|
Junction (road)
A junction is where two or more roads meet. History Roads began as a means of linking locations of interest: towns, forts and geographic features such as river fords. Where roads met outside of an existing settlement, these junctions often led to a new settlement. Scotch Corner is an example of such a location. In the United Kingdom and other countries, the practice of giving names to junctions emerged, to help travellers find their way. Junctions took the name of a prominent nearby business or a point of interest. As of the road networks increased in density and traffic flows followed suit, managing the flow of traffic across the junction became of increasing importance, to minimize delays and improve safety. The first innovation was to add traffic control devices, such as stop signs and traffic lights that regulated traffic flow. Next came lane controls that limited what each lane of traffic was allowed to do while crossing. Turns across oncoming traffic might be prohibited, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Road
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation. There are many types of roads, including parkways, avenues, controlled-access highways (freeways, motorways, and expressways), tollways, interstates, highways, thoroughfares, and local roads. The primary features of roads include lanes, sidewalks (pavement), roadways (carriageways), medians, shoulders, verges, bike paths (cycle paths), and shared-use paths. Definitions Historically many roads were simply recognizable routes without any formal construction or some maintenance. The Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) defines a road as "a line of communication (travelled way) using a stabilized base other than rails or air strips open to public traffic, primarily for the use of road motor vehicles running on their own wheels", whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Highway Administration
The Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) is a division of the United States Department of Transportation that specializes in highway transportation. The agency's major activities are grouped into two programs, the Federal-aid Highway Program and the Federal Lands Highway Program. Its role had previously been performed by the Office of Road Inquiry, Office of Public Roads and the Bureau of Public Roads. History Background The organization has several predecessor organizations and complicated history. The Office of Road Inquiry (ORI) was founded in 1893. In 1905, that organization's name was changed to the Office of Public Roads (OPR) which became a division of the United States Department of Agriculture. The name was changed again to the Bureau of Public Roads in 1915 and to the Public Roads Administration (PRA) in 1939. It was then shifted to the Federal Works Agency which was abolished in 1949 when its name reverted to Bureau of Public Roads under the Department of Commerce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stack Interchange
A directional interchange, colloquially known as a stack interchange, is a type of grade-separated junction between two controlled-access highways that allows for free-flowing movement to and from all directions of traffic. These interchanges eliminate the problems of weaving, have the highest vehicle capacity, and vehicles travel shorter distances when compared to different types of interchanges. The first directional interchange built in the world was the Four Level Interchange which opened to Los Angeles traffic in 1949. Definition A directional interchange is a grade separated junction between two roads where all turns that require crossing over or under the opposite road's lanes of travel in order to complete the turn utilize ramps that make a direct or semi-direct connection. The difference between direct and semi-direct connections is how much the motorist deviates from the intended direction of travel while on the ramp; direct ramps are shorter and can handle higher t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-point Urban Interchange
A single-point urban interchange (SPUI, or ), also called a single-point interchange (SPI) or single-point diamond interchange (SPDI), is a type of highway interchange. The design was created in order to help move large volumes of traffic through limited amounts of space safely and efficiently. Description A SPUI is similar in form to a diamond interchange but has the advantage of allowing opposing left turns to proceed simultaneously by compressing the two intersections of a diamond into one single intersection over or under the free-flowing road. The term "single-point" refers to the fact that all through traffic on the arterial street, as well as the traffic turning left onto or off the interchange, can be controlled from a single set of traffic signals. Due to the space efficiency of SPUIs relative to the volume of traffic they can handle, the interchange design is being used extensively in the reconstruction of existing freeways as well as constructing new freeways, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
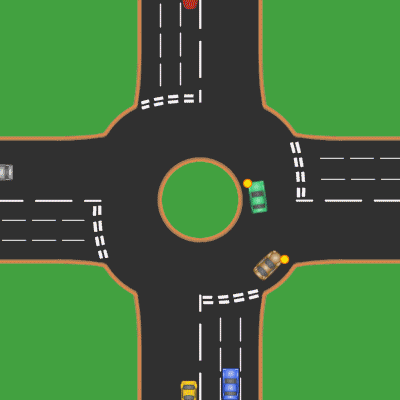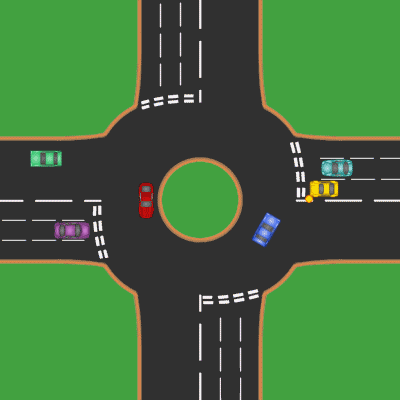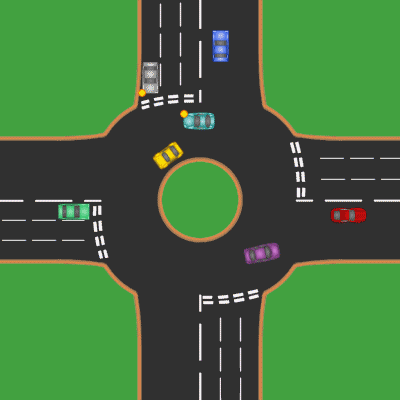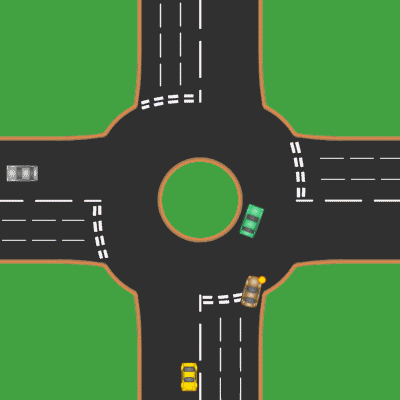
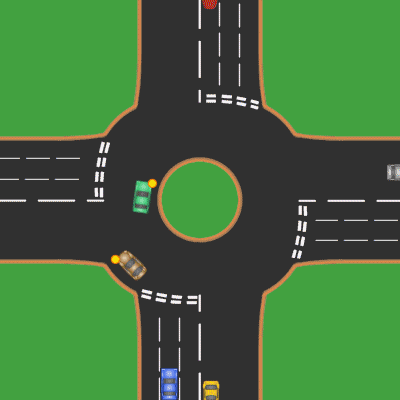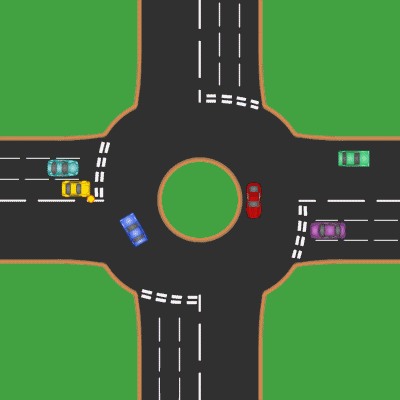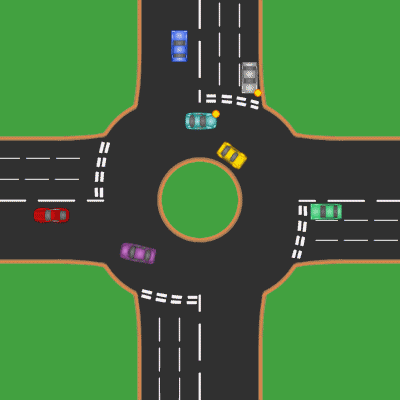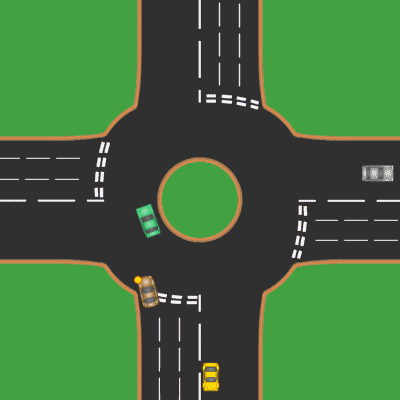
Roundabout
A roundabout is a type of circular intersection or junction in which road traffic is permitted to flow in one direction around a central island, and priority is typically given to traffic already in the junction.''The New Shorter Oxford English Dictionary,'' Volume 2, Clarendon Press, Oxford (1993), page 2632 Engineers use the term modern roundabout to refer to junctions installed after 1960 that incorporate various design rules to increase safety. Both modern and non-modern roundabouts, however, may bear street names or be identified colloquially by local names such as rotary or traffic circle. Compared to stop signs, traffic signals, and earlier forms of roundabouts, modern roundabouts reduce the likelihood and severity of collisions greatly by reducing traffic speeds and minimizing T-bone and head-on collisions. Variations on the basic concept include integration with tram or train lines, two-way flow, higher speeds and many others. For pedestrians, traffic exiting th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Roundabout Interchange
A diamond interchange is a common type of road junction, used where a controlled-access highway crosses a minor road. Design The freeway itself is grade-separated from the minor road, one crossing the other over a bridge. Approaching the interchange from either direction, an off-ramp diverges only slightly from the freeway and runs directly across the minor road, becoming an on-ramp that returns to the freeway in similar fashion. The two places where the ramps meet the road are treated as conventional intersections. In the United States, where this form of interchange is very common, particularly in rural areas, traffic on the off-ramp typically faces a stop sign at the minor road, while traffic turning onto the freeway is unrestricted. The diamond interchange uses less space than most types of freeway interchange, and avoids the interweaving traffic flows that occur in interchanges such as the cloverleaf. Thus, diamond interchanges are most effective in areas where tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raindrop Interchange
A roundabout is a type of circular intersection or junction in which road traffic is permitted to flow in one direction around a central island, and priority is typically given to traffic already in the junction.''The New Shorter Oxford English Dictionary,'' Volume 2, Clarendon Press, Oxford (1993), page 2632 Engineers use the term modern roundabout to refer to junctions installed after 1960 that incorporate various design rules to increase safety. Both modern and non-modern roundabouts, however, may bear street names or be identified colloquially by local names such as rotary or traffic circle. Compared to stop signs, traffic signals, and earlier forms of roundabouts, modern roundabouts reduce the likelihood and severity of collisions greatly by reducing traffic speeds and minimizing T-bone and head-on collisions. Variations on the basic concept include integration with tram or train lines, two-way flow, higher speeds and many others. For pedestrians, traffic exiting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Cloverleaf Interchange
A partial cloverleaf interchange or parclo is a modification of a cloverleaf interchange. The design has been well received, and has since become one of the most popular freeway-to-arterial interchange designs in North America. It has also been used occasionally in some European countries, such as Germany, Hungary, Italy, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom. Comparison with other interchanges *A diamond interchange has four ramps. *A cloverleaf interchange has eight ramps, as does a stack interchange. They are fully grade separated, unlike a parclo, and have traffic flow without stops on all ramps and throughways. *A parclo generally has either four or six ramps but less commonly has five ramps. Naming In Ontario, the specific variation is identified by a letter/number suffix after the name. Ontario's naming conventions are used in this article. The letter ''A'' designates that two ramps meet the freeway ''ahead'' of the arterial road, while ''B'' designates that two ram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free-flow Interchange
A free-flow interchange is an interchange in which all roads are grade-separated, and where movement from one road to another does not require the driver to stop for traffic (for example, the interchange may not include traffic lights or unsignalized at-grade intersections). Free-flow interchanges are less likely to induce traffic congestion than non-free-flow, but are typically more expensive both in money and in land. Some free-flow interchanges bring additional problems such as weaving or passing lane/fast lane exits (i.e. left exits in areas with right-hand traffic, and vice versa) that may be necessary to avoid additional costs, but lead to congestion and accidents and ultimately to an upgrade to another type of interchange. A free flow interchange design, called double crossover merging interchange (DCMI), has received a patent."United States Patent 8,950,970: Double Crossover Merging Interchange". United States Patent and Trademark Office. February 10, 2015. Retrieved A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dumbbell Interchange
A diamond interchange is a common type of road junction, used where a controlled-access highway crosses a minor road. Design The freeway itself is grade-separated from the minor road, one crossing the other over a bridge. Approaching the interchange from either direction, an off-ramp diverges only slightly from the freeway and runs directly across the minor road, becoming an on-ramp that returns to the freeway in similar fashion. The two places where the ramps meet the road are treated as conventional intersections. In the United States, where this form of interchange is very common, particularly in rural areas, traffic on the off-ramp typically faces a stop sign at the minor road, while traffic turning onto the freeway is unrestricted. The diamond interchange uses less space than most types of freeway interchange, and avoids the interweaving traffic flows that occur in interchanges such as the cloverleaf. Thus, diamond interchanges are most effective in areas where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Transportation Engineers
The Institute of Transportation Engineers (ITE) is an international educational and scientific association of transportation professionals who are responsible for meeting mobility and safety needs. ITE facilitates the application of technology and scientific principles to research, planning, functional design, implementation, operation, policy development, and management for any mode of ground transportation. History The organization formed in 1930 amid growing public demand for experts to alleviate traffic congestion and the frequency of crashes that came from the rapid development of automotive transportation. It formed as the Institute of Traffic Engineers and its first president was Ernest P. Goodrich. The organization consists of 10 districts, 62 sections, and 30 chapters from various parts of the world. Standards development ITE is also a standards development organization designated by the United States Department of Transportation (USDOT). One of the current standardizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Crossover Merging Interchange
A diverging diamond interchange (DDI), also called a double crossover diamond interchange (DCD), is a subset of diamond interchange in which the opposing directions of travel on the non-freeway road cross each other on either side of the interchange so that traffic crossing the freeway on the overpass or underpass is operating on the opposite driving side from that which is customary for the jurisdiction. The crossovers may employ one-side overpasses or be at-grade and controlled by traffic light. The diverging diamond interchange has advantages in both efficiency and safety, and—despite having been in use in France since the 1970s—was cited by ''Popular Science'' as one of the best engineering innovations of 2009 and in the U.S. has been promoted as part of the Federal Highway Administration's Every Day Counts initiative. The flow through a diverging diamond interchange using overpasses at the crossovers is limited only by weaving, and the flow through an implementation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)