|
Joseph Favre
Joseph Favre (; 17 February 1849 – 17 February 1903) was a famously skilled Swiss chef who worked in Switzerland, France, Germany, and England. Although he initially only received primary education because of his humble origins, as an adult he audited science and nutrition classes at the University of Geneva, and would eventually publish his four-volume , an encyclopedia of culinary science, in 1895. As a young man, he enlisted in Giuseppe Garibaldi's army during the Franco-Prussian War and became an anarchist and a member of the International Workingmen's Association (IWA), also known as the First International. He founded and wrote for various left-wing journals and a magazine for chefs, and also sponsored cooking competitions and exhibitions and launched a chefs' trade union. He would come to favour a more moderate socialism and, like other members of the IWA in Switzerland, eventually rejected anarchism, though he remained active in radical politics. The Bishop of Orléa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vex, Switzerland
Vex is a municipality and capital of the district of Hérens in the canton of Valais in Switzerland. Geography Vex has an area, , of . Of this area, or 32.1% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 47.5% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 13.2% is settled (buildings or roads), or 0.5% is either rivers or lakes and or 6.7% is unproductive land.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data Retrieved 25 March 2010 Of the built up area, housing and buildings made up 7.2% and transportation infrastructure made up 4.8%. Out of the forested land, 38.6% of the total land area is heavily forested and 7.7% is covered with orchards or small clusters of trees. Of the agricultural land, 0.2% is used for growing crops and 18.3% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considered fundamental principles of liberal democracy, while phrases like ''liberté, égalité, fraternité'' reappeared in other revolts, such as the 1917 Russian Revolution, and inspired campaigns for the abolition of slavery and universal suffrage. The values and institutions it created dominate French politics to this day. Its causes are generally agreed to be a combination of social, political and economic factors, which the ''Ancien Régime'' proved unable to manage. In May 1789, widespread social distress led to the convocation of the Estates General, which was converted into a National Assembly in June. Continuing unrest culminated in the Storming of the Bastille on 14 July, which led to a series of radical measures by the Assembly, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
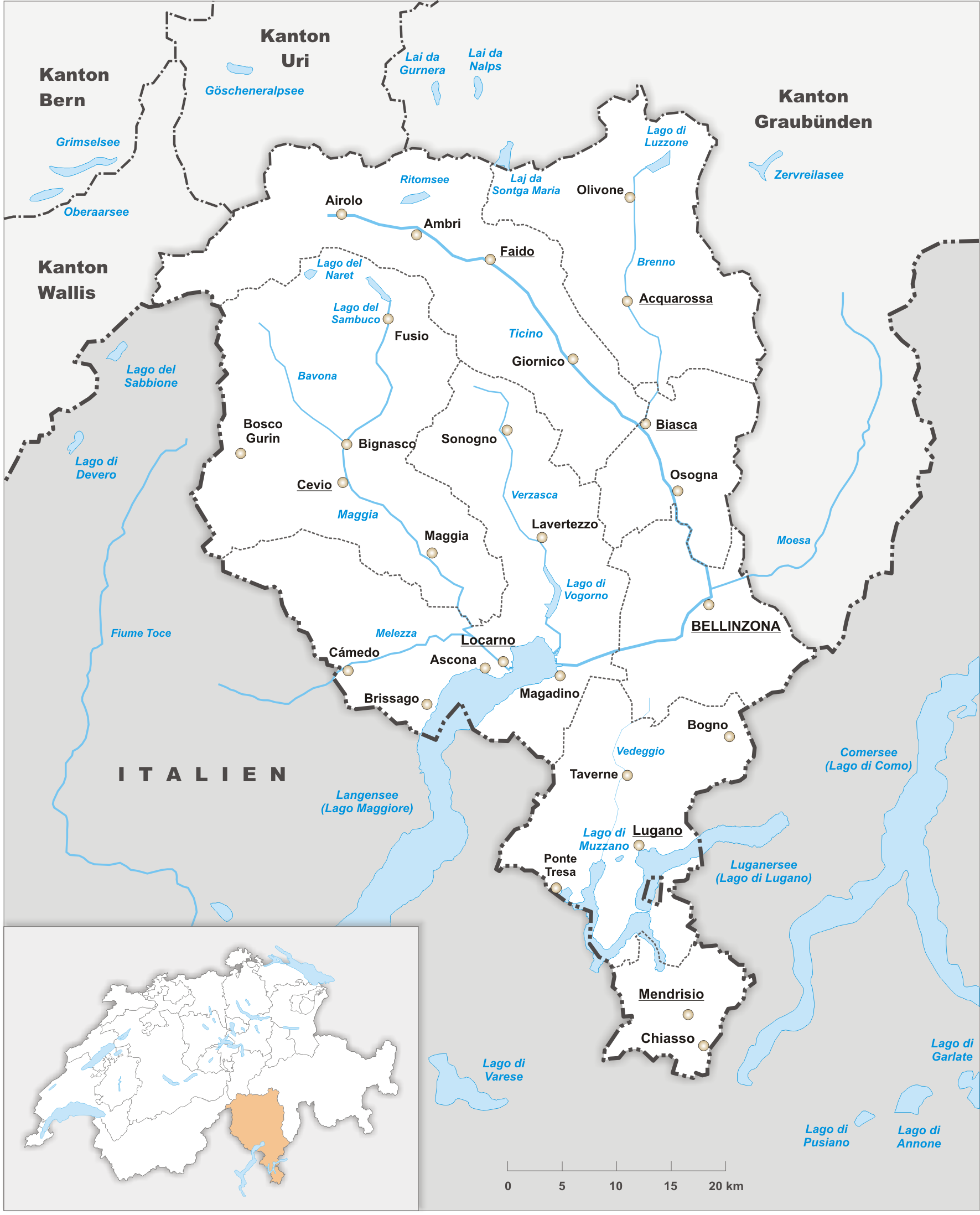
Ticino
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts and its capital city is Bellinzona. It is also traditionally divided into the Sopraceneri and the Sottoceneri, respectively north and south of Monte Ceneri. Red and blue are the colours of its flag. Ticino is the southernmost canton of Switzerland. It is one of the three large southern Alpine cantons, along with Valais and the Grisons. However, unlike all other cantons, it lies almost entirely south of the Alps, and has no natural access to the Swiss Plateau. Through the main crest of the Gotthard and adjacent mountain ranges, it borders the canton of Valais to the northwest, the canton of Uri to the north and the canton of Grisons to the northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lugano
Lugano (, , ; lmo, label=Ticinese dialect, Ticinese, Lugan ) is a city and municipality in Switzerland, part of the Lugano District in the canton of Ticino. It is the largest city of both Ticino and the Italian-speaking southern Switzerland. Lugano has a population () of , and an urban agglomeration of over 150,000. It is the List of cities in Switzerland, ninth largest Swiss city. The city lies on Lake Lugano, at its largest width, and, together with the adjacent town of Paradiso, Switzerland, Paradiso, occupies the entire bay of Lugano. The territory of the municipality encompasses a much larger region on both sides of the lake, with numerous isolated villages. The region of Lugano is surrounded by the Lugano Prealps, the latter extending on most of the Sottoceneri region, the southernmost part of Ticino and Switzerland. Both western and eastern parts of the municipality share an international border with Italy. Described as a market town since 984, Lugano was the object of con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vevey
Vevey (; frp, Vevê; german: label=former German, Vivis) is a town in Switzerland in the canton of Vaud, on the north shore of Lake Geneva, near Lausanne. The German name Vivis is no longer commonly used. It was the seat of the district of the same name until 2006, and is now part of the Riviera-Pays-d'Enhaut District. It is part of the French-speaking area of Switzerland. Vevey is home to the world headquarters of the international food and beverage company Nestlé, founded here in 1867. Milk chocolate was invented in Vevey by Daniel Peter in 1875, with the aid of Henri Nestlé. The English actor and comedian Charlie Chaplin resided in Vevey from 1952 until his death in 1977. History A piloti settlement existed here as early as the 2nd millennium BC. Under Rome, it was known as Viviscus or ''Vibiscum''. It was mentioned for the first time by the ancient Greek astronomer and philosopher Ptolemy, who gave it the name Ouikos. In the Middle Ages it was a station on the Via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clarens, Switzerland
Clarens-Montreux or Clarens is a neighborhood in the municipality of Montreux, in the canton of Vaud, in Switzerland. This neighborhood is the biggest and most populated of the city of Montreux. Clarens was made famous throughout Europe by the immense success of the book '' La Nouvelle Héloïse'' by Jean-Jacques Rousseau. Notable people ; Lived in Clarens * Élisée Reclus (1830–1905), renowned French geographer, writer and anarchist; resided in Clarens from 1872 * Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky (1840–1893), the Russian composer of the Romantic period, wrote his Violin Concerto in Clarens in 1878; it is one of the best known violin concertos ever written. * Igor Stravinsky (1882–1971), the Russian composer, lived in Clarens during the summers of 1910 to 1915. He composed his ballets ''The Rite of Spring'' and ''Pulcinella'' here. ; Died in Clarens * David Urquhart (1805–1877), Scottish diplomat, writer and politician, MP for Stafford 1847 to 1852, introduced the Turkish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustave Courbet
Jean Désiré Gustave Courbet ( , , ; 10 June 1819 – 31 December 1877) was a French painter who led the Realism movement in 19th-century French painting. Committed to painting only what he could see, he rejected academic convention and the Romanticism of the previous generation of visual artists. His independence set an example that was important to later artists, such as the Impressionists and the Cubists. Courbet occupies an important place in 19th-century French painting as an innovator and as an artist willing to make bold social statements through his work. Courbet's paintings of the late 1840s and early 1850s brought him his first recognition. They challenged convention by depicting unidealized peasants and workers, often on a grand scale traditionally reserved for paintings of religious or historical subjects. Courbet's subsequent paintings were mostly of a less overtly political character: landscapes, seascapes, hunting scenes, nudes, and still lifes. Courbet, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Guesde
Jules Bazile, known as Jules Guesde (; 11 November 1845 – 28 July 1922) was a French socialist journalist and politician. Guesde was the inspiration for a famous quotation by Karl Marx. Shortly before Marx died in 1883, he wrote a letter to Guesde and Paul Lafargue, both of whom already claimed to represent "Marxist" principles. Marx accused them of "revolutionary phrase-mongering". This exchange is the source of Marx's remark, reported by Friedrich Engels: "''ce qu'il y a de certain c'est que moi, je ne suis pas marxiste''" ("what is certain is that f they are Marxists henI myself am not a Marxist"). Biography Early years Jules Bazile was born in Paris, on the Ile-St-Louis. He began his career as a clerk in the Interior Ministry. He wrote in republican newspapers under the Second Empire and chose "Jules Guesde" as a pen name after his mother's name, Eléonore Guesde. On the outbreak of the Franco-Prussian War, he was editing ''Les Droits de l'Homme'' at Montpellier, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Arnould
Arthur Arnould (17 April 1833, Dieuze - 26 November 1895) was a French writer, and journalist. He wrote under the pen name ''Arthur Matthey''. He was a member of the Hermetic Brotherhood of Luxor and the Theosophical Society. He married the widowed painter Delphine de Cool in 1890. He is listed in the French dictionary of anarchists. in the ''Dictionnaire des anarchistes'' References External links * * :s:fr:Auteur:Arthur Arnould - on French |
Élisée Reclus
Jacques Élisée Reclus (; 15 March 18304 July 1905) was a French geographer, writer and anarchist. He produced his 19-volume masterwork, ''La Nouvelle Géographie universelle, la terre et les hommes'' ("Universal Geography"), over a period of nearly 20 years (1875–1894). In 1892 he was awarded the Gold Medal of the Société de Géographie, Paris Geographical Society for this work, despite having been banished from France because of his political activism. Biography Reclus was born at Sainte-Foy-la-Grande (Gironde). He was the second son of a Protestant pastor and his wife. From the family of fourteen children, several brothers, including fellow geographers Onésime Reclus, Onésime and Élie Reclus, went on to achieve renown either as Intellectual#Man of Letters, men of letters, politicians or members of the learned professions. Reclus began his education in Rhenish Prussia, and continued higher studies at the Protestant college of Montauban. He completed his studies at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Vosges
The Army of the Vosges (french: Armée des Vosges) was a volunteer force placed under the command of Giuseppe Garibaldi, formed in order to ensure the defense of the road to Lyon from the Prussian Army during the Franco-Prussian war. Background Garibaldi had led volunteer forces with great success during the unification of Italy, and had also fought in South America. He had a worldwide reputation as a liberal revolutionary. Most Italians including Garibaldi had supported Prussia against France in this war. However, after Napoleon III was defeated and the French Third Republic was proclaimed, and Bismarck demanded the cession of Alsace, Italian opinion reversed completely. This was best exemplified by the reaction of Garibaldi, who told the ''Movimento'' of Genoa on 7 September 1870 that ''"Yesterday I said to you: war to the death to Bonaparte. Today I say to you: rescue the French Republic by every means."'' Subsequently, Garibaldi wrote a letter to the government of the new r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
_-_WGA05486.jpg)

