|
Kahn Process Networks
A Kahn process network (KPN, or process network) is a distributed ''model of computation'' in which a group of deterministic sequential processes communicate through unbounded first in, first out channels. The model requires that reading from a channel is blocking while writing is non-blocking. Due to these key restrictions, the resulting process network exhibits deterministic behavior that does not depend on the timing of computation nor on communication delays. Kahn process networks were originally developed for modeling parallel programs, but have proven convenient for modeling embedded systems, high-performance computing systems, signal processing systems, stream processing systems, dataflow programming languages, and other computational tasks. KPNs were introduced by Gilles Kahn in 1974. Execution model KPN is a common model for describing signal processing systems where infinite streams of data are incrementally transformed by processes executing in sequence or paral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Computing
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by passing messages to one another from any system. Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. The components of a distributed system interact with one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from SOA-based systems to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer applications. A computer program that runs within a distributed system is called a distributed program, and ''distributed programming'' is the process of writing such programs. There are many different types of implementations for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Element
In metadata, the term data element is an atomic unit of data that has precise meaning or precise semantics. A data element has: # An identification such as a data element name # A clear data element definition # One or more representation terms # Optional enumerated values Code (metadata) # A list of synonyms to data elements in other metadata registries Synonym ring Data elements usage can be discovered by inspection of software applications or application data files through a process of manual or automated Application Discovery and Understanding. Once data elements are discovered they can be registered in a metadata registry. In telecommunication, the term data element has the following components: #A named unit of data that, in some contexts, is considered indivisible and in other contexts may consist of data items. #A named identifier of each of the entities and their attributes that are represented in a database. #A basic unit of information built on standard structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE Computer Society
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massively Parallel Processor Array
A massively parallel processor array, also known as a multi purpose processor array (MPPA) is a type of integrated circuit which has a massively parallel array of hundreds or thousands of CPUs and RAM memories. These processors pass work to one another through a reconfigurable interconnect of channels. By harnessing a large number of processors working in parallel, an MPPA chip can accomplish more demanding tasks than conventional chips. MPPAs are based on a software parallel programming model for developing high-performance embedded system applications. Architecture MPPA is a MIMD (Multiple Instruction streams, Multiple Data) architecture, with distributed memory accessed locally, not shared globally. Each processor is strictly encapsulated, accessing only its own code and memory. Point-to-point communication between processors is directly realized in the configurable interconnect. The MPPA's massive parallelism and its distributed memory MIMD architecture distinguishes it fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambric
Ambric, Inc. was a designer of computer processors that developed the Ambric architecture. Its Am2045 Massively Parallel Processor Array (MPPA) chips were primarily used in high-performance embedded systems such as medical imaging, video, and signal-processing. Ambric was founded in 2003 in Beaverton, Oregon by Jay Eisenlohr and Anthony Mark Jones. Eisenlohr previously founded ansold Rendition, Inc. to Micron Technologyfor $93M, while Jones is a leading expert in analog, digital, and system IC design and is the named inventor on over 120 U.S. patents. Jones was also the founder of a number of companies prior to Ambric, and has since co-foundeVitek IPwith technology and patent expert Dan Buri in 2019. Ambric developed and introduced the Am2045 and its software tools in 2007, but fell victim to the financial crisis of 2007–2008. Ambric's Am2045 and tools remained available through Nethra Imaging, Inc., which closed in 2012. Architecture and programming model Ambric architecture is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field-programmable Gate Array
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation tools. FPGAs contain an array of programmable logic blocks, and a hierarchy of reconfigurable interconnects allowing blocks to be wired together. Logic blocks can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or act as simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops or more complete blocks of memory. Many FPGAs can be reprogrammed to implement different logic functions, allowing flexible reconfi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leiden University
Leiden University (abbreviated as ''LEI''; nl, Universiteit Leiden) is a public research university in Leiden, Netherlands. The university was founded as a Protestant university in 1575 by William, Prince of Orange, as a reward to the city of Leiden for its defence against Spanish attacks during the Eighty Years' War. As the oldest institution of higher education in the Netherlands, it enjoys a reputation across Europe and the world. Known for its historic foundations and emphasis on the social sciences, the university came into particular prominence during the Dutch Golden Age, when scholars from around Europe were attracted to the Dutch Republic due to its climate of intellectual tolerance and Leiden's international reputation. During this time, Leiden became the home to individuals such as René Descartes, Rembrandt, Christiaan Huygens, Hugo Grotius, Baruch Spinoza and Baron d'Holbach. The university has seven academic faculties and over fifty subject departments w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Order
In mathematics, a total or linear order is a partial order in which any two elements are comparable. That is, a total order is a binary relation \leq on some set X, which satisfies the following for all a, b and c in X: # a \leq a ( reflexive). # If a \leq b and b \leq c then a \leq c ( transitive). # If a \leq b and b \leq a then a = b ( antisymmetric). # a \leq b or b \leq a ( strongly connected, formerly called total). Total orders are sometimes also called simple, connex, or full orders. A set equipped with a total order is a totally ordered set; the terms simply ordered set, linearly ordered set, and loset are also used. The term ''chain'' is sometimes defined as a synonym of ''totally ordered set'', but refers generally to some sort of totally ordered subsets of a given partially ordered set. An extension of a given partial order to a total order is called a linear extension of that partial order. Strict and non-strict total orders A on a set X is a strict partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monotonic Function
In mathematics, a monotonic function (or monotone function) is a function between ordered sets that preserves or reverses the given order. This concept first arose in calculus, and was later generalized to the more abstract setting of order theory. In calculus and analysis In calculus, a function f defined on a subset of the real numbers with real values is called ''monotonic'' if and only if it is either entirely non-increasing, or entirely non-decreasing. That is, as per Fig. 1, a function that increases monotonically does not exclusively have to increase, it simply must not decrease. A function is called ''monotonically increasing'' (also ''increasing'' or ''non-decreasing'') if for all x and y such that x \leq y one has f\!\left(x\right) \leq f\!\left(y\right), so f preserves the order (see Figure 1). Likewise, a function is called ''monotonically decreasing'' (also ''decreasing'' or ''non-increasing'') if, whenever x \leq y, then f\!\left(x\right) \geq f\!\left(y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deterministic
Determinism is a philosophical view, where all events are determined completely by previously existing causes. Deterministic theories throughout the history of philosophy have developed from diverse and sometimes overlapping motives and considerations. The opposite of determinism is some kind of indeterminism (otherwise called nondeterminism) or randomness. Determinism is often contrasted with free will, although some philosophers claim that the two are compatible.For example, see Determinism is often used to mean ''causal determinism'', which in physics is known as cause-and-effect. This is the concept that events within a given paradigm are bound by causality in such a way that any state of an object or event is completely determined by its prior states. This meaning can be distinguished from other varieties of determinism mentioned below. Debates about determinism often concern the scope of determined systems; some maintain that the entire universe is a single determi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KPN As Finite State Machine
KPN (in full Koninklijke KPN N.V., also Royal KPN N.V.) is a Dutch landline and mobile telecommunications company. KPN originated from a government-run postal, telegraph and telephone service and is based in Rotterdam, Netherlands. History Until 1998 What is now KPN was first officially established as a postal service called the Statenpost in 1752. In 1799, Dutch postal services were reformed into a single, national system, and in 1807, was placed under the administration of the Ministry of Finance. In 1893, postal system and telegraph and telephone services were brought together to form the Staatsbedrijf der Posterijen, Telegrafie en Telefonie (approximately, “National corporation for Postage, Telegraphy and Telephony”), shortened to PTT or internationally as PTT-NL, under the Ministry of Agriculture, Industry and Commerce. Around a hundred years later, post codes were introduced in the Netherlands in 1977, which allowed full automation of the postal system. On 1 Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
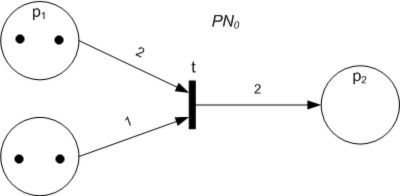
Petri Net
A Petri net, also known as a place/transition (PT) net, is one of several mathematical modeling languages for the description of distributed systems. It is a class of discrete event dynamic system. A Petri net is a directed bipartite graph that has two types of elements, places and transitions. Place elements are depicted as white circles and transition elements are depicted as rectangles. A place can contain any number of tokens, depicted as black circles. A transition is enabled if all places connected to it as inputs contain at least one token. Some sources state that Petri nets were invented in August 1939 by Carl Adam Petri—at the age of 13—for the purpose of describing chemical processes. Like industry standards such as UML activity diagrams, Business Process Model and Notation, and event-driven process chains, Petri nets offer a graphical notation for stepwise processes that include choice, iteration, and concurrent execution. Unlike these standards, Petri nets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)