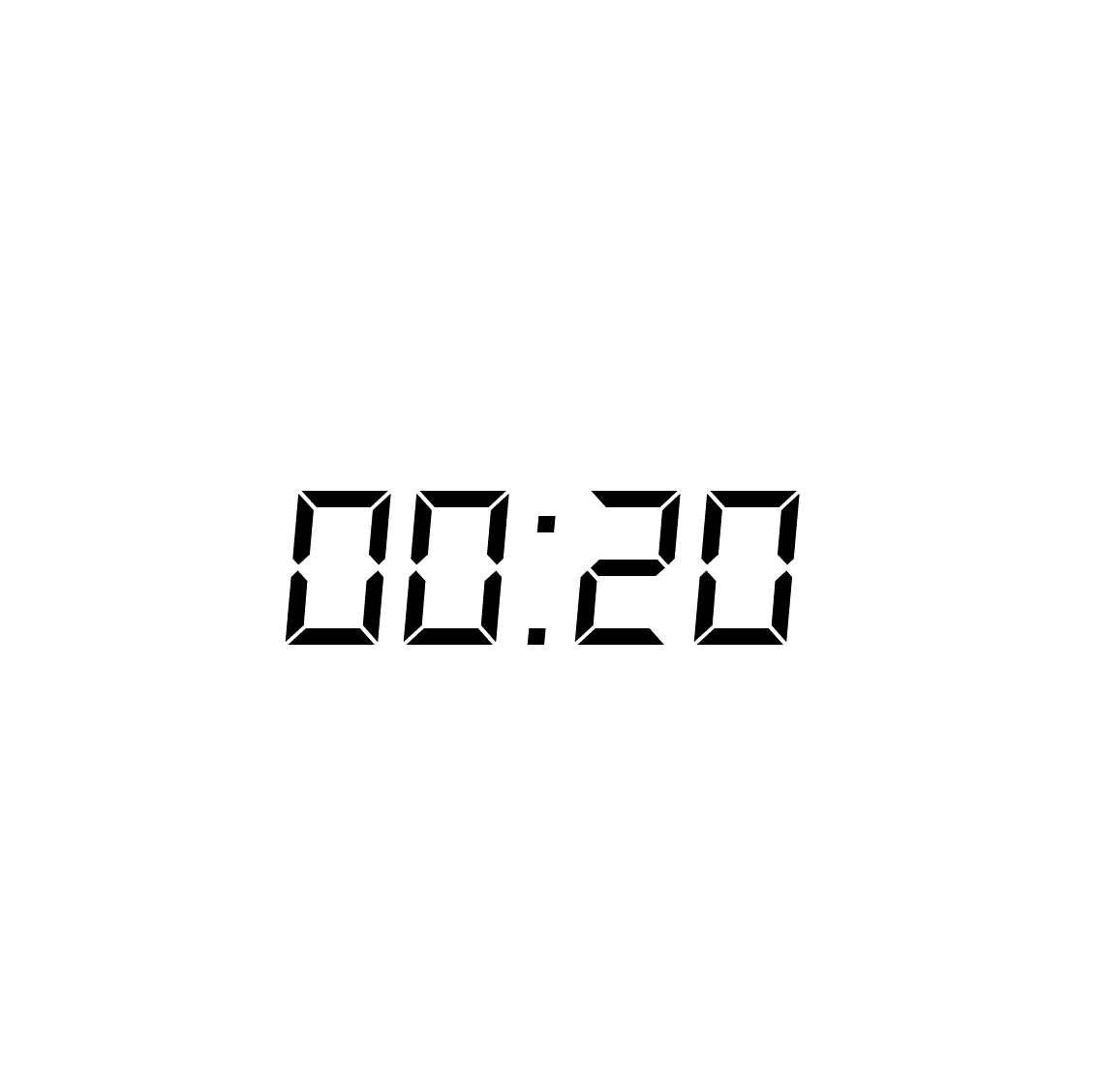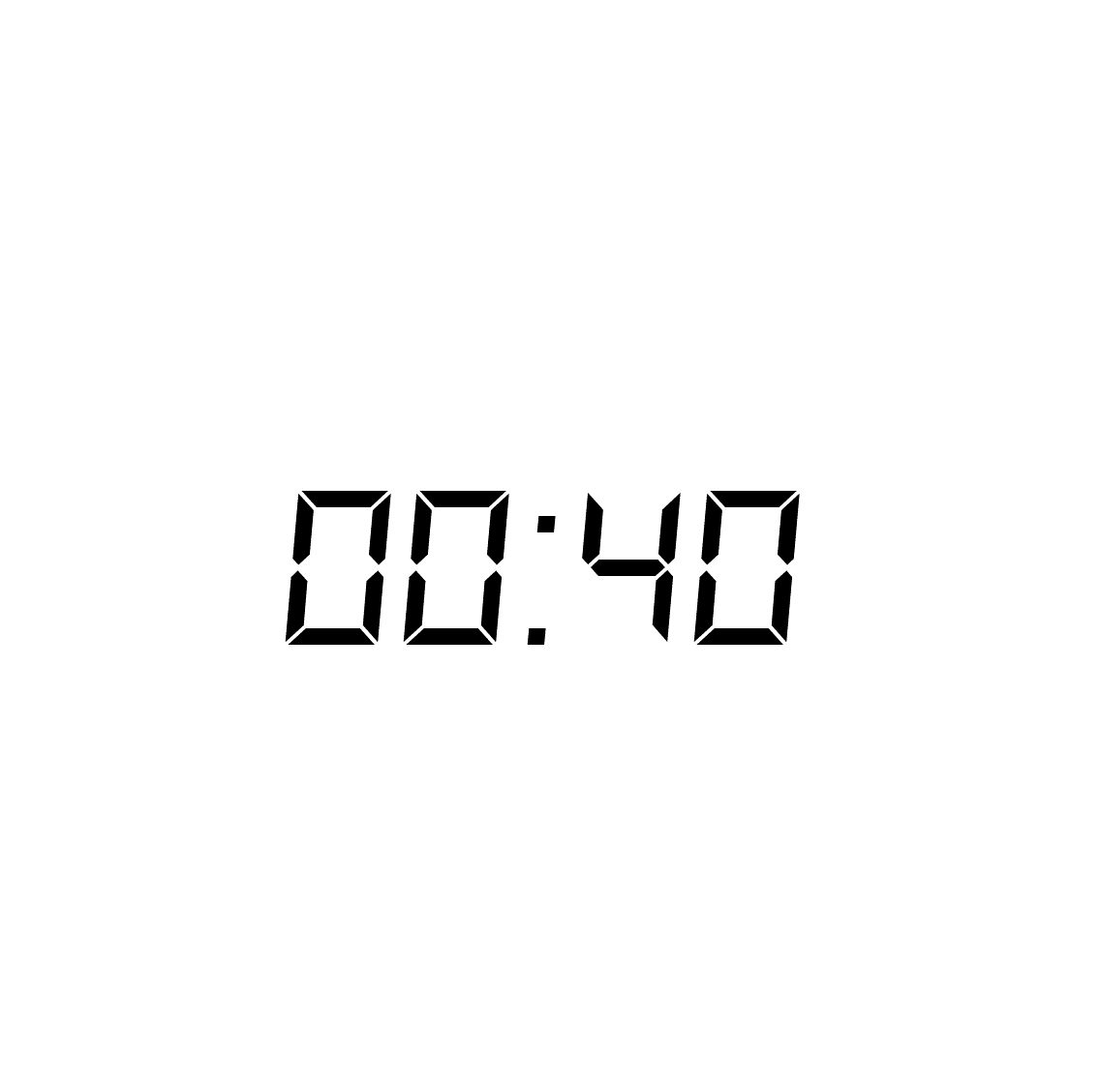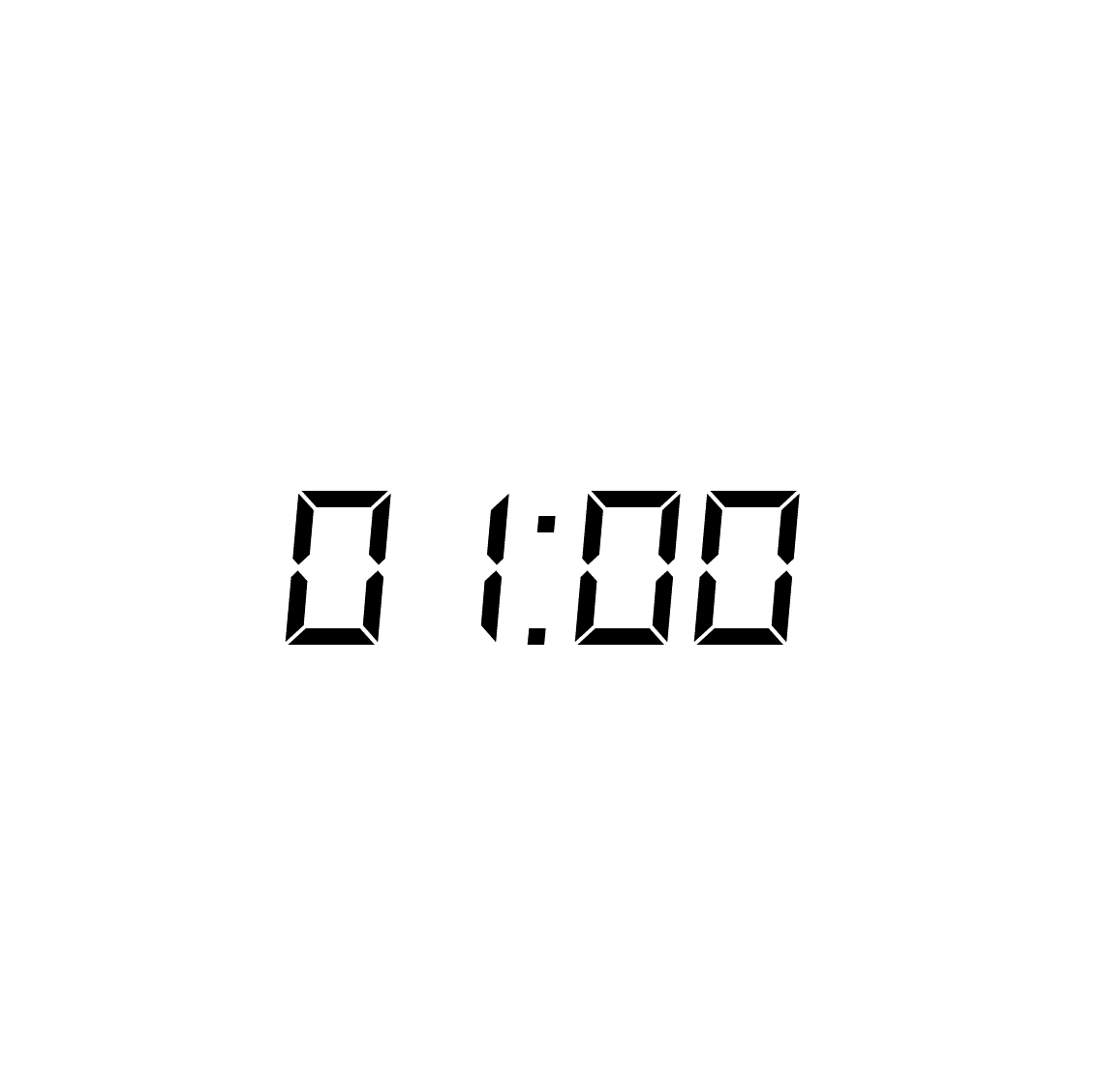|
Knot (unit)
The knot () is a unit of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour, exactly (approximately or ). The ISO standard symbol for the knot is kn. The same symbol is preferred by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers ( IEEE), while kt is also common, especially in aviation, where it is the form recommended by the International Civil Aviation Organization ( ICAO). The knot is a non- SI unit. The knot is used in meteorology, and in maritime and air navigation. A vessel travelling at 1 knot along a meridian travels approximately one minute of geographic latitude in one hour. Definitions ;1 international knot = :1 nautical mile per hour (by definition), : (exactly), : (approximately), : (approximately), : (approximately) : (approximately). The length of the internationally agreed nautical mile is . The US adopted the international definition in 1954, having previously used the US nautical mile (). The UK adopted the international nautical mile defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airspeed Indicator
The airspeed indicator (ASI) or airspeed gauge is a flight instrument indicating the airspeed of an aircraft in kilometres per hour (km/h), knots (kn or kt), miles per hour (MPH) and/or metres per second (m/s). The recommendation by ICAO is to use km/h, however knots (kt) is currently the most used unit. The ASI measures the pressure differential between static pressure from the static port, and total pressure from the pitot tube. This difference in pressure is registered with the ASI pointer on the face of the instrument. Colour-coded speeds and ranges The ASI has standard colour-coded markings to indicate safe operation within the limitations of the aircraft. At a glance, the pilot can determine a recommended speed (V speeds) or if speed adjustments are needed. Single and multi-engine aircraft have common markings. For instance, the green arc indicates the normal operating range of the aircraft, from ''V''S1 to ''V''NO. The white arc indicates the flap operating range ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watercraft
A watercraft or waterborne vessel is any vehicle designed for travel across or through water bodies, such as a boat, ship, hovercraft, submersible or submarine. Types Historically, watercraft have been divided into two main categories. *Rafts, which gain their buoyancy from the fastening together of components that are each buoyant in their own right. Generally, a raft is a "flow through" structure, whose users would have difficulty keeping dry as it passes through waves. Consequently, apart from short journeys (such as a river crossing), their use is confined to warmer regions (roughly 40° N to 40° S). Outside this area, use of rafts at sea is impracticable due to the risks of exposure to the crew. *Boats and ships, which float by having the submergeable part of their structure exclude water with a waterproof surface, so creating a space that contains air, as well as cargo, passengers, crew, etc. In total, this structure weighs less than the water that would occupy the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocity Made Good
Velocity made good, or VMG, is a term used in sailing, especially in yacht racing, indicating the speed of a sailboat towards (or from) the direction of the wind. The concept is useful because a sailboat cannot sail directly upwind, and thus often can not, or should not, sail directly to a mark to reach it as quickly as possible. It is also often less than optimal to sail directly downwind. Concept Instead of sailing directly toward a windward mark, the helmsman chooses a point of sail towards the direction of the wind that maximizes velocity made good (either towards the destination - or towards better winds). To actually reach a mark, the boat needs to alternate between courses (''tacks'') where the wind approaches from alternating sides. The helmsman uses VMG to find exactly what the optimum angle against the wind is. At the optimum boat speed and angle to the wind, VMG is maximized, steering closer to the direction of the wind will reduce boat speed, while steering further awa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Speed
Ground speed is the horizontal component of the velocity of an aircraft relative to the Earth’s surface, also referred to as "speed over the ground". It is vital for accurate navigation that the pilot has an estimate of the ground speed that will be achieved during each leg of a flight. Theoretically, an aircraft diving vertically and unaffected by wind would have a ground speed of zero. Information displayed to passengers through the entertainment system of airline aircraft usually gives the aircraft ground speed rather than airspeed. Ground speed can be determined by the vector sum of the aircraft's true airspeed and the current wind speed and direction; a headwind subtracts from the ground speed, while a tailwind adds to it. Winds at other angles to the heading will have components of either headwind or tailwind as well as a crosswind component. An airspeed indicator indicates the aircraft's speed relative to the air mass it is flying through. The air mass may be moving ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wind Speed
In meteorology, wind speed, or wind flow speed, is a fundamental atmospheric quantity caused by air moving from high to low pressure, usually due to changes in temperature. Wind speed is now commonly measured with an anemometer. Wind speed affects weather forecasting, aviation and maritime operations, construction projects, growth and metabolism rates of many plant species, and has countless other implications. Wind direction is usually almost parallel to isobars (and not perpendicular, as one might expect), due to Earth's rotation. Units The meter per second (m/s) is the SI unit for velocity and the unit recommended by the World Meteorological Organization for reporting wind speeds, and used amongst others in weather forecasts in the Nordic countries. Since 2010 the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) also recommends meters per second for reporting wind speed when approaching runways, replacing their former recommendation of using kilometers per hour ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
River Current
In hydrology, a current in a water body is the flow of water in any one particular direction. The current varies spatially as well as temporally, dependent upon the flow volume of water, stream gradient, and channel geometry. In tidal zones, the current and streams may reverse on the flood tide before resuming on the ebb tide. On a global scale, wind and the rotation of the earth greatly influence the flow of ocean currents. In a stream or river there the current is influenced by gravity, the term ''upstream'' (or ''upriver'') refers to the direction towards the source of the stream (or river), i.e. against the direction of flow. Likewise, the term ''downstream'' or ''downriver'' describes the direction towards the mouth of the stream or river, in which the current flows. The term "left bank" and "right bank In geography, a bank is the land alongside a body of water. Different structures are referred to as ''banks'' in different fields of geography. In limnology (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Stream (marine Science)
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or "tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see ''Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. Tides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocean Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents move both horizontally, on scales that can span entire oceans, as well as vertically, with vertical currents (upwelling and downwelling) playing an important role in the movement of nutrients and gases, such as carbon dioxide, between the surface and the deep ocean. Ocean currents flow for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth's regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Speed
In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air it is flying through (which itself is usually moving relative to the ground due to wind). In contrast, the ground speed is the speed of an aircraft with respect to the surface of the Earth (whether over land or presumed-stationary water). It is difficult to measure the exact airspeed of the aircraft (true airspeed), but other measures of airspeed, such as indicated airspeed and Mach number give useful information about the capabilities and limitations of airplane performance. The common measures of airspeed are: * Indicated airspeed (IAS), what is read on an airspeed gauge connected to a pitot-static system. * Calibrated airspeed (CAS), indicated airspeed adjusted for pitot system position and installation error. * True airspeed (TAS) is the actual speed the airplane is moving through the air. When combined with aircraft direction, wind speed and direction, it can be used to calculate ground speed and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a liquid, gas, or other material that may continuously motion, move and Deformation (physics), deform (''flow'') under an applied shear stress, or external force. They have zero shear modulus, or, in simpler terms, are Matter, substances which cannot resist any shear force applied to them. Although the term ''fluid'' generally includes both the liquid and gas phases, its definition varies among branches of science. Definitions of ''solid'' vary as well, and depending on field, some substances can have both fluid and solid properties. Non-Newtonian fluids like Silly Putty appear to behave similar to a solid when a sudden force is applied. Substances with a very high viscosity such as Pitch (resin), pitch appear to behave like a solid (see pitch drop experiment) as well. In particle physics, the concept is extended to include fluidic matters other than liquids or gases. A fluid in medicine or biology refers to any liquid constituent of the body (body fluid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Admiralty
The Admiralty was a Departments of the Government of the United Kingdom, department of the Government of the United Kingdom that was responsible for the command of the Royal Navy. Historically, its titular head was the Lord High Admiral of the United Kingdom, Lord High Admiral – one of the Great Officers of State. For much of its history, from the early Admiralty in the 18th century, 18th century until its abolition, the role of the Lord High Admiral was almost invariably put "in commission" and exercised by the Lords Commissioner of the Admiralty, who sat on the governing Board of Admiralty, rather than by a single person. The Admiralty was replaced by the Admiralty Board (United Kingdom), Admiralty Board in 1964, as part of the reforms that created the Ministry of Defence (United Kingdom), Ministry of Defence and its Navy Department (Ministry of Defence), Navy Department (later Navy Command (Ministry of Defence), Navy Command). Before the Acts of Union 1707, the Office of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hour
An hour (symbol: h; also abbreviated hr) is a unit of time historically reckoned as of a day and defined contemporarily as exactly 3,600 seconds ( SI). There are 60 minutes in an hour, and 24 hours in a day. The hour was initially established in the ancient Near East as a variable measure of of the night or daytime. Such seasonal hours, also known as temporal hours or unequal hours, varied by season and latitude. Equal hours or equinoctial hours were taken as of the day as measured from noon to noon; the minor seasonal variations of this unit were eventually smoothed by making it of the mean solar day. Since this unit was not constant due to long term variations in the Earth's rotation, the hour was finally separated from the Earth's rotation and defined in terms of the atomic or physical second. It is a non-SI unit that is accepted for use with SI. In the modern metric system, one hour is defined as 3,600 atomic seconds. However, on rare occasions an hour may inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |