|
Kiangsuaspis
''Kiangsuaspis nankingensis'' is an extinct phyllocarid crustaceans from Late Silurian China. It was originally described in 1962 by Kiang P'an as an incomplete ventral plate of a cyathaspidid heterostracan agnathan with a unique pattern of raised, sculptured tubercles that fuse together into anastomosing ridges.P'an, Kiang 1962. A new Silurian fish from Nanking, China. (Chinese with English summary). Acta Palaeont. Sinica, 10, no. 3, pp. 402-409, fig. 1, pi. 1. In 1984, Jiang P'an then reappraised it as a ceratiocaridid crustacea Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean gro ...n. References Prehistoric Malacostraca Prehistoric crustacean genera Silurian crustaceans {{paleo-crustacean-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozoic Era. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods (myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) became fully terrestrialized. A significant evolutionary milestone during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacean
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Malacostraca
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustacea
Crustaceans (Crustacea, ) form a large, diverse arthropod taxon which includes such animals as decapods, seed shrimp, branchiopods, fish lice, krill, remipedes, isopods, barnacles, copepods, amphipods and mantis shrimp. The crustacean group can be treated as a subphylum under the clade Mandibulata. It is now well accepted that the hexapods emerged deep in the Crustacean group, with the completed group referred to as Pancrustacea. Some crustaceans (Remipedia, Cephalocarida, Branchiopoda) are more closely related to insects and the other hexapods than they are to certain other crustaceans. The 67,000 described species range in size from '' Stygotantulus stocki'' at , to the Japanese spider crab with a leg span of up to and a mass of . Like other arthropods, crustaceans have an exoskeleton, which they moult to grow. They are distinguished from other groups of arthropods, such as insects, myriapods and chelicerates, by the possession of biramous (two-parted) limbs, and by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anastomosis
An anastomosis (, plural anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf#Veins, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be normal (such as the foramen ovale (heart), foramen ovale in a fetus's heart) or abnormal (such as the atrial septal defect#Patent foramen ovale, patent foramen ovale in an adult's heart); it may be acquired (such as an arteriovenous fistula) or innate (such as the arteriovenous shunt of a metarteriole); and it may be natural (such as the aforementioned examples) or artificial (such as a surgical anastomosis). The reestablishment of an anastomosis that had become blocked is called a reanastomosis. Anastomoses that are abnormal, whether congenital disorder, congenital or acquired, are often called fistulas. The term is used in medicine, biology, mycology, geology, and geography. Etymology Anastomosis: medical or Modern Latin, from Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
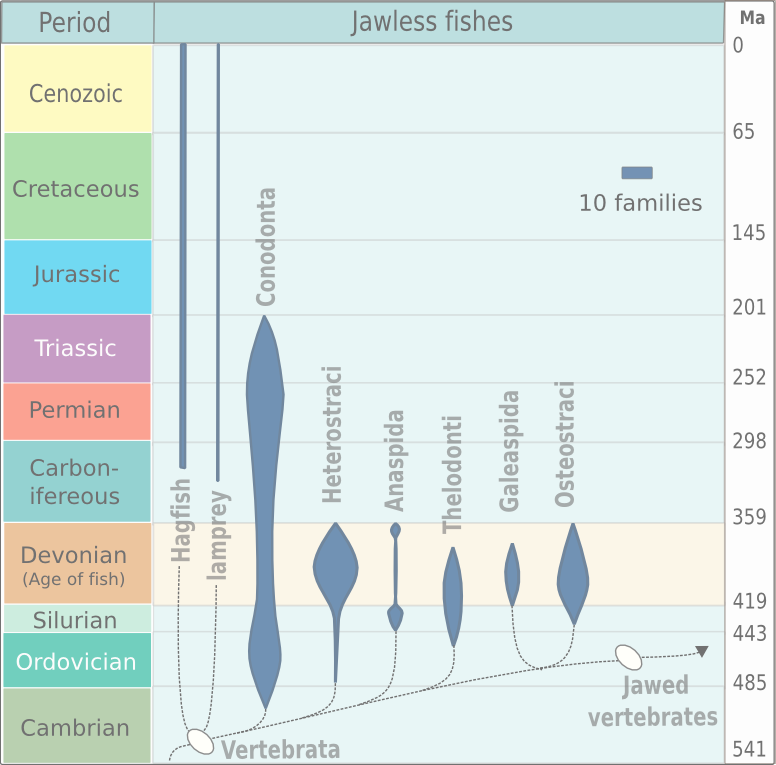
Agnathan
Agnatha (, Ancient Greek 'without jaws') is an infraphylum of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata, consisting of both present (cyclostomes) and extinct (conodonts and ostracoderms) species. Among recent animals, cyclostomes are sister to all vertebrates with jaws, known as gnathostomes. Recent molecular data, both from rRNA and from mtDNA as well as embryological data, strongly supports the hypothesis that living agnathans, the cyclostomes, are monophyletic. The oldest fossil agnathans appeared in the Cambrian, and two groups still survive today: the lampreys and the hagfish, comprising about 120 species in total. Hagfish are considered members of the subphylum Vertebrata, because they secondarily lost vertebrae; before this event was inferred from molecular and developmental data, the group Craniata was created by Linnaeus (and is still sometimes used as a strictly morphological descriptor) to reference hagfish plus vertebrates. While a few scientist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterostraci
Heterostraci (Ancient Greek, ἕτερος+ὄστρακον "those itha different shell" i is pl. of -us is an extinct subclass of pteraspidomorph jawless vertebrate that lived primarily in marine and estuary environments. Heterostraci existed from the mid-Ordovician to the conclusion of the Devonian. Description and anatomy The Heterostracans differed from other Paleozoic agnathan taxa both in the arrangement and histology of their scales. Most heterostracans had two plates which form a large dorsal shield and a large ventral shield, and had series of scales arranged in various patterns on the sides of their bodies, the exact pattern differing from one group to another. In a few primitive forms, such as '' Lepidaspis'', the dorsal and ventral shields are composed of a mosaic of tiny scales. In most other known forms, though, these tiny scales have fused together to form the shield-plates. The scales of heterostracans are histologically distinct from other vertebrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |