|
Keynesian Economists
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output and inflation. In the Keynesian view, aggregate demand does not necessarily equal the productive capacity of the economy. Instead, it is influenced by a host of factors – sometimes behaving erratically – affecting production, employment, and inflation. Keynesian economists generally argue that aggregate demand is volatile and unstable and that, consequently, a market economy often experiences inefficient macroeconomic outcomes – a recession, when demand is low, or inflation, when demand is high. Further, they argue that these economic fluctuations can be mitigated by economic policy responses coordinated between government and central bank. In particular, fiscal policy actions (taken by the government) and monetary policy actions ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Maynard Keynes
John Maynard Keynes, 1st Baron Keynes, ( ; 5 June 1883 – 21 April 1946), was an English economist whose ideas fundamentally changed the theory and practice of macroeconomics and the economic policies of governments. Originally trained in mathematics, he built on and greatly refined earlier work on the causes of business cycles. One of the most influential economists of the 20th century, he produced writings that are the basis for the school of thought known as Keynesian economics, and its various offshoots. His ideas, reformulated as New Keynesianism, are fundamental to mainstream macroeconomics. Keynes's intellect was evident early in life; in 1902, he gained admittance to the competitive mathematics program at King's College at the University of Cambridge. During the Great Depression of the 1930s, Keynes spearheaded a revolution in economic thinking, challenging the ideas of neoclassical economics that held that free markets would, in the short to medium term, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Economics
Classical economics, classical political economy, or Smithian economics is a school of thought in political economy that flourished, primarily in Britain, in the late 18th and early-to-mid 19th century. Its main thinkers are held to be Adam Smith, Jean-Baptiste Say, David Ricardo, Thomas Robert Malthus, and John Stuart Mill. These economists produced a theory of market economies as largely self-regulating systems, governed by natural laws of production and exchange (famously captured by Adam Smith's metaphor of the invisible hand). Adam Smith's '' The Wealth of Nations'' in 1776 is usually considered to mark the beginning of classical economics.Smith, Adam (1776) An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of The Wealth of Nations. (accessible by table of contents chapter titles) AdamSmith.org The fundamental message in Smith's book was that the wealth of any nation was determined not by the gold in the monarch's coffers, but by its national income. This income was in turn bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. For example, using interest rates, taxes, and government spending to regulate an economy's growth and stability. This includes regional, national, and global economies. According to a 2018 assessment by economists Emi Nakamura and Jón Steinsson, economic "evidence regarding the consequences of different macroeconomic policies is still highly imperfect and open to serious criticism." Macroeconomists study topics such as Gross domestic product, GDP (Gross Domestic Product), unemployment (including Unemployment#Measurement, unemployment rates), national income, price index, price indices, output (economics), output, Consumption (economics), consumption, inflation, saving, investment (macroeconomics), investment, Energy economics, energy, international trade, and international finance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2008–2009 Keynesian Resurgence
Following the global financial crisis of 2007–2008, there was a worldwide resurgence of interest in Keynesian economics among prominent economists and policy makers. This included discussions and implementation of economic policies in accordance with the recommendations made by John Maynard Keynes in response to the Great Depression of the 1930s, most especially fiscal stimulus and expansionary monetary policy. From the end of the Great Depression until the early 1970s, Keynesian economics provided the main inspiration for economic policy makers in Western industrialized countries. The influence of Keynes's theories waned in the 1970s due to stagflation and critiques from Friedrich Hayek, Milton Friedman, Robert Lucas Jr., and other economists, who were less optimistic about the ability of interventionist government policy to positively regulate the economy, or otherwise opposed to Keynesian policies. From the early 1980s to 2008, the normative consensus among economists was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Crisis Of 2007–2008
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of financial economics bridges the two). Finance activities take place in financial systems at various scopes, thus the field can be roughly divided into personal, corporate, and public finance. In a financial system, assets are bought, sold, or traded as financial instruments, such as currencies, loans, bonds, shares, stocks, options, futures, etc. Assets can also be banked, invested, and insured to maximize value and minimize loss. In practice, risks are always present in any financial action and entities. A broad range of subfields within finance exist due to its wide scope. Asset, money, risk and investment management aim to maximize value and minimize volatility. Financial analysis is viability, stability, and profitability a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainstream Economics
Mainstream economics is the body of knowledge, theories, and models of economics, as taught by universities worldwide, that are generally accepted by economists as a basis for discussion. Also known as orthodox economics, it can be contrasted to heterodox economics, which encompasses various schools or approaches that are only accepted by a minority of economists. The economics profession has traditionally been associated with neoclassical economics. This association has however been challenged by prominent historians of economic thought like David Collander. They argue the current economic mainstream theories, such as game theory, behavioral economics, industrial organization, information economics, and the like, share very little common ground with the initial axioms of neoclassical economics. History Economics has always featured multiple schools of economic thought, with different schools having different prominence across countries and over time. The current use of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Neoclassical Synthesis
The new neoclassical synthesis (NNS), which is now generally referred to as New Keynesian economics, and occasionally as the New Consensus, is the fusion of the major, modern macroeconomic schools of thought – new classical macroeconomics/ real business cycle theory and early New Keynesian economics – into a consensus view on the best way to explain short-run fluctuations in the economy. This new synthesis is analogous to the neoclassical synthesis that combined neoclassical economics with Keynesian macroeconomics. The new synthesis provides the theoretical foundation for much of contemporary mainstream macroeconomics. It is an important part of the theoretical foundation for the work done by the Federal Reserve and many other central banks. Prior to the synthesis, macroeconomics was split between partial-equilibrium New Keynesian work on market imperfections demonstrated with small models and new classical work on real business cycle theory that used fully specified gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Keynesian Economics
New Keynesian economics is a school of macroeconomics that strives to provide microeconomic foundations for Keynesian economics. It developed partly as a response to criticisms of Keynesian macroeconomics by adherents of new classical macroeconomics. Two main assumptions define the New Keynesian approach to macroeconomics. Like the New Classical approach, New Keynesian macroeconomic analysis usually assumes that households and firms have rational expectations. However, the two schools differ in that New Keynesian analysis usually assumes a variety of market failures. In particular, New Keynesians assume that there is imperfect competition in price and wage setting to help explain why prices and wages can become " sticky", which means they do not adjust instantaneously to changes in economic conditions. Wage and price stickiness, and the other market failures present in New Keynesian models, imply that the economy may fail to attain full employment. Therefore, New Keynesians ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
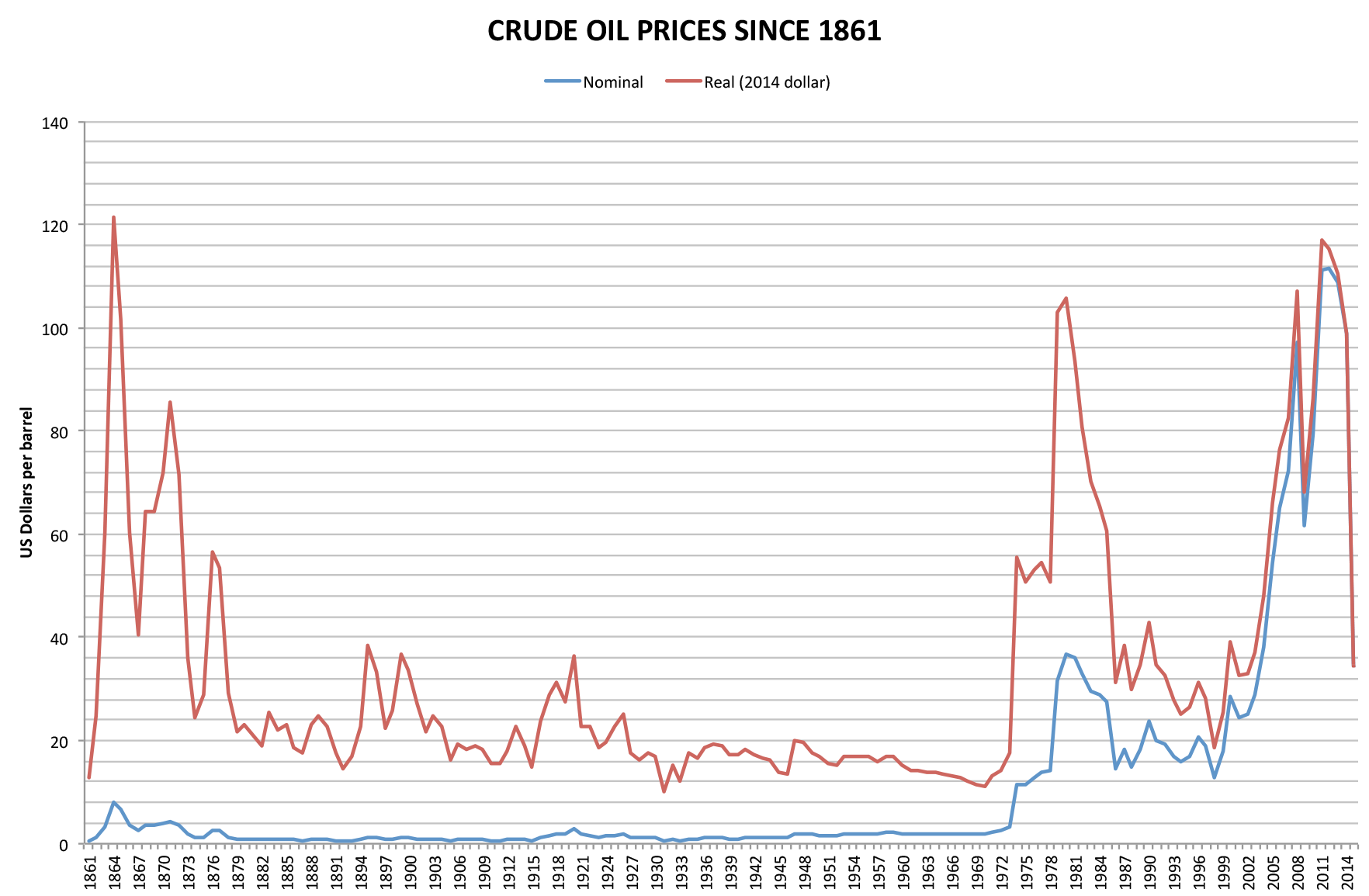
1973 Oil Crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supported Israel during the Yom Kippur War. The initial nations targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom and the United States, though the embargo also later extended to Portugal, Rhodesia and South Africa. By the end of the embargo in March 1974, the price of oil had risen nearly 300%, from US to nearly globally; US prices were significantly higher. The embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on global politics and the global economy. It was later called the "first oil shock", followed by the 1979 oil crisis, termed the "second oil shock". Background Arab-Israeli conflict Ever since the recreation of the State of Israel in 1948 there has been Arab–Israeli confli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, massa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |