|
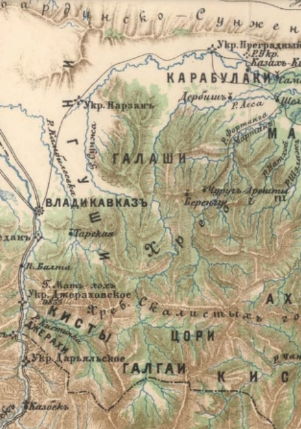
Kistin
Kists or Kistins; ce, кистӀий, kisthiy; ka, ქისტები, tr is an old exonym of all Nakh peoples (Ingush, Chechens and Batsbi), under which local societies later were designated, and conditionally divided into ''nearby Kistins'' and ''distant Kistins''. In Russian sources of the 19th century, the term ''nearby Kistins'' referred to the inhabitants of the Kistin Gorge in the vicinity of river Armkhi, and ''distant Kistins'' referred to the inhabitants of the upper reaches of the Argun. Today the name is mostly used to refer to the Chechens who compactly live in the Pankisi Gorge of Georgia. History In 1795, when describing the peoples inhabiting Russia, the Kists are mentioned as follows: Kistins, or Kisti, who are divided into different tracts of which it is known to exist: Chechens, Ingush and Karabulaks, they live along the Sunzha River, and in the middle mountains of the Caucasus. The historian of the Caucasus S. M. Bronevsky described the bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fyappiy
The ''Fyappins'' ( inh, фаьппий, fäppiy) were an Ingush subgroup (''society'') that mostly inhabited the mountainous Fappi region of Ingushetia in the Caucasus. Historically they bordered on the west with Dzherakh, on the east with Khamkhins, on the north with Nazranians, and lastly in the south with Gudomakarians. The centre of the society was the fortified village (''aul'') of Erzi or Metskhal. During the 16–17th centuries, part of the ''Fyappins'' migrated to Tusheti, Georgia, due to a lack of land. The descendants of the migrants are known as Bats people. In the 17–18th centuries, another wave of migration accured, to the region of Aukh (modern day Dagestan). In 1733, due to the worry of expansion of Ottoman Turks in the region, ''Fyappins'' tried to establish ties with Kingdom of Kartli. As the Russian Empire started expanding its territories in the Caucasus Region 19th century, Caucasian War broke out. During the war, ''Fyappin'' Society was devasted aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kistinka (river)
Kistinka ( ka, ხდე, ქისტურა, inh, Оахкара-хий, Кисти-хий, Oakhkara-khi, Kisti-khi russian: Кистинка) is a river in Georgia that flows in the Khevi region. It originates at the foot of the Kibishi Glacier and flows to the northwest into the river Terek near the Russian-Georgian border. The length of the river is 17 km, the basin area is 79 km². Nomenclature The hydronym ''Kistinka'' derives from one of the old Ingush ethnonyms — ''Kisti'', and is used to refer to both rivers Arm-khi ( inh , Ӏарам-хий, Aram-khi; ka, ქისტეთისწყალი, ''Kistetis-tskali'') in the Dzheyrakhsky District and Oakhkara-khi ( ka, ხდე, ქისტურა, tr) in the Kazbegi Municipality. In 1910, Foma Gorepekin composes a short guide titled: ''«In the mountains of the Terek region»'', where he mentions being escorted along the gorge of the river ''Kistinka'' by the Buzurtanov brothers — well-known local gui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armkhi
Armkhi ( inh, МохтIе, ''Moxthe''; russian: Армхи) is a village in Dzheyrakhsky District of the Republic of Ingushetia, located on the ''Armkhi'' or ''Kistinka'' river ( inh, Ӏарам-хий, Кисти-хий, ''Aram-khi'', ''Kisti-khiï''; ka, ქისტეთისწყალი, ''Kistetis-tskali''; russian: Армхи, Кистинка). The village is known for its year-round recreation resort. Armkhi is one of six rural localities constituting the Dzheyrakh rural settlement. History The name of the village derives from the river ''Armkhi'', a tributary of the Terek river. Several variations exist with regard to the meaning of the term "Armkhi". One is that the toponym derives from Ingush for "prohibited water/river"; another, that it comes from the Ingush words ''amr'' 'lake' and ''khi'' 'water'. The hydronym ''Kistinka'' derives from one of the old Ingush ethnonyms — '' Kisti''. In 1745, Vakhushti Bagrationi mentions it as ''"Kistetian river"'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kistin Gorge
Kistin Gorge ( inh, Кистий чӀож) is a gorge of the Armkhi River in the Dzheyrakhsky District of the Republic of Ingushetia. The name of the gorge comes from the historical name of the river Armkhi — Kistinka, which in turn comes from one of the ethnonyms of the Ingush — Kists. Historically, the area where the gorge is located was called " Kistetia". It is mentioned in medieval Georgian sources, in particular, in the work of Vakhushti Bagrationi. History According to the legends, this road was controlled by the Tsurovs and the Yandievs. They "kept guard there and took tribute for the passage". In Russian documents, the name was first mentioned in the first half of the XIX century, in military reports from the period of the Caucasian War, for example, in the Report of the Commander-in-Chief of the Separate Caucasian Caucasian may refer to: Anthropology *Anything from the Caucasus region ** ** ** ''Caucasian Exarchate'' (1917–1920), an ecclesiastical exarc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vakhushti Bagrationi
Vakhushti ( ka, ვახუშტი, tr) (1696–1757) was a Georgian royal prince (''batonishvili''), geographer, historian and cartographer. His principal historical and geographic works, ''Description of the Kingdom of Georgia'' and the ''Geographical Atlas'', were inscribed on UNESCO's Memory of the World Register in 2013. Life A natural son of King Vakhtang VI of Kartli (ruled 1716–24), he was born in Tbilisi, 1696. Educated by the brothers Garsevanishvili and a Roman Catholic mission, he was fluent in Greek, Latin, French, Turkish, Russian and Armenian. His name Vakhushti derives from Old Iranian ''vahišta-'' ("paradise", superlative of ''veh'' "good", i.e., "superb, excellent"). Its equivalent in Middle Persian is ''wahišt'' and in New Persian ''behešt''. In 1719 and 1720, he took part in two successive campaigns against the rebel duke (''eristavi'') Shanshe of the Ksani. From August to November 1722, he was a governor of the kingdom during his father's absenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunzha (river)
The Sunzha ( rus, Су́нжа, p=ˈsunʐə, inh, Шолжа, Sholʒə, ce, Соьлжа, Sölƶa, p=sɥølʒə) is a river in North Ossetia, Ingushetia and Chechnya, Russia, a tributary of the Terek. It flows northeast inside the great northwest bend of the Terek River and catches most of the rivers that flow north from the mountains before they reach the Terek. It is long, and has a drainage basin of . The Sunzha rises on the Northern slope of the Caucasus Major. Its major tributaries are the Assa and Argun. With a turbidity of , it carries 12.2 million tons of alluvium per year. It is used for irrigation. Cities that lie on the Sunzha include Nazran, Karabulak, Grozny (the capital of Chechnya), and Gudermes. During the First and Second Chechen Wars, the destruction of petroleum reservoirs caused the Sunzha to become polluted with petroleum. Nomenclature The origin of the name of the river is disputed. The most probable of versions name Sunzha has come from Mongol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically been considered as a natural barrier between Eastern Europe and Western Asia. Mount Elbrus in Russia, Europe's highest mountain, is situated in the Western Caucasus. On the southern side, the Lesser Caucasus includes the Javakheti Plateau and the Armenian highlands, part of which is in Turkey. The Caucasus is divided into the North Caucasus and South Caucasus, although the Western Caucasus also exists as a distinct geographic space within the North Caucasus. The Greater Caucasus mountain range in the north is mostly shared by Russia and Georgia as well as the northernmost parts of Azerbaijan. The Lesser Caucasus mountain range in the south is occupied by several independent states, mostly by Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, but also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgians
The Georgians, or Kartvelians (; ka, ქართველები, tr, ), are a nation and indigenous Caucasian ethnic group native to Georgia and the South Caucasus. Georgian diaspora communities are also present throughout Russia, Turkey, Greece, Iran, Ukraine, United States, and European Union. Georgians arose from Colchian and Iberian civilizations of classical antiquity; Colchis was interconnected with the Hellenic world, whereas Iberia was influenced by the Achaemenid Empire until Alexander the Great conquered it. In the 4th century, the Georgians became one of the first to embrace Christianity and now the majority of Georgians are Orthodox Christians, with most following their national autocephalous Georgian Orthodox Church, although there are small Georgian Catholic and Muslim communities as well as a significant number of irreligious Georgians. Located in the Caucasus, on the continental crossroads of Europe and Asia, the High Middle Ages saw Georgian people form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vakhushti
Vakhushti ( ka, ვახუშტი, tr) (1696–1757) was a Georgian royal prince (''batonishvili''), geographer, historian and cartographer. His principal historical and geographic works, ''Description of the Kingdom of Georgia'' and the ''Geographical Atlas'', were inscribed on UNESCO's Memory of the World Register in 2013. Life A natural son of King Vakhtang VI of Kartli (ruled 1716–24), he was born in Tbilisi, 1696. Educated by the brothers Garsevanishvili and a Roman Catholic mission, he was fluent in Greek, Latin, French, Turkish, Russian and Armenian. His name Vakhushti derives from Old Iranian ''vahišta-'' ("paradise", superlative of ''veh'' "good", i.e., "superb, excellent"). Its equivalent in Middle Persian is ''wahišt'' and in New Persian ''behešt''. In 1719 and 1720, he took part in two successive campaigns against the rebel duke (''eristavi'') Shanshe of the Ksani. From August to November 1722, he was a governor of the kingdom during his father's absenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingushetia
Ingushetia (; russian: Ингуше́тия; inh, ГӀалгӏайче, Ghalghayče), officially the Republic of Ingushetia,; inh, Гӏалгӏай Мохк, Ghalghay Moxk is a republic of Russia located in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe. The republic is part of the North Caucasian Federal District, and shares land borders with the country of Georgia to its south; and borders the Russian republics of North Ossetia–Alania and Chechnya to its west and east, respectively; while having a border with Stavropol Krai to its north. It also is one of the least-populated republics of Russia at under 500,000. Its capital is the town of Magas, while the largest city is Nazran. At 4,000 square km, in terms of area, the republic is the smallest of Russia's non-city federal subjects. It was established on June 4, 1992, after the Checheno-Ingush Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic was split in two.Law of June 4, 1992Official website of the Republic of IngushetiaSocial-Econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingush Societies
Ingush societies/shahars ( inh, ГIалгIай шахьараш, Ghalghaj šaꜧaraš) were territorial associations of the Ingush based on the geographical association of several villages and intended for conditional administrative-territorial delimitation of the Ingush ethnic group. The formation and functioning of most of them dates back to the late Middle Ages (XVI-XIX centuries). During this period, their boundaries, number and names changed. The names of societies mainly came from the names of the area of their localization, that is, they were based on the geographical principle. Despite the fact that during this period the Ingush lived in relatively closed conditions of mountain gorges, which contributed to more demarcation in terms of territoriality than rallying around a single center, they retained the self-consciousness of a single ethnic group based on a common culture and a single language. Ingush societies in the literature are sometimes called "shahars" ( in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)