|
Kandyan Law
Kandyan law is the customary law that originates from the Kingdom of Kandy, which is applicable to Sri Lankans who are Buddhist and from the former provinces of the Kandyan Kingdom. It is one of three customary laws which are still in use in Sri Lanka. The other two customary laws are the Thesavalamai and the Muslim law. At present it governs aspects of marriage, adoption, transfer of property and inheritance, as codified in 1938 in the ''Kandyan Law Declaration and Amendment Ordinance''. Jurisdiction Areas where kandyan law is applied; * Central Province * North Central Province * Uva Province * Sabaragamuwa Province * Chinnachchedkulam East and West and Kilakkumoolai South of Vavuniya District in the Northern Province * Kurunegala District and Demala Hathpattu of Puttalam District in the North Western Province Marriage Traditionally Kandyan law recognizes two types of marriage; *''Binna'' marriage - A marriage in which the husband joins the wife's family, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Custom (law)
A legal custom is the established pattern of behavior that can be objectively verified within a particular social setting. A claim can be carried out in defense of "what has always been done and accepted by law". Customary law (also, consuetudinary or unofficial law) exists where: #a certain legal practice is observed and #the relevant actors consider it to be an opinion of law or necessity ('' opinio juris''). Most customary laws deal with ''standards of the community'' that have been long-established in a given locale. However, the term can also apply to areas of international law where certain standards have been nearly universal in their acceptance as correct bases of action – for example, laws against piracy or slavery (see ''hostis humani generis''). In many, though not all instances, customary laws will have supportive court rulings and case law that have evolved over time to give additional weight to their rule as law and also to demonstrate the trajectory of evolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dowry
A dowry is a payment, such as property or money, paid by the bride's family to the groom or his family at the time of marriage. Dowry contrasts with the related concepts of bride price and dower. While bride price or bride service is a payment by the Bridegroom, groom, or his family, to the bride, or her family, dowry is the wealth transferred from the bride, or her family, to the groom, or his family. Similarly, dower is the property settled on the bride herself, by the groom at the time of marriage, and which remains under her ownership and control. Dowry is an ancient custom that is already mentioned in some of the earliest writings, and its existence may well predate records of it. Dowries continue to be expected and demanded as a condition to accept a marriage proposal in some parts of the world, mainly in parts of Asia, The custom of dowry is most common in cultures that are strongly patrilineal and that expect women to reside with or near their husband's family (patriloca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
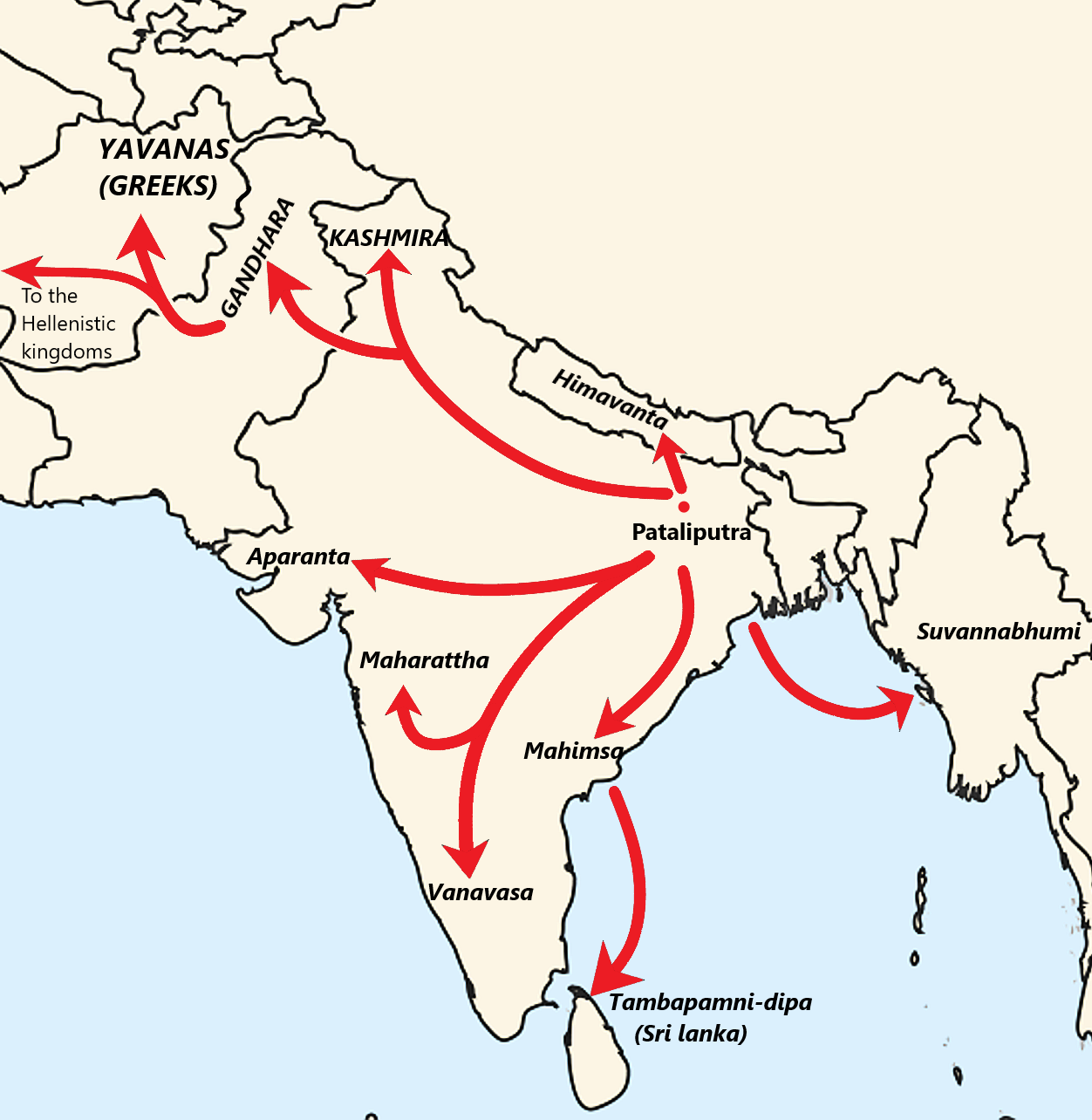
Buddhism In Sri Lanka
Theravada Buddhism is the largest and official religion of Sri Lanka, practiced by 70.2% of the population as of 2012. Practitioners of Sri Lankan Buddhism can be found amongst the majority Sinhalese population as well as among the minority ethnic groups. Sri Lankan Buddhists share many similarities with Southeast Asian Buddhists, specifically Myanmar Buddhists and Thai Buddhists due to traditional and cultural exchange. Sri Lanka is one of five nations with a Theravada Buddhist majority. Buddhism has been declared as the state religion under Article 9 of the Sri Lankan Constitution which can be traced back to an attempt to bring the status of Buddhism back to the status it enjoyed prior to the colonial era. Proselytizing from Buddhism has been illegal in Sri Lanka since 2009, due to the increase in conversions to Catholicism, however converting into Buddhism is highly encouraged by the government to be considered a person of Sinhalese origin. Sri Lanka is one of the oldest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Sri Lanka
The legal system in Sri Lanka comprises collections of codified and uncodified forms of law, of many origins subordinate to the Constitution of Sri Lanka which is the highest law of the island. Its legal framework is a mixture of legal systems of Roman-Dutch law, English law, Kandian law, Thesavalamai and Muslim law. This mixture is a result of the diverse history of the island as a result criminal law is based on English law while much of the common law is Roman-Dutch law, with certain aspects such as marriage, divorce, and inheritance associated with Kandian law, Thesavalamai and Muslim law based on the community and geography. ''Daily News'' The |
Supreme Court Of Sri Lanka
The Supreme Court of Sri Lanka ( si, ශ්රී ලංකා ශ්රේෂ්ඨාධිකරණය, Sri Lanka Sreshthadikaranaya; ta, இலங்கை உயர் நீதிமன்றம், Ilankai uyar neetimanram) is the highest court in Sri Lanka and the final judicial instance of record. Established in 1801 and empowered to exercise its powers subject to the provisions of the Constitution of Sri Lanka, the Supreme Court has ultimate appellate jurisdiction in constitutional matters and takes precedence over all lower courts. The Sri Lankan judicial system is a complex blend of common law and civil law. In some cases, such as those involving capital punishment, the decision may be passed on to the President of Sri Lanka for clemency petitions. The current Chief Justice of Sri Lanka is Jayantha Jayasuriya. History The Supreme Court of Sri Lanka was created on 18 April 1801 with the "Royal Charter of Justice of 1801 of King George the 3rd establishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vijayabahu VII Of Kotte
Vijayabahu VI was the son of Vira Parakrama Bahu VIII, who was an adopted child of Parakrama Bahu VI who founded the Kingdom of Kotte. He was born in c. 1445 and grew up with his brothers Sri Rajasinghe, Dharma Parakramabahu IX, and Raigam Bandara. He also had a sister who was married to Manamperi Arachchi. Reign After the death of the elder brother, Dharma Parakramabahu IX, the people of Kotte wanted his half brother, Sakalakala Valla, to become king. At the time he was reigning as a Viceroy at Udugampola. However, according to the Rajavaliya, a narrative of Sinhalese Kings, Vijaya Bahu was crowned as Vijaya Bahu VII by his half brother Sakalakala Valla. He came to the throne in 1513 A.D. Family Vijaya Bahu had two wives. The first was Anula Kahatuda, who Vijaya Bahu had cohabited with, along with his brother Sri Rajasinghe who died at Menikkadawara. Anula produced three sons to Vijaya Bahu: Bhuvaneka Bahu, Mayadunne and Maha Raigam Bandara. He also took a queen from Kiravella ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyandry
Polyandry (; ) is a form of polygamy in which a woman takes two or more husbands at the same time. Polyandry is contrasted with polygyny, involving one male and two or more females. If a marriage involves a plural number of "husbands and wives" participants of each gender, then it can be called polygamy, group marriage, group or conjoint marriage. In its broadest use, polyandry refers to sexual relations with multiple males within or without marriage. Of the 1,231 societies listed in the 1980 Ethnographic Atlas, 186 were found to be monogamous, 453 had occasional polygyny, 588 had more frequent polygyny, and 4 had polyandry.''Ethnographic Atlas Codebook'' derived from George P. Murdock's ''Ethnographic Atlas'' recording the marital composition of 1,231 societies from 1960 to 1980. Polyandry is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakadadoli
Yakadadoli were aristocratic concubines in the harem of the Kings of the Kingdom of Kandy in Sri Lanka. Kandyan Kings maintained harems, in addition to a chief queen and one or two secondary queens. The concubines in the harem, consisted of two categories, the Randoli who were concubines of royal blood and Yakadadoli who were primarily from the Radala caste. Children of both Randoli and Yakadadoli were disqualified from kingship. This was the case with Vira Narendra Sinha who had Sri Vijaya Rajasinha the brother of his queen succeed him as opposed to his sons from his Randoli. Favorite concubines frequently received land grants and their offspring were appointed as high officials of the royal court, and in a few cases captured kingdoms by deposing less scandalous and more legitimate heirs to the throne. The daughter of the Bintenne Disawe and granddaughter of Mámpitiye Disawe The Mahâ Dissâvas was a Great Officer in the Amātya Mandalaya, or Sinhalese Council of State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randoli
Randoli were consorts of royal blood in the harem of the Kings of the Kingdom of Kandy in Sri Lanka. Kandyan Kings maintained a harem, in addition to a chief queen and one or two secondary queens. The concubines in the harem, consisted of three categories, 1. Level I - Rondoli 2. Level II - Rididoli 3. Level III - Yakadadoli the Randoli who were consorts (level I) of royal blood, Rididoli who were consorts (level II) from either noble families of royal lineage or sisters of Randoli(Queen Consort) and Yakadadoli (level III) who were commoners from Radala and other noble castes. Queen Consort was ranked in the Randoli category. Her children ware only qualified to succeed the throne. Children of both Rididoli and Yakadadoli were disqualified from kingship. This was the case with Vira Narendra Sinha who had Sri Vijaya Rajasinha the brother of his queen succeed him as opposed to his sons from his Yakadadolis. Hindu princesses were brought over from Madurai in South India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harem
Harem (Persian: حرمسرا ''haramsarā'', ar, حَرِيمٌ ''ḥarīm'', "a sacred inviolable place; harem; female members of the family") refers to domestic spaces that are reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A harem may house a man's wife or wives, their pre-pubescent male children, unmarried daughters, female domestic servants, and other unmarried female relatives. In harems of the past, slave concubines were also housed in the harem. In former times some harems were guarded by eunuchs who were allowed inside. The structure of the harem and the extent of monogamy or polygamy has varied depending on the family's personalities, socio-economic status, and local customs. Similar institutions have been common in other Mediterranean and Middle Eastern civilizations, especially among royal and upper-class families, and the term is sometimes used in other contexts. In traditional Persian residential architecture the women's quarters were known as ''andar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygamy
Crimes Polygamy (from Late Greek (') "state of marriage to many spouses") is the practice of marrying multiple spouses. When a man is married to more than one wife at the same time, sociologists call this polygyny. When a woman is married to more than one husband at a time, it is called polyandry. In contrast to polygamy, monogamy is marriage consisting of only two parties. Like "monogamy", the term "polygamy" is often used in a ''de facto'' sense, applied regardless of whether a state recognizes the relationship.For the extent to which states can and do recognize potentially and actual polygamous forms as valid, see Conflict of marriage laws. In sociobiology and zoology, researchers use ''polygamy'' in a broad sense to mean any form of multiple mating. Worldwide, different societies variously encourage, accept or outlaw polygamy. In societies which allow or tolerate polygamy, in the vast majority of cases the form accepted is polygyny. According to the ''Ethnographic A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Interest
A life interest (or life rent in Scotland) is a form of right, usually under a trust, that lasts only for the lifetime of the person benefiting from that right. A person with a life interest is known as a life tenant. A life interest ends when the life tenant dies. An '' interest in possession trust'' is the most common example of a ''life interest trust''. In a typical interest in possession trust, the life tenant receives all the income from the trust for the rest of his or her life. On the life tenant's death, the trust comes to an end, and the capital of the trust is paid to another person, known as the remainderman, as specified by the trust document. One form of life interest is a life estate, an ownership interest in property that lasts for the life of the party to whom it has been granted. Unlike the beneficiary of a trust, the owner of a life estate in property has the right to possession of the property and may use it as any other owner, subject only to a duty to avoid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |