|
Kehr's Sign
Kehr's sign is the occurrence of acute pain in the tip of the shoulder due to the presence of blood or other irritants in the peritoneal cavity when a person is lying down and the legs are elevated. Kehr's sign in the left shoulder is considered a classic symptom of a ruptured spleen. May result from diaphragmatic or peridiaphragmatic lesions, renal calculi, splenic injury or ruptured ectopic pregnancy. Kehr's sign is a classic example of referred pain: irritation of the diaphragm is signaled by the phrenic nerve as pain in the area above the collarbone. This is because the supraclavicular nerves have the same cervical nerves origin as the phrenic nerve, C3 and C4. The discovery of this is often attributed to a German gall bladder surgeon named Hans Kehr, but extensive studies into research he conducted during his life shows inconclusive evidence as to whether he actually discovered it. See also * Ruptured spleen A splenic injury, which includes a ruptured spleen, is any injur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peritoneal Cavity
The peritoneal cavity is a potential space between the parietal peritoneum (the peritoneum that surrounds the abdominal wall) and visceral peritoneum (the peritoneum that surrounds the internal organs). The parietal and visceral peritonea are layers of the peritoneum named depending on their function/location. It is one of the spaces derived from the coelomic cavity of the embryo, the others being the pleural cavities around the lungs and the pericardial cavity around the heart. It is the largest serosal sac, and the largest fluid-filled cavity, in the body and secretes approximately 50 ml of fluid per day. This fluid acts as a lubricant and has anti-inflammatory properties. The peritoneal cavity is divided into two compartments – one above, and one below the transverse colon. Compartments The peritoneal cavity is divided by the transverse colon (and its mesocolon) into an upper supracolic compartment, and a lower infracolic compartment. The liver, spleen, stomach, and lesser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruptured Spleen
A splenic injury, which includes a ruptured spleen, is any injury to the spleen. The rupture of a normal spleen can be caused by trauma, such as a traffic collision. Signs and symptoms In minor injuries with little bleeding, there may be abdominal pain, tenderness in the epigastrium and pain in the left flank. Often there is a sharp pain in the left shoulder, known as Kehr's sign. In larger injuries with more extensive bleeding, signs of hypovolemic shock are most prominent. This might include a rapid pulse, low blood pressure, rapid breathing, paleness, and anxiety. Causes The most common cause of a ruptured spleen is blunt abdominal trauma, such as in traffic collisions or sports accidents. Direct, penetrating injuries, for example, stab or gunshot wounds are rare. Non-traumatic causes are less common. These include infectious diseases, medical procedures such as colonoscopy, haematological diseases, medications, and pregnancy. In less than one percent of cases of infectiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Referred Pain
Referred pain, also called reflective pain, is pain perceived at a location other than the site of the painful stimulus. An example is the case of angina pectoris brought on by a myocardial infarction (heart attack), where pain is often felt in the left side of neck, left shoulder, and back rather than in the thorax (chest), the site of the injury. The International Association for the Study of Pain has not officially defined the term; hence several authors have defined it differently. Referred pain is when the pain is located away from or adjacent to the organ involved; for instance, when a person has pain only in their jaw or left arm, but not in the chest. Referred pain has been described since the late 1880s. Despite an increasing amount of literature on the subject, the biological mechanism of referred pain is unknown, although there are several hypotheses. Characteristics * The size of referred pain is related to the intensity and duration of ongoing/evoked pain. * Tempora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
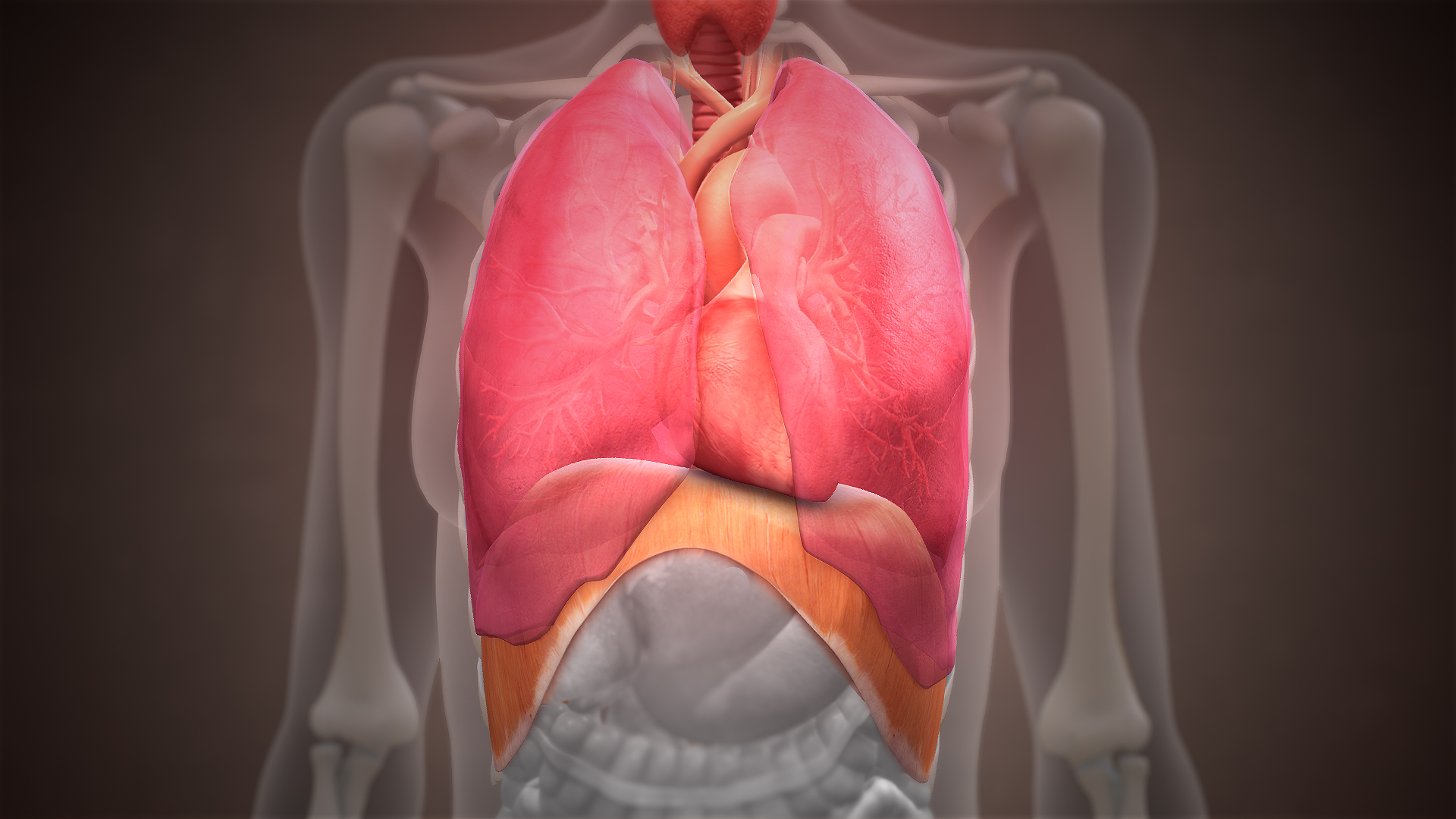
Diaphragm (anatomy)
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is higher up (superior) to the left half, since the large liver res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrenic Nerve
The phrenic nerve is a mixed motor/sensory nerve which originates from the C3-C5 spinal nerves in the neck. The nerve is important for breathing because it provides exclusive motor control of the diaphragm, the primary muscle of respiration. In humans, the right and left phrenic nerves are primarily supplied by the C4 spinal nerve, but there is also contribution from the C3 and C5 spinal nerves. From its origin in the neck, the nerve travels downward into the chest to pass between the heart and lungs towards the diaphragm. In addition to motor fibers, the phrenic nerve contains sensory fibers, which receive input from the central tendon of the diaphragm and the mediastinal pleura, as well as some sympathetic nerve fibers. Although the nerve receives contributions from nerves roots of the cervical plexus and the brachial plexus, it is usually considered separate from either plexus. The name of the nerve comes from Ancient Greek ''phren'' 'diaphragm'. Structure The phrenic n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
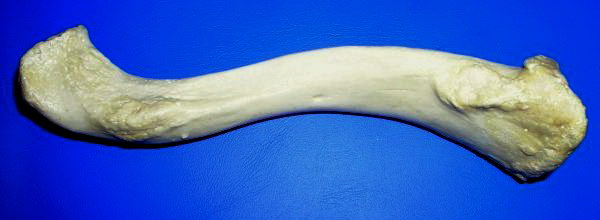
Collarbone
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut to keep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraclavicular Nerves
The supraclavicular nerves (descending branches) arise from the third and fourth cervical nerves. They emerge beneath the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus (sternocleidomastoid muscle), and descend in the posterior triangle of the neck beneath the platysma muscle and the deep cervical fascia. Together, they innervate skin over the shoulder. The supraclavicular nerve can be blocked during shoulder surgery. Branches The supraclavicular nerves arise from C3 and C4 spinal nerve roots. Near the clavicle, the supraclavicular nerves perforate the fascia and the platysma muscle to become cutaneous. They are arranged, according to their position, into three groups—anterior, middle, and posterior. Medial supraclavicular nerve The medial supraclavicular nerves or ''anterior supraclavicular nerves'' (nn. supraclaviculares anteriores; suprasternal nerves) cross obliquely over the external jugular vein and the clavicular and sternal heads of the sternocleidomastoideus, and supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Nerves
A spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, which carries motor, sensory, and autonomic signals between the spinal cord and the body. In the human body there are 31 pairs of spinal nerves, one on each side of the vertebral column. These are grouped into the corresponding cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral and coccygeal regions of the spine. There are eight pairs of cervical nerves, twelve pairs of thoracic nerves, five pairs of lumbar nerves, five pairs of sacral nerves, and one pair of coccygeal nerves. The spinal nerves are part of the peripheral nervous system. Structure Each spinal nerve is a mixed nerve, formed from the combination of nerve fibers from its dorsal and ventral roots. The dorsal root is the afferent sensory root and carries sensory information to the brain. The ventral root is the efferent motor root and carries motor information from the brain. The spinal nerve emerges from the spinal column through an opening (intervertebral foramen) between adjacent vertebrae. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gall Bladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, infec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Kehr
Johannes Otto Kehr (27 April 1862 – 20 May 1916) was a German surgeon and professor of surgery born in Waltershausen, Saxe-Coburg and Gotha. He practiced surgery at a private clinic in Halberstädt, and from 1910 worked in Berlin. He is known for the development of operative procedures for the treatment of gall bladder and bile duct diseases. In the late 19th century, Kehr popularized the cholecystectomy for the treatment of gallstones. He is credited with performing 2600 operations of the biliary tract during his career. Hans Kehr; not first, but foremost Eponyms His name is lent to , which is in an indication of acute pain in the left |
Ruptured Spleen
A splenic injury, which includes a ruptured spleen, is any injury to the spleen. The rupture of a normal spleen can be caused by trauma, such as a traffic collision. Signs and symptoms In minor injuries with little bleeding, there may be abdominal pain, tenderness in the epigastrium and pain in the left flank. Often there is a sharp pain in the left shoulder, known as Kehr's sign. In larger injuries with more extensive bleeding, signs of hypovolemic shock are most prominent. This might include a rapid pulse, low blood pressure, rapid breathing, paleness, and anxiety. Causes The most common cause of a ruptured spleen is blunt abdominal trauma, such as in traffic collisions or sports accidents. Direct, penetrating injuries, for example, stab or gunshot wounds are rare. Non-traumatic causes are less common. These include infectious diseases, medical procedures such as colonoscopy, haematological diseases, medications, and pregnancy. In less than one percent of cases of infectiou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |