|
June 4 (Eastern Orthodox Liturgics)
June 3 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics), June 3 - Eastern Orthodox liturgical calendar, Eastern Orthodox Church calendar - June 5 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics), June 5 All fixed Synaxarium, commemorations below celebrated on June 17 by Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Churches on the Julian Calendar, Old Calendar. For June 4th, Orthodox Churches on the Old Calendar commemorate the Saints listed on May 22 (Eastern Orthodox liturgics), May 22. Saints * Saints Mary, sister of Lazarus, Mary and Martha of Bethany, Martha, sisters of Saint Lazarus of Bethany, Lazarus (1st century)June 4/17 Orthodox Calendar (PRAVOSLAVIE.RU). Συναξαριστής. 4 Ιουνίου '' ECCLESI ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titus Of Byzantium
Titus (died 272) was Bishop of Byzantium Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ... from 242 to 272. {{authority control 272 deaths Year of birth unknown Bishops of Byzantium 3rd-century Romans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monagri
Monagri ( gr, Μονάγρι) is a village in the Limassol District of Cyprus, located 20 km north of Limassol Limassol (; el, Λεμεσός, Lemesós ; tr, Limasol or ) is a city on the southern coast of Cyprus and capital of the district with the same name. Limassol is the second largest urban area in Cyprus after Nicosia, with an urban population .... References Communities in Limassol District {{cyprus-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Babylon Fortress
Babylon Fortress (; ) is an Ancient Roman fortress, built around 30 BC with the arrival of emperor Augustus in Egypt, on the eastern bank of the Nile Delta, located in the area known today as Coptic Cairo. It is situated in the former area of the Heliopolite Nome, upon the east bank of the Nile, at latitude 30°N, near the commencement of the Pharaonic Canal (also called Ptolemy's Canal and Trajan's Canal), from the Nile to the Red Sea. It was at the boundary between Lower and Middle Egypt, where the river craft paid tolls when ascending or descending the Nile. Diodorus ascribes the erection of the first fort to rebel Assyrian captives in the reign of Sesostris, and Ctesias dates it to the time of Semiramis; but Josephus, with greater probability, attributes its structure to some Babylonian followers of Cambyses, in 525 BC. The Romans built a new fortress nearer the river, with typically Roman red and white banded masonry. Within the fortress's enclosure are the Coptic Museu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scetis
Wadi El Natrun (Arabic: "Valley of Natron"; Coptic: , "measure of the hearts") is a depression in northern Egypt that is located below sea level and below the Nile River level. The valley contains several alkaline lakes, natron-rich salt deposits, salt marshes and freshwater marshes. In Christian literature it is usually known as Scetis ( in Hellenistic Greek) or Skete (, plural in ecclesiastical Greek). It is one of the three early Christian monastic centers located in the Nitrian Desert of the northwestern Nile Delta. The other two monastic centers are Nitria and Kellia. Scetis, now called Wadi El Natrun, is best known today because its ancient monasteries remain in use, unlike Nitria and Kellia which have only archaeological remains. The desertified valley around Scetis in particular may be called the Desert of Scetis.. Fossil discoveries The area is one of the best known sites containing large numbers of fossils of large pre-historic animals in Egypt, and was known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Gibbons
James Cardinal Gibbons (July 23, 1834 – March 24, 1921) was a senior-ranking American prelate of the Catholic Church who served as Apostolic Vicar of North Carolina from 1868 to 1872, Bishop of Richmond from 1872 to 1877, and as ninth Archbishop of Baltimore from 1877 until his death. He was elevated to the rank of cardinal in 1886. Gibbons was consecrated a bishop on August 16, 1868, at the Baltimore Cathedral. The principal consecrator was Archbishop Martin J. Spalding. He was 34 years of age, serving as the first Apostolic Vicar of North Carolina. He attended the First Vatican Council, where he voted in favor of defining the dogma of papal infallibility. In 1872, he was named Bishop of Richmond by Pope Pius IX. In 1877, Gibbons was appointed Archbishop of Baltimore, the premier episcopal see in the United States. During his 44 years as Baltimore's archbishop, Gibbons became one of the most recognizable Catholic figures in the country. He defended the rights of labo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabine Baring-Gould
Sabine Baring-Gould ( ; 28 January 1834 – 2 January 1924) of Lew Trenchard in Devon, England, was an Anglican priest, hagiographer, antiquarian, novelist, folk song collector and eclectic scholar. His bibliography consists of more than 1,240 publications, though this list continues to grow. His family home, the manor house of Lew Trenchard, near Okehampton, Devon, has been preserved as he had it rebuilt and is now a hotel. He is remembered particularly as a writer of hymns, the best-known being "Onward, Christian Soldiers", "Sing Lullaby", and "Now the Day Is Over". He also translated the carol "Gabriel's Message" from the Basque language to English. Origins Sabine Baring-Gould was born in the parish of St Sidwells, St Sidwell, Exeter, on 28 January 1834. He was the eldest son and heir of Edward Baring-Gould (1804–1872), lord of the manor of Lew Trenchard, a Justice of the Peace and Deputy Lieutenant of Devon, formerly a lieutenant in the Madras Army#Madras Light Cavalry, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archbishop Of Constantinople
The ecumenical patriarch ( el, Οἰκουμενικός Πατριάρχης, translit=Oikoumenikós Patriárchēs) is the archbishop of Constantinople (Istanbul), New Rome and ''primus inter pares'' (first among equals) among the heads of the several autocephalous churches which compose the Eastern Orthodox Church. The ecumenical patriarch is regarded as the representative and spiritual leader of many Orthodox Christians worldwide. The term ''ecumenical'' in the title is a historical reference to the Ecumene, a Greek designation for the civilised world, i.e. the Roman Empire, and it stems from Canon 28 of the Council of Chalcedon. The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople is one of the most enduring institutions in the world and has had a prominent part in world history. The ecumenical patriarchs in ancient times helped in the spread of Christianity and the resolution of various doctrinal disputes. In the Middle Ages they played a major role in the affairs of the Eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metrophanes Of Byzantium
Saint Metrophanes (? – 326) was the bishop of Byzantium from 306 to 314. He may have retired from his episcopacy and died as late as 326. There is a tradition that, before his death, the Emperor Constantine I bestowed upon him the honorary title of Patriarch; however, Byzantium did not become the capital of the Empire until 330 (when it was renamed New Rome or Constantinople), and the see was not elevated to a patriarchate until 451. Metrophanes I could not partake in the first Ecumenical Council, which was held at Nicaea, due to age and ill health (he was already bedridden). He sent instead Alexander, the first among his presbyters, an honest man, whom he destined as his successor. For it is said that, when the Council had ended and the king with the god-bearing fathers returned, he was told by God that Alexander, and after him Paul, pleased God, and are good for this position. Metrophanes has been canonized a saint, and is revered in both the Eastern Orthodox Church and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
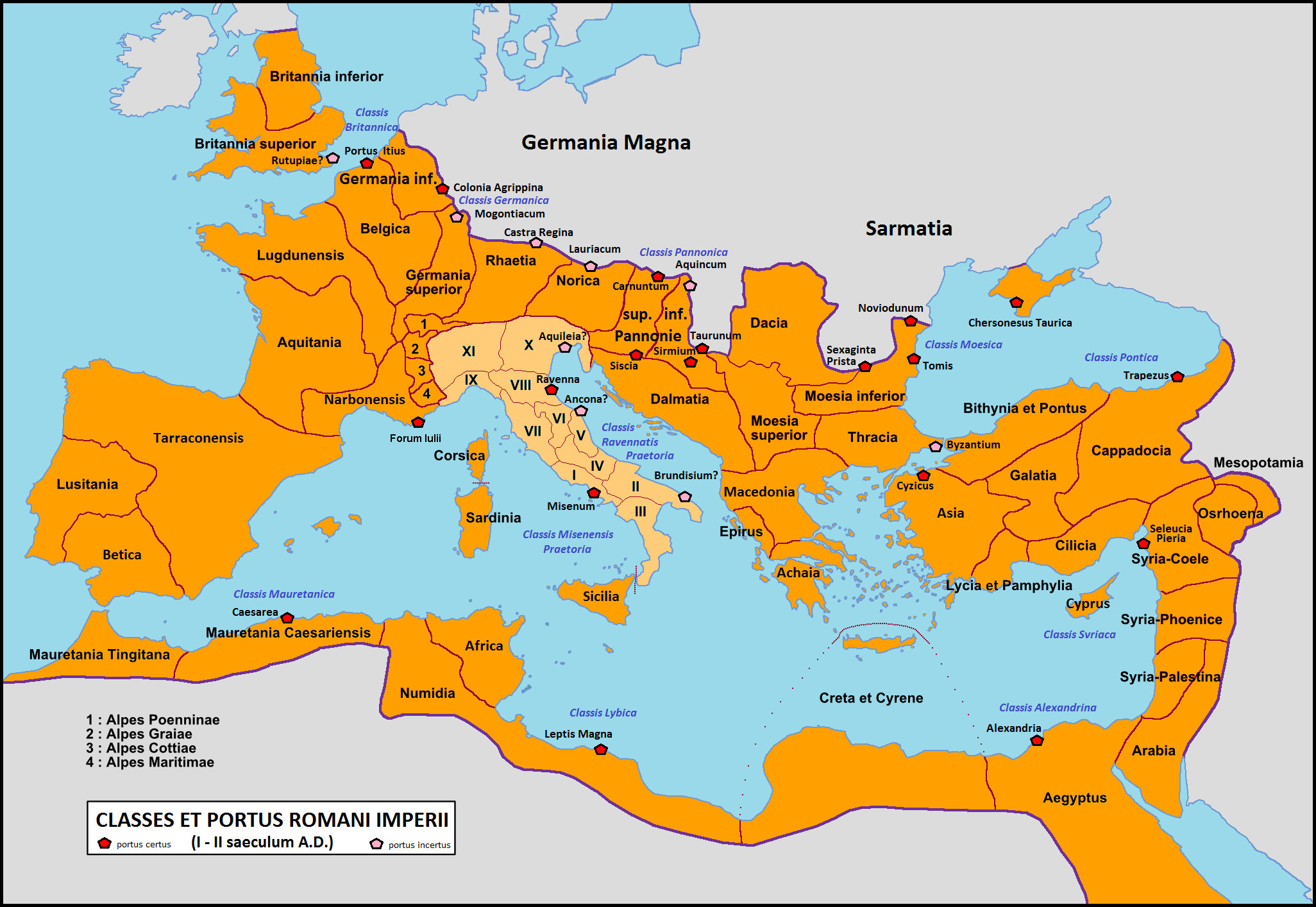
Scythia Minor (Roman Province)
Scythia Minor or Lesser Scythia (Greek: , ) was a Roman province in late antiquity, corresponding to the lands between the Danube and the Black Sea, today's Dobruja divided between Romania and Bulgaria. It was detached from Moesia Inferior by the Emperor Diocletian to form a separate province sometime between 286 and 293 AD. The capital of province was Tomis (today Constanța). The province ceased to exist around 679–681, when the region was overrun by the Bulgars, which the Emperor Constantine IV was forced to recognize in 681. According to the ''Laterculus Veronensis'' of and the ''Notitia Dignitatum'' of , Scythia belonged to the Diocese of Thrace. Its governor held the title of ''praeses'' and its ''dux'' commanded two legions, Legio I Iovia and Legio II Herculia. The office of ''dux'' was replaced by that of ''quaestor exercitus'', covering a wider area, in 536. The indigenous population of Scythia Minor was Dacian and their material culture is apparent archaeologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noviodunum (castra)
Noviodunum, known also as ''Noviodunum ad Istrum'', was a fort and a port in the Roman province of Moesia located on the lower Danube. History The geographical position of this settlement offered to the Romans the possibility of supervision and control of the border of the entire Roman limes in the north of the Danube. The strategic importance has been determinant in the economic and administrative function around which developed the military and naval legionaries. Noviodunum was passed under Roman control with the annexation of Thrace in 46 AD, being then attached to the Roman province of Moesia. It became an important port of ''Classis Flavia Moesica'' and a military center of the region starting from Domitian–Trajan, after the conquest of Dacia. Here some ''vexillationes'' of Legio V Macedonica were detached, at least until the reign of Marcus Aurelius. Then followed ''vexillationes'' of Legio I Italica, and then from the Diocletian Legio I Iovia. It was probably dest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |