|
Kanakanahalli Ramachandra
Kanakanahalli Ramachandra (18 August 1933 – 17 January 2011) was an Indian mathematician working in both analytic number theory and algebraic number theory. Early career After his father's death at age 13, he had to look for a job. Ramachandra worked as a clerk at the Minerva Mills where Ramachandra's father had also worked. In spite of taking up a job quite remote from mathematics, Ramachandra studied number theory all by himself in his free time; especially the works of Ramanujan. Ramachandra completed his graduation and post graduation from Central College, Bangalore. Later, he worked as a lecturer in BMS College of Engineering. Ramachandra also served a very short stint of only six days as a teacher in the Indian Institute of Science, Bangalore. Ramachandra went to the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR), Bombay, for his graduate studies in 1958. He obtained his PhD from University of Mumbai in 1965; his doctorate was guided by K. G. Ramanathan. Later career ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandya
Mandya is a city in the state of Karnataka. It is the headquarter of Mandya district and is located from Mysore and from Bangalore. Sugar factories contribute to the major economic output. It is also called Sugar city (which in Kannada means Sakkare nagara) because sugarcane is a major crop. Mandya city has district offices premises. Currently the city is having 35 municipal wards of Mandya city municipal corporation. History There is a brief history of 75 years to Mandya. Mandya celebrated it 75th year (Amrutha Mahothsava) in 2015. The magnificent KRS dam was built by Krishna Raja Wadiyar IV and M. Visvesvaraya in Mandya. There are a lot of historical places of importance in Mandya. In 2016, Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) excavated another statue of Bahubali, a much revered figure among Jains. He was the son of Adinath, the first tirthankara of Jainism, and the younger brother of Bharata Chakravartin, identified with the 3rd – 9th centuries in Arthipura, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Reviews
''Mathematical Reviews'' is a journal published by the American Mathematical Society (AMS) that contains brief synopses, and in some cases evaluations, of many articles in mathematics, statistics, and theoretical computer science. The AMS also publishes an associated online bibliographic database called MathSciNet which contains an electronic version of ''Mathematical Reviews'' and additionally contains citation information for over 3.5 million items as of 2018. Reviews Mathematical Reviews was founded by Otto E. Neugebauer in 1940 as an alternative to the German journal ''Zentralblatt für Mathematik'', which Neugebauer had also founded a decade earlier, but which under the Nazis had begun censoring reviews by and of Jewish mathematicians. The goal of the new journal was to give reviews of every mathematical research publication. As of November 2007, the ''Mathematical Reviews'' database contained information on over 2.2 million articles. The authors of reviews are volunteers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Deaths
This is a list of deaths of notable people, organised by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked here. 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 See also * Lists of deaths by day The following pages, corresponding to the Gregorian calendar, list the historical events, births, deaths, and holidays and observances of the specified day of the year: Footnotes See also * Leap year * List of calendars * List of non-standard ... * Deaths by year {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1933 Births
Events January * January 11 – Sir Charles Kingsford Smith makes the first commercial flight between Australia and New Zealand. * January 17 – The United States Congress votes in favour of Philippines independence, against the wishes of U.S. President Herbert Hoover. * January 28 – "Pakistan Declaration": Choudhry Rahmat Ali publishes (in Cambridge, UK) a pamphlet entitled ''Now or Never; Are We to Live or Perish Forever?'', in which he calls for the creation of a Muslim state in northwest India that he calls " Pakstan"; this influences the Pakistan Movement. * January 30 ** National Socialist German Workers Party leader Adolf Hitler is appointed Chancellor of Germany by President of Germany Paul von Hindenburg. ** Édouard Daladier forms a government in France in succession to Joseph Paul-Boncour. He is succeeded on October 26 by Albert Sarraut and on November 26 by Camille Chautemps. February * February 1 – Adolf Hitler gives his "Proclamation to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
21st-century Indian Mathematicians
The 1st century was the century spanning AD 1 ( I) through AD 100 ( C) according to the Julian calendar. It is often written as the or to distinguish it from the 1st century BC (or BCE) which preceded it. The 1st century is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period. The 1st century also saw the appearance of Christianity. During this period, Europe, North Africa and the Near East fell under increasing domination by the Roman Empire, which continued expanding, most notably conquering Britain under the emperor Claudius (AD 43). The reforms introduced by Augustus during his long reign stabilized the empire after the turmoil of the previous century's civil wars. Later in the century the Julio-Claudian dynasty, which had been founded by Augustus, came to an end with the suicide of Nero in AD 68. There followed the famous Year of Four Emperors, a brief period of civil war and instability, which was finally brought to an end by Vespasian, ninth Roman emperor, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People From Mandya
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Srinivasa Ramanujan Medal
The Srinivasa Ramanujan Medal, named after the Indian mathematician Srinivasa Ramanujan, is awarded by the Indian National Science Academy for work in the mathematical sciences. Past recipients include: *1962 S. Chandrasekhar *1964 B. P. Pal *1966 K. S. Chandrasekharan *1968 P. C. Mahalanobis *1972 G. N. Ramachandran *1974 Harish-Chandra *1979 R. P. Bambah *1982 S. Chowla *1985 C. S. Seshadri *1988 M. S. Narasimhan *1991 M. S. Raghunathan *1997 K. Ramachandra *2003 C. R. Rao *2006 R. Parimala *2008 S. Ramanan *2013 K. R. Parthasarathy *2016 Tyakal Nanjundiah Venkataramana *2019 K. B. Sinha See also * List of mathematics awards This list of mathematics awards is an index to articles about notable awards for mathematics. The list is organized by the region and country of the organization that sponsors the award, but awards may be open to mathematicians from around the wor ... References {{reflistSrinivasa Ramanujan Medal recipients Mathematics awards Awards establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardy–Ramanujan Journal
The ''Hardy–Ramanujan Journal'' is a mathematics journal covering prime numbers, Diophantine equations, and transcendental numbers. It is named for G. H. Hardy and Srinivasa Ramanujan. Together with the ''The Ramanujan Journal, Ramanujan Journal'' and the ''Journal of the Ramanujan Mathematical Society'', it is one of three journals named after Ramanujan. It was established in 1978 by R. Balasubramanian and Kanakanahalli Ramachandra, K. Ramachandra and is published once a year on Ramanujan's birthday December 22. It is indexed in MathSciNet.Journal Information for "Hardy-Ramanujan Journal" MathSciNet, accessed 2011-07-24. Both Balasubramanian and Ramachandra are respected mathematicians and accomplished a great deal in the field of mathematics. They both also focused thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serge Lang
Serge Lang (; May 19, 1927 – September 12, 2005) was a French-American mathematician and activist who taught at Yale University for most of his career. He is known for his work in number theory and for his mathematics textbooks, including the influential ''Algebra''. He received the Frank Nelson Cole Prize in 1960 and was a member of the Bourbaki group. As an activist, Lang campaigned against the Vietnam War, and also successfully fought against the nomination of the political scientist Samuel P. Huntington to the National Academies of Science. Later in his life, Lang was an HIV/AIDS denialist. He claimed that HIV had not been proven to cause AIDS and protested Yale's research into HIV/AIDS. Biography and mathematical work Lang was born in Saint-Germain-en-Laye, close to Paris, in 1927. He had a twin brother who became a basketball coach and a sister who became an actress. Lang moved with his family to California as a teenager, where he graduated in 1943 from Beverly Hills H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
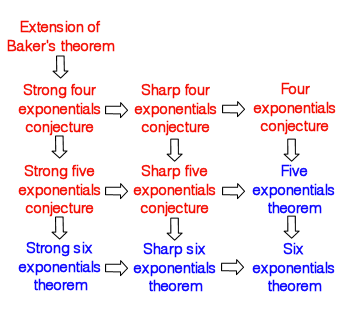
Six Exponentials Theorem
In mathematics, specifically transcendental number theory, the six exponentials theorem is a result that, given the right conditions on the exponents, guarantees the transcendence of at least one of a set of exponentials. Statement If ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., ''x''''d'' are ''d'' complex numbers that are linearly independent over the rational numbers, and ''y''1, ''y''2, ..., ''y''''l'' are ''l'' complex numbers that are also linearly independent over the rational numbers, and if ''dl'' > ''d'' + ''l'', then at least one of the following ''dl'' numbers is transcendental: :\exp(x_i y_j),\quad (1 \leq i \leq d,\ 1 \leq j \leq l). The most interesting case is when ''d'' = 3 and ''l'' = 2, in which case there are six exponentials, hence the name of the result. The theorem is weaker than the related but thus far unproved four exponentials conjecture, whereby the strict inequality ''dl'' > ''d'' + ''l'' is replaced with ''dl' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcendental Number Theory
Transcendental number theory is a branch of number theory that investigates transcendental numbers (numbers that are not solutions of any polynomial equation with rational coefficients), in both qualitative and quantitative ways. Transcendence The fundamental theorem of algebra tells us that if we have a non-constant polynomial with rational coefficients (or equivalently, by clearing denominators, with integer coefficients) then that polynomial will have a root in the complex numbers. That is, for any non-constant polynomial P with rational coefficients there will be a complex number \alpha such that P(\alpha)=0. Transcendence theory is concerned with the converse question: given a complex number \alpha, is there a polynomial P with rational coefficients such that P(\alpha)=0? If no such polynomial exists then the number is called transcendental. More generally the theory deals with algebraic independence of numbers. A set of numbers is called algebraically independent ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1938.jpg)