|
Kansas In The American Civil War
At the outbreak of the American Civil War in April 1861, Kansas was the newest U.S. state, admitted just months earlier in January. The state had formally rejected slavery by popular vote and vowed to fight on the side of the Union, though ideological divisions with neighboring Missouri, a slave state, had led to violent conflict in previous years and persisted for the duration of the war. While Kansas was a rural frontier state distant from the major theaters of war and its Unionist government was never seriously threatened by Confederate military forces, several engagements did occur within its borders, as well as countless raids and skirmishes between local irregulars, including the Lawrence Massacre by pro-Confederate guerrillas under William Quantrill in August 1863. Later the state witnessed the defeat of Confederate General Sterling Price by Union General Alfred Pleasonton at the Battle of Mine Creek, the second-largest cavalry action of the war. The decision of how Kansa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Missouri Compromise
The Missouri Compromise was a federal legislation of the United States that balanced desires of northern states to prevent expansion of slavery in the country with those of southern states to expand it. It admitted Missouri as a Slave states and free states, slave state and Maine#Statehood, Maine as a free state and declared a policy of prohibiting slavery in the remaining Louisiana Purchase lands north of the parallel 36°30′ north, 36°30′ parallel. The 16th United States Congress passed the legislation on March 3, 1820, and President James Monroe signed it on March 6, 1820. Earlier, in February 1819, Representative James Tallmadge Jr., a Democratic-Republican Party, Democratic-Republican (Jeffersonian Republican) from New York (state), New York, had submitted two amendments to Missouri's request for statehood that included restrictions on slavery. Southerners objected to any bill that imposed federal restrictions on slavery and believed that it was a state issue, as settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
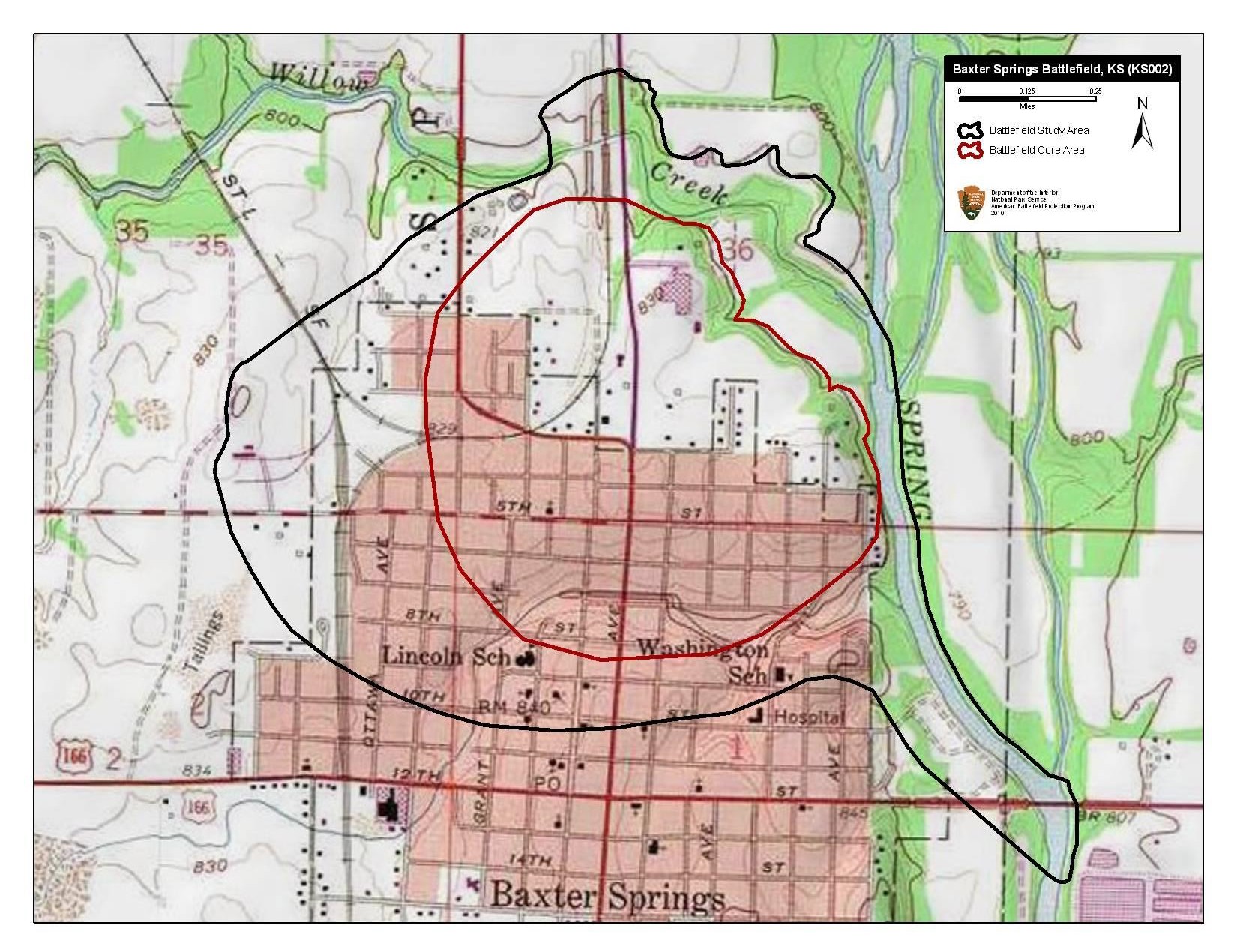
Battle Of Baxter Springs
The Battle of Baxter Springs, more commonly known as the Baxter Springs Massacre, was a minor battle of the American Civil War fought on 6 October 1863, near the present-day town of Baxter Springs, Kansas. In late 1863, Quantrill's Raiders, a large band of pro-Confederate bushwhackers led by William Quantrill, was traveling south through Kansas along the Texas Road to winter in Texas. Numbering about 400, this group captured and killed two Union teamsters who had come from a small Federal Army post called Fort Baxter (frequently referred to as Fort Blair). The bushwhackers assaulted the fort but were repulsed, eventually retreating to the prairie, where they attacked a separate Union column, leaving only a few survivors. Fight at the fort Quantrill decided to attack Fort Baxter and divided his force into two columns, one under him and the other commanded by a subordinate, David Poole. Poole and his men proceeded down the Texas Road, where they encountered Union soldiers, most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partisan Ranger Act
The Partisan Ranger Act was passed on April 21, 1862 by the Confederate Congress. It was intended as a stimulus for recruitment of irregulars for service into the Confederate Army during the American Civil War. The Confederate leadership, like the Union leadership, later opposed the use of unconventional warfare out of fear the lack of discipline among rival guerrilla groups could spiral out of control. On February 17, 1864, the law was repealed after pressure from General Robert E. Lee and other Confederate regulars. Only two partisan Ranger groups were exempt and allowed to continue to operate: Mosby's Raiders and McNeill's Rangers. Background Initially, Confederate President Jefferson Davis did not approve of unconventional warfare because it reduced the number of able men eligible to serve in the regular army. However, after conventional Confederate forces were driven out of western Virginia in the summer and early fall of 1861, pro-Confederate unconventional combata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osceola, Missouri
Osceola is a city in St. Clair County, Missouri, United States. The population was 909 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of St. Clair County. During the American Civil War, Osceola was the site of the Sacking of Osceola. History Located on the Osage River, the land that became the town of Osceola was inhabited by the tribe of Osage Native Americans, also known as NiuKonska, Native Americans who gave the river its name. NiuKonska means "Little Ones of the Middle Waters". Two treaties, in 1808 and 1825, signed by the Osage and the U.S. government gave up all the tribe's land in Missouri. With the way cleared for non-native settlers, more people began to arrive in the St. Clair County area in the mid-1830s. The town was the site of the September 1861 Sacking of Osceola by Jayhawkers (anti-slavery patrols) in which the town was burned and its courthouse looted. The event inspired the 1976 Clint Eastwood film ''The Outlaw Josey Wales''. Prior to the attack the town had a po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jayhawkers
Jayhawkers and red legs are terms that came to prominence in Kansas Territory during the Bleeding Kansas period of the 1850s; they were adopted by militant bands affiliated with the free-state cause during the American Civil War. These gangs were guerrillas who often clashed with pro-slavery groups from Missouri, known at the time in Kansas Territory as "Border Ruffians" or "Bushwhackers". After the Civil War, the word "Jayhawker" became synonymous with the people of Kansas, or anybody born in Kansas. Today a modified version of the term, Jayhawk, is used as a nickname for a native-born Kansan, Origin The origin of the term "Jayhawker" may go back as far as the Revolutionary War, when it was reportedly used to describe a group associated with American Founding Father John Jay, who was also the First Chief Justice of the United States. Jay believed in the abolition of slavery and that America should be governed by Christians; he has been described by historians as a "Christian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence, Kansas
Lawrence is the county seat of Douglas County, Kansas, Douglas County, Kansas, United States, and the sixth-largest city in the state. It is in the northeastern sector of the state, astride Interstate 70, between the Kansas River, Kansas and Wakarusa River, Wakarusa Rivers. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population of the city was 94,934. Lawrence is a college town and the home to both the University of Kansas and Haskell Indian Nations University. Lawrence was founded by the New England Emigrant Aid Company (NEEAC) and was named for Amos A. Lawrence, an abolitionist from Massachusetts, who offered financial aid and support for the settlement. Lawrence was central to the "Bleeding Kansas" period (1854–1861), and the site of the Wakarusa War (1855) and the Sacking of Lawrence (1856). During the American Civil War it was also the site of the Lawrence massacre (1863). Lawrence began as a center of Free-Stater (Kansas), free-state politics. Its economy diver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bushwhacker
Bushwhacking was a form of guerrilla warfare common during the American Revolutionary War, War of 1812, American Civil War and other conflicts in which there were large areas of contested land and few governmental resources to control these tracts. This was particularly prevalent in rural areas during the Civil War where there were sharp divisions between those favoring the Union and Confederacy in the conflict. The perpetrators of the attacks were called bushwhackers. The term "bushwhacking" is still in use today to describe ambushes done with the aim of attrition. Bushwhackers were generally part of the irregular military forces on both sides. While bushwhackers conducted well-organized raids against the military, the most dire of the attacks involved ambushes of individuals and house raids in rural areas. In the countryside, the actions were particularly inflammatory since they frequently amounted to fighting between neighbors, often to settle personal accounts. Since the at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
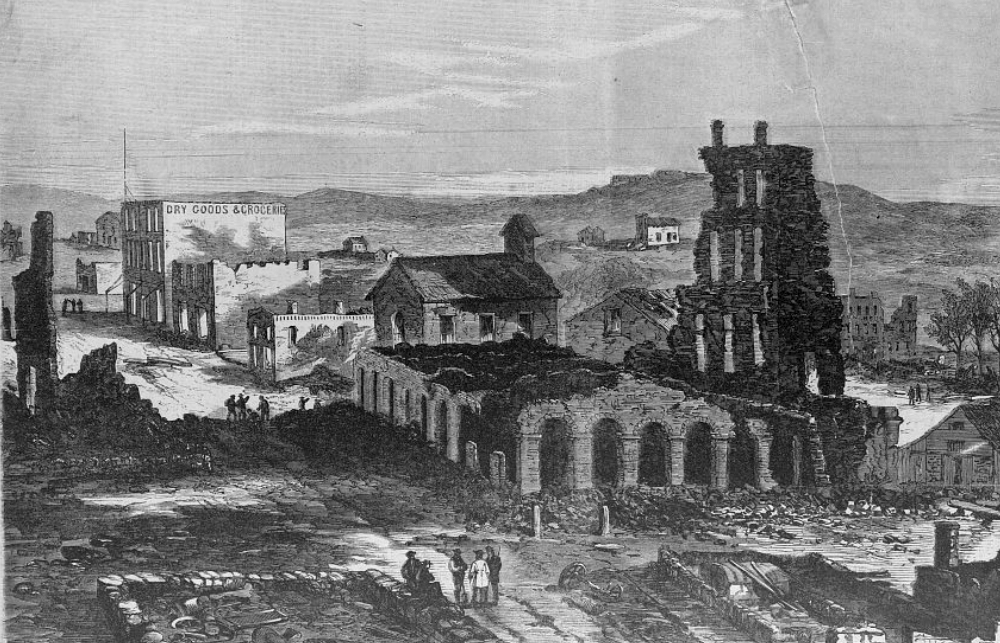
Battle Of Lawrence
The Lawrence Massacre, also known as Quantrill's Raid, was an attack during the American Civil War (186165) by Quantrill's Raiders, a Confederate guerrilla group led by William Quantrill, on the Unionist town of Lawrence, Kansas, killing around 150 unarmed men and boys. The attack on the morning of Friday, August 21, 1863 targeted Lawrence due to the town's long support of abolition and its reputation as a center for the Jayhawkers, who were free-state militia and vigilante groups known for attacking plantations in pro-slavery Missouri's western counties. Background By 1863, Kansas had long been the center of strife and warfare over the admission of slave versus free states. In the summer of 1856, the first sacking of Lawrence sparked a guerrilla war in Kansas that lasted for years. John Brown might be the best known participant in the violence of the late 1850s participating on the abolitionist or Jayhawker side, but numerous groups fought for each side during the "Bleedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bleeding Kansas
Bleeding Kansas, Bloody Kansas, or the Border War was a series of violent civil confrontations in Kansas Territory, and to a lesser extent in western Missouri, between 1854 and 1859. It emerged from a political and ideological debate over the legality of slavery in the proposed state of Kansas. The conflict was characterized by years of electoral fraud, raids, assaults, and murders carried out in the Kansas Territory and neighboring Missouri by proslavery "border ruffians" and antislavery " free-staters". According to ''Kansapedia'' of the Kansas Historical Society, 56 political killings were documented during the period, and the total may be as high as 200. It has been called a Tragic Prelude, or an overture, to the American Civil War, which immediately followed it. The conflict centered on the question of whether Kansas, upon gaining statehood, would join the Union as a slave state or a free state. The question was of national importance because Kansas's two new senators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-Stater (Kansas)
Free-Staters was the name given to settlers in Kansas Territory during the "Bleeding Kansas" period in the 1850s who opposed the expansion of slavery. The name derives from the term " free state", that is, a U.S. state without slavery. Many of the "free-staters" joined the Jayhawkers in their fight against slavery and to make Kansas a free state. Overview Many Free-Staters were abolitionists from New England, in part because there was an organized emigration of settlers to Kansas Territory arranged by the New England Emigrant Aid Company beginning in 1854. Other Free-Staters were abolitionists who came to Kansas Territory from Ohio, Iowa, and other midwestern states. Holton, Kansas was named for the Milwaukee, Wisconsin free-stater Edward Dwight Holton. What united the Free-Staters was a desire to defeat the southern, pro-slavery settlers in Kansas Territory on the question of whether Kansas would be admitted to the Union as a slave state. (The Kansas–Nebraska Act of 1854 had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |