|
Juliet (PRR)
The Railway Museum of Greater Cincinnati is a railway museum, railroad museum in Covington, Kentucky. Collection The museum owns and maintains a collection of 80 historic railroad equipment located on a site. The museum was founded in 1975 when a club of local railroad enthusiasts decided to run passenger cars on Amtrak trains. Several local members purchased cars for this goal. In the late 1980s, Amtrak tightened its restrictions on passenger cars, making it too expensive for most private citizens to keep them up. Though the Amtrak excursions ended, the cars remained as the core of the present collection. At that point the goal of the museum changed and now focuses on the preservation of the equipment. Tom Holley, former chairman of the board, stated "Now the primary purpose of the museum is the collection of the equipment that belonged to the seven railroads then entered Cincinnati." Pennsylvania Railroad E8 locomotive #5888 has been undergoing restoration for the past few year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Museum
A railway museum is a museum that explores the history of all aspects of rail related transportation, including: locomotives ( steam, diesel, and electric), railway cars, trams, and railway signalling equipment. They may also operate historic equipment on museum grounds. Africa Egypt *Egypt's Railway Museum (Cairo) Kenya * Nairobi Railway Museum in Nairobi Nigeria * NRC/Legacy Railway Museum in Lagos Sierra Leone *Sierra Leone National Railway Museum in Freetown South Africa *Outeniqua Transport Museum in George Sudan * Railway Museum in Atbarah Zambia *Railway Museum in Livingstone Zimbabwe * Bulawayo Railway Museum in Bulawayo Asia China *Chan T'ien-yu Memorial Hall, Badaling, Beijing * China Railway Museum, Beijing * Da'anbei Railway Station, Da'an, Jilin Province *Hong Kong Railway Museum * Qingdao-Jinan Railway Museum, Jinan, Shandong Province *Shanghai Railway Museum, Shanghai *Shenyang Railway Museum, Shenyang, Liaoning Province *Wuhan Metro Museum, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Troop Sleeper
In United States railroad terminology, a troop sleeper was a railroad passenger car which had been constructed to serve as something of a mobile barracks (essentially, a sleeping car) for transporting troops over distances sufficient to require overnight accommodations. This method allowed part of the trip to be made overnight, reducing the amount of transit time required and increasing travel efficiency. History Background and development Between December 1941 and June 1945 U.S. railroads carried almost 44 million armed services personnel. As there were not enough cars and coaches available to meet the massive need for troop transit created by World War II, in late 1943 the U.S. Office of Defense Transportation contracted with the Pullman Company to build 2,400 troop sleepers, and with American Car and Foundry to build 440 troop kitchen cars. This new rolling stock was either converted from existing boxcars or built from scratch based on Association of American Railroads standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railroad Museums In Kentucky
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in Track (rail transport), tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on Railroad tie, sleepers (ties) set in track ballast, ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower friction, frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The rail transport operations, operation is carried out by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observation Car
An observation car/carriage/coach (in US English, often abbreviated to simply observation or obs) is a type of railroad passenger car, generally operated in a passenger train as the rearmost carriage, with windows or a platform on the rear of the car for passengers' viewing pleasure. The cars were nearly universally removed from service on American railroads beginning in the 1950s as a cost-cutting measure in order to eliminate the need to "turn" the trains when operating out of stub-end terminals. The push-pull mode of operation removes this limitation. In Europe, various trains are now fitted with observation cars at either or both ends. Configuration The main spotting feature of observation cars is at the "B" end (tail) of the car; the walls of lightweight and streamlined cars usually round together to form a tapered U shape, smoothly or with a door, and larger panoramic windows were installed all around the end of the car. On older heavyweight cars, the rear end of the car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
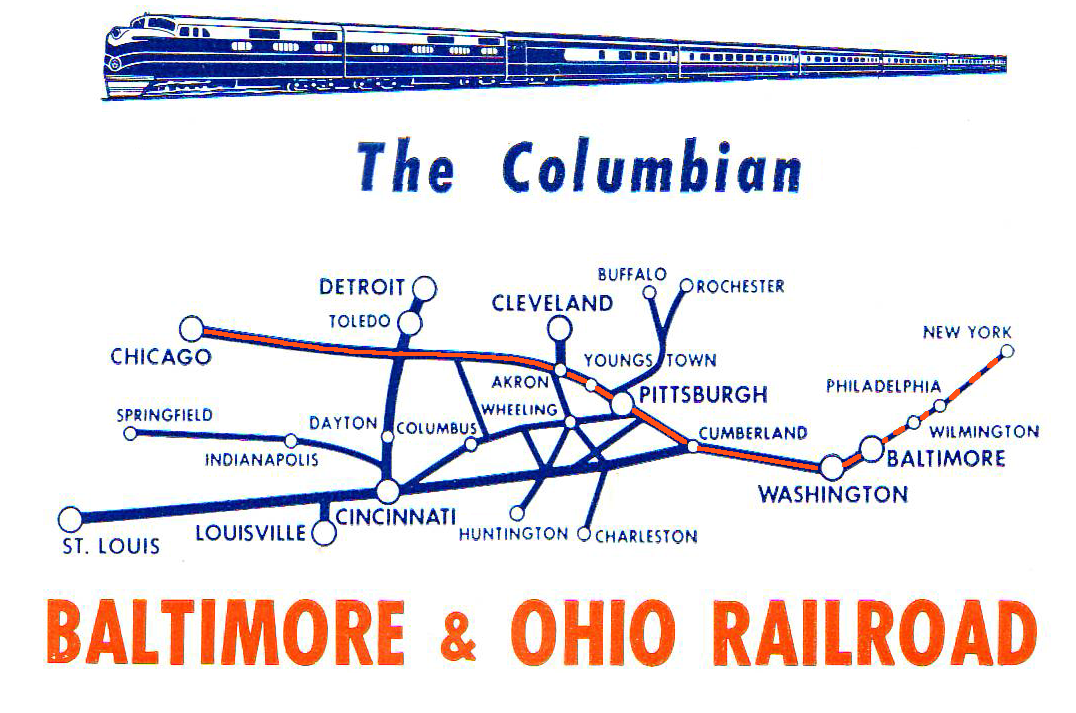
Columbian (B&O Train)
The ''Columbian'' was a named passenger train operated by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad. It was the all-coach supplemental train of the all-Pullman ''Capitol Limited''. It operated from 1931 to 1964. The train's initial route was between Jersey City, New Jersey and Washington, D.C., but in 1941 the ''Columbian'' route was lengthened to Jersey Illinois. It was the first air-conditioned train in the United States. History The ''Columbian'' between Jersey City and Washington was the first air-conditioned passenger train in North America.Herbert H. Harwood, Jr., ''Royal Blue Line''. Sykesville, Md.: Greenberg Publishing, 1990 (), p. 138. Air-conditioned equipment began operating on the train on May 24, 1931.Harry Stegmaier, ''Baltimore & Ohio Passenger Service, Vol. 2 – Route of the Capitol Limited''. Lynchburg, Va.: TLC Publishing, 1997 (). In 1937 the B&O re-equipped the ''Columbian'' with cars from the ''Royal Blue''. On December 19, 1941 the B&O extended the ''Colum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sleeping Car
The sleeping car or sleeper (often ) is a railway passenger car (rail), passenger car that can accommodate all passengers in beds of one kind or another, for the purpose of sleeping. George Pullman was the American innovator of the sleeper car. The first such cars saw sporadic use on American and English railways in the 1830s; they could be configured for Coach (rail), coach seating during the day. History Possibly the earliest example of a sleeping car (or ''bed carriage'', as it was then called) was on the London & Birmingham and Grand Junction Railways between London and Lancashire, England. The bed carriage was first made available to first-class passengers in 1838. In the spring of 1839, the Cumberland Valley Railroad pioneered sleeping car service in America with a car named "Chambersburg", between Chambersburg, Pennsylvania, Chambersburg and Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. A couple of years later a second car, the "Carlisle", was introduced into service. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waltersburg
''Waltersburg'' is a heavyweight Pullman sleeping car named for a city in Western Pennsylvania. The unit was built by the Pullman Company in 1924 as 12-section 1-drawing room heavyweight sleeper (colloquially a “12-1”). The car featured open sections with fold-down upper berths and lower berths made by folding the seats down in each section, and a drawing room — a large enclosed room with three berths and its own toilet and sink. ''Waltersburg'' was one of 71 cars built on Lot 4762, all to Plan 3410. It was fitted with mechanical air-conditioning in June 1935, and redesignaled Plan 3410A. As a consequence of the Pullman antitrust action, the car was sold to the Pennsylvania Railroad in 1948 as PRR 8968, ''Waltersburg'', and leased back to Pullman. It was renamed ''J. Finley Wilson'' in December 1952. The Pullman lease was terminated in May 1957 . The unit went to the Long Island Rail Road around 1957, where it was operated as private commuter club car. Upon retire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pullman Company
The Pullman Company, founded by George Pullman, was a manufacturer of railroad cars in the mid-to-late 19th century through the first half of the 20th century, during the boom of railroads in the United States. Through rapid late-19th century development of mass production and takeover of rivals, the company developed a virtual monopoly on production and ownership of sleeper cars. During a severe economic downturn, the 1894 Pullman Strike by company workers proved a transforming moment in American labor history. At the company's peak in the early 20th century, its cars accommodated 26 million people a year, and it in effect operated "the largest hotel in the world". Its production workers initially lived in a planned worker community (or "company town") named Pullman, Chicago. Pullman developed the sleeping car, which carried his name into the 1980s. Pullman did not just manufacture the cars, it also operated them on most of the railroads in the United States, paying rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baggage Car
A passenger railroad car or passenger car (United States), also called a passenger carriage, passenger coach (United Kingdom and International Union of Railways), or passenger bogie (India) is a railroad car that is designed to carry passengers. The term ''passenger car'' can also be associated with a sleeping car, a baggage car, a dining car, railway post office and prisoner transport cars. The first passenger cars were built in the early 1800s with the advent of the first railroads, and were small and little more than converted freight cars. Early passenger cars were constructed from wood; in the 1900s construction shifted to steel and later aluminum for improved strength. Passenger cars have increased greatly in size from their earliest versions, with modern bi-level passenger cars capable of carrying over 100 passengers. Amenities for passengers have also improved over time, with developments such as lighting, heating, and air conditioning added for improved passenge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
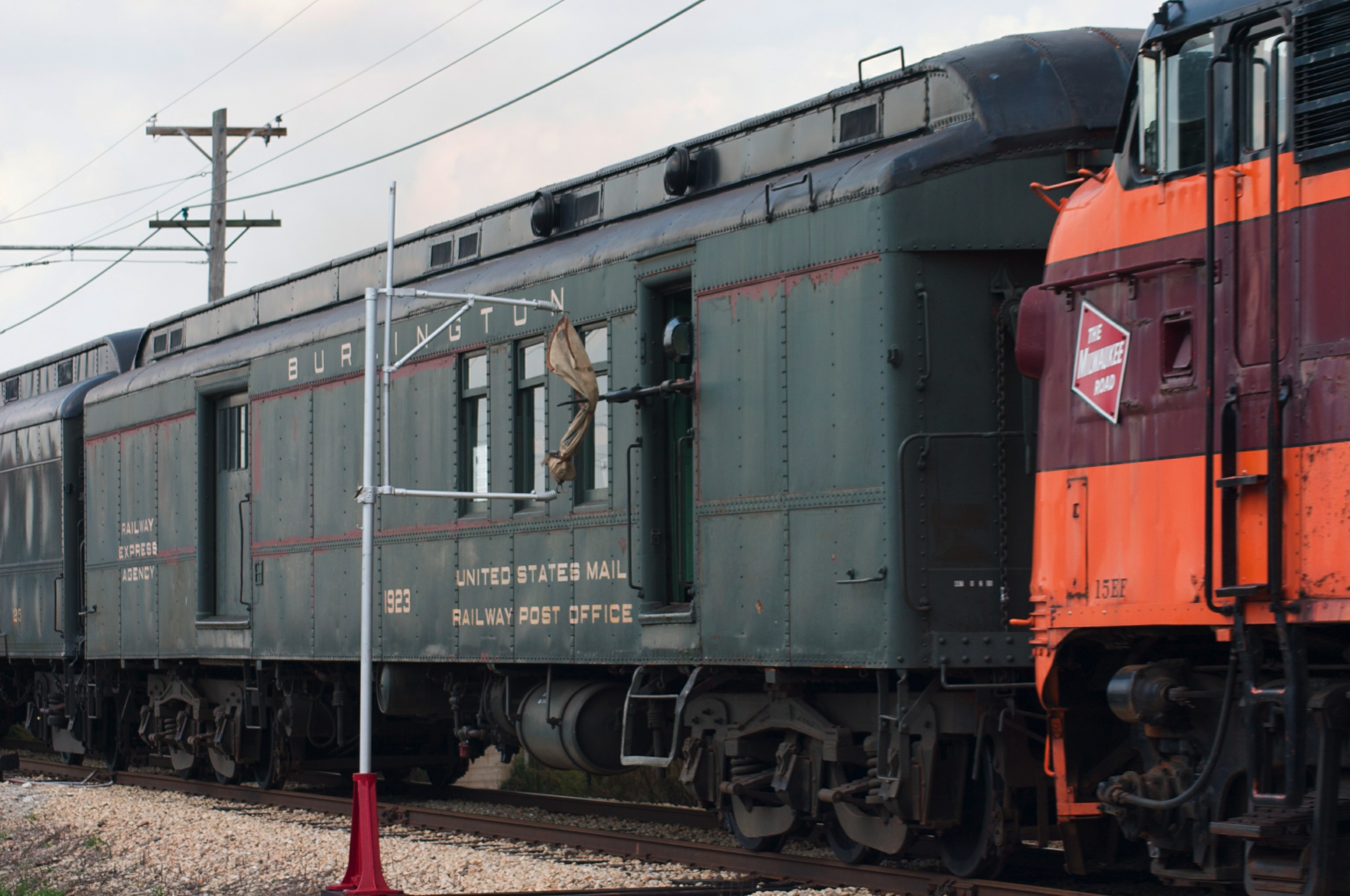
Railway Post Office
In Canada and the United States, a railway post office, commonly abbreviated as RPO, was a railroad car that was normally operated in passenger service as a means to sort mail en route, in order to speed delivery. The RPO was staffed by highly trained Railway Mail Service postal clerks, and was off-limits to the passengers on the train. In the UK and Ireland, the equivalent term was travelling post office (TPO). From the middle of the 19th century, many American railroads earned substantial revenues through contracts with the U.S. Post Office Department (USPOD) to carry mail aboard high-speed passenger trains; and the Railway Mail Service enforced various standardized designs on RPOs. In fact, a number of companies maintained passenger routes where the financial losses from moving people were more than offset by transporting the mail. History The world's first official carriage of mail by rail was by the United Kingdom's General Post Office in November 1830, using adapted rail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EMD E8
The E8 is a , A1A-A1A passenger-train locomotive built by General Motors' Electro-Motive Division (EMD) of La Grange, Illinois. A total of 450 cab versions, or E8As, were built from August 1949 to January 1954, 447 for the U.S. and 3 for Canada. 46 E8Bs were built from December 1949 to January 1954, all for the U.S. The 2,250 hp came from two 12 cylinder model 567B engines, each driving a generator to power the two traction motors on one truck. The E8 was the ninth model in the line of passenger diesels of similar design known as EMD E-units. Starting in September 1953, a total of 21 E8As were built which used either the 567BC or 567C engines. In profile the front of the nose of E7, E8, and E9 units is less slanted than earlier EMD units, and E7/8/9s (and their four axle cousins, the F-unit series) have been nicknamed " bulldog nose" units. Earlier E-unit locomotives were nicknamed "slant nose" units. After passenger trains were canceled on the Erie Lackawanna in 1970 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
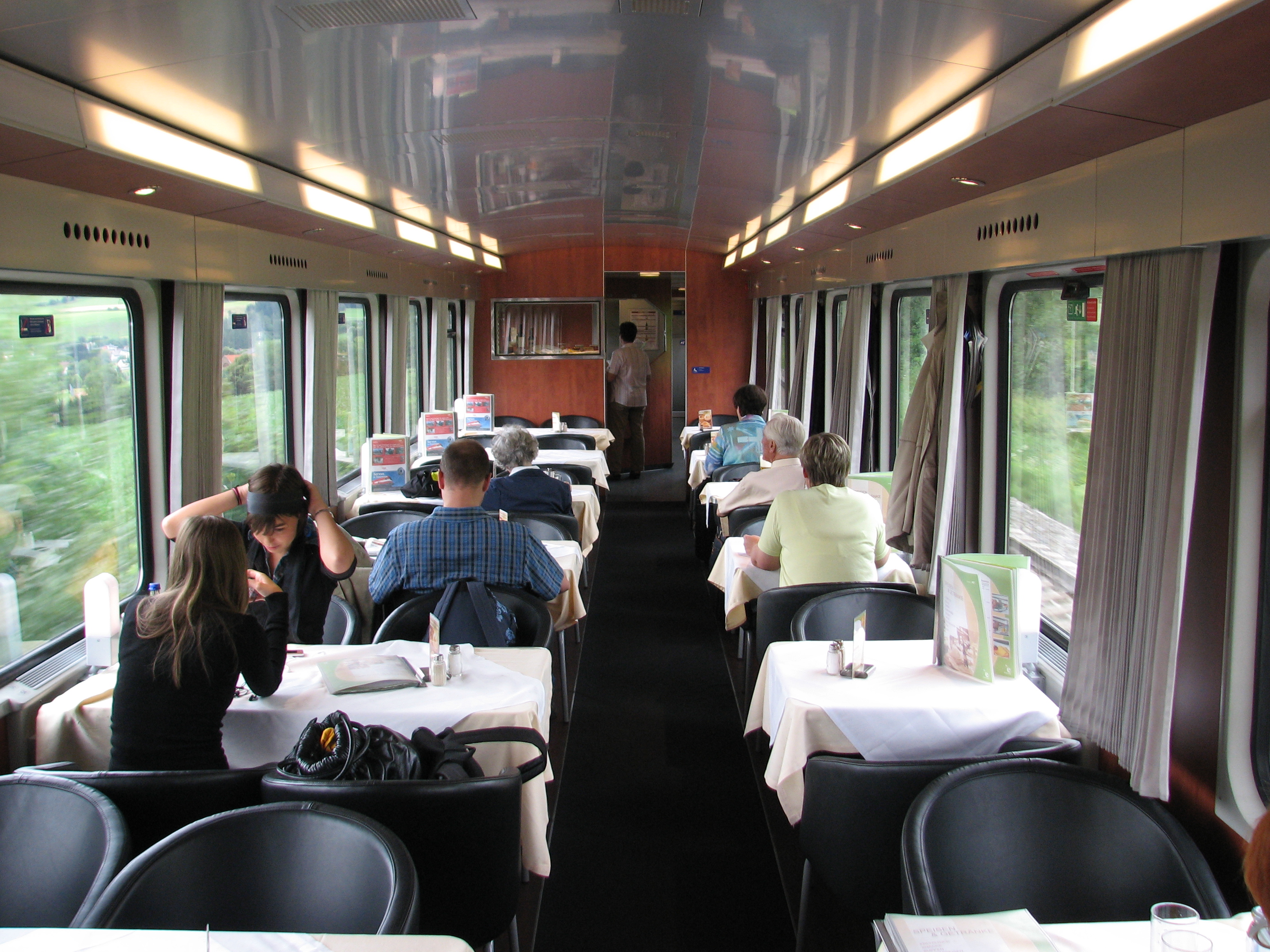
Dining Car
A dining car (American English) or a restaurant car (British English), also a diner, is a railroad passenger car that serves meals in the manner of a full-service, sit-down restaurant. It is distinct from other railroad food service cars that do not duplicate the full-service restaurant experience, such as buffet cars, cars in which one purchases food from a walk-up counter to be consumed either within the car or elsewhere in the train. Grill cars, in which customers sit on stools at a counter and purchase and consume food cooked on a grill behind the counter are generally considered to be an "intermediate" type of dining car. History United States Before dining cars in passenger trains were common in the United States, a rail passenger's option for meal service in transit was to patronize one of the roadhouses often located near the railroad's "water stops". Fare typically consisted of rancid meat, cold beans, and old coffee. Such poor conditions discouraged many from makin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |