|
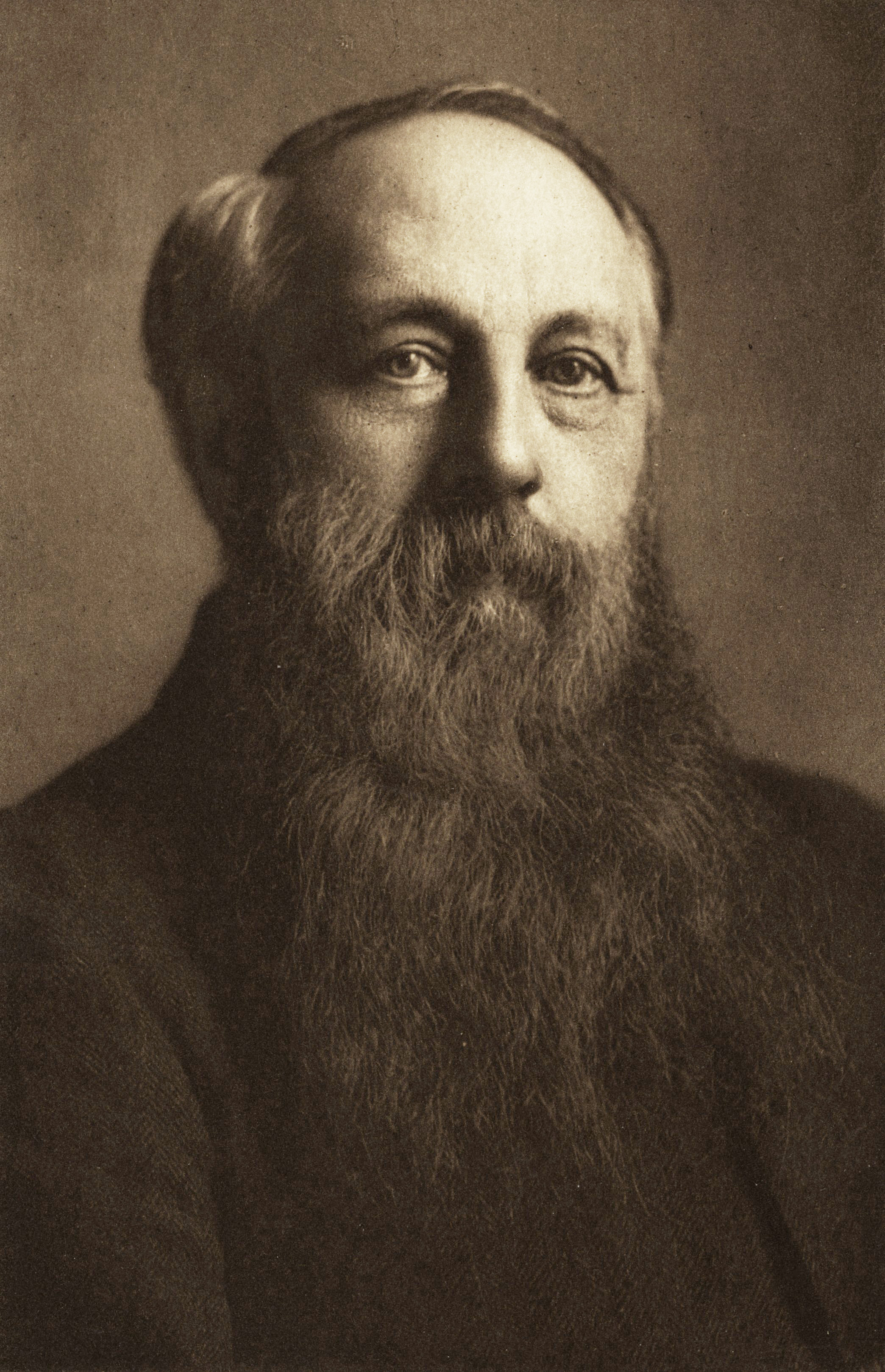
John Stuart Stuart-Glennie
John Stuart Stuart-Glennie (1841–1910) was a Scottish barrister, folklorist, philosopher, founding sociologist, and socialist. Life He was the son of Alexander Glennie of Maybank Aberdeen; John Stuart of Inchbreck was his maternal grandfather He was educated in law at the University of Aberdeen and University of Bonn and was called to the bar at the Middle Temple. Stuart-Glennie later left the law and travelled in Europe and Asia to collect folklore. He wrote a series of books and numerous articles, developing a broad philosophy of history. He also contributed to the Folklore Society. His ideas were ahead of the time. Views and associations Eugene Halton has claimed that Stuart-Glennie’s most significant idea was his theory, first published in 1873, of what he termed "the moral revolution", delineating deep changes across different civilizations in the period 2,500 years ago, roughly centered around 600-500 BCE. It formed the second stage of his three stage "Ultimate Law ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folklorist
Folklore studies, less often known as folkloristics, and occasionally tradition studies or folk life studies in the United Kingdom, is the branch of anthropology devoted to the study of folklore. This term, along with its synonyms, gained currency in the 1950s to distinguish the academic study of traditional culture from the Cultural artifact, folklore artifacts themselves. It became established as a field across both Europe and North America, coordinating with ''Volkskunde'' (German language, German), ''folkeminner'' (Norwegian language, Norwegian), and ''folkminnen'' (Swedish language, Swedish), among others. Overview The importance of folklore and folklore studies was recognized globally in 1982 in the UNESCO document "Recommendation on the Safeguarding of Traditional Culture and Folklore". UNESCO again in 2003 published a Convention for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage. Parallel to these global statements, the American Folklife Preservation Act (P.L. 94-20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Mackinnon Robertson
John Mackinnon Robertson (14 November 1856 – 5 January 1933) was a prolific Scottish journalist, advocate of rationalism and secularism, and Liberal Member of Parliament for Tyneside from 1906 to 1918. Robertson was best known as an advocate of the Christ myth theory. Biography Robertson was born in Brodick on the Isle of Arran; his father moved the family to Stirling while he was still young, and he attended school there until the age of 13. He worked first as a clerk and then as a journalist, eventually becoming assistant editor of the ''Edinburgh Evening News''. He wrote in February 1906 to a friend that he "gave up the 'divine'" when he was a teenager. His first contact with the freethought movement was a lecture by Charles Bradlaugh in Edinburgh in 1878. Robertson became active in the Edinburgh Secular Society, soon after. It was through the Edinburgh Secular Society that he met William Archer and became writer for the ''Edinburgh Evening News''. He eventually mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurence Gomme
Sir George Laurence Gomme, FSA (18 December 1853 – 23 February 1916) was a public servant and leading British folklorist. He helped found both the Victoria County History and the Folklore Society. He also had an interest in old buildings and persuaded the London County Council to take up the blue plaque commemorative scheme. Life Gomme was born in the London district of Stepney, the second of ten children of William Laurence Gomme (1828–1887), an engineer, and his wife Mary (1831–1921). He attended the City of London School to the age of sixteen, when he started work, first with a railway company, then with the Fulham board of works, finally, in 1873, with the Metropolitan Board of Works: he remained with it and its successor, the London County Council, until his retirement in 1914. His position as statistical officer, from 1893, and then as clerk to the council, from 1900, gave him a major role in policy and administration. His interests included folklore and history. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrew Lang
Andrew Lang (31 March 1844 – 20 July 1912) was a Scottish poet, novelist, literary critic, and contributor to the field of anthropology. He is best known as a collector of folk and fairy tales. The Andrew Lang lectures at the University of St Andrews are named after him. Biography Lang was born in 1844 in Selkirk, Scottish Borders. He was the eldest of the eight children born to John Lang, the town clerk of Selkirk, and his wife Jane Plenderleath Sellar, who was the daughter of Patrick Sellar, factor to the first Duke of Sutherland. On 17 April 1875, he married Leonora Blanche Alleyne, youngest daughter of C. T. Alleyne of Clifton and Barbados. She was (or should have been) variously credited as author, collaborator, or translator of '' Lang's Color/Rainbow Fairy Books'' which he edited. He was educated at Selkirk Grammar School, Loretto School, and the Edinburgh Academy, as well as the University of St Andrews and Balliol College, Oxford, where he took a first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edwin Sidney Hartland
Edwin Sidney Hartland (1848–1927) was an author of works on folklore. His works include anthologies of tales, and theories on anthropology and mythology with an ethnological perspective. He believed that the assembling and study of persistent and widespread folklore provided a scientific insight into custom and belief. Hartland was president of the Folklore Society, 1899–1901, and contributed to its journal ''Folk-Lore''; his earlier contributions included a dispute with Andrew Lang. Hartland was born in Islington, eventually making his career as a solicitor in Swansea Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea ( cy, links=no, Dinas a Sir Abertawe). The city is the twenty-fifth largest in .... His father, E. J. Hartland, was a congregational minister. Throughout his life he served in many judicial positions and on public committees in Swansea and at G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Burnett Tylor
Sir Edward Burnett Tylor (2 October 18322 January 1917) was an English anthropologist, and professor of anthropology. Tylor's ideas typify 19th-century cultural evolutionism. In his works '' Primitive Culture'' (1871) and ''Anthropology'' (1881), he defined the context of the scientific study of anthropology, based on the evolutionary theories of Charles Lyell. He believed that there was a functional basis for the development of society and religion, which he determined was universal. Tylor maintained that all societies passed through three basic stages of development: from savagery, through barbarism to civilization. Tylor is a founding figure of the science of social anthropology, and his scholarly works helped to build the discipline of anthropology in the nineteenth century.Paul Bohannan, ''Social Anthropology'' (New York: Holt, Rinehart & Winston, 1969) He believed that "research into the history and prehistory of man ..could be used as a basis for the reform of Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrick Geddes
Sir Patrick Geddes (2 October 1854 – 17 April 1932) was a British biologist, sociologist, Comtean positivist, geographer, philanthropist and pioneering town planner. He is known for his innovative thinking in the fields of urban planning and sociology. Following the philosophies of Auguste Comte and Frederic LePlay, he introduced the concept of "region" to architecture and planning and coined the term "conurbation". Later, he elaborated "neotechnics" as the way of remaking a world apart from over-commercialization and money dominance. An energetic Francophile, Geddes was the founder in 1924 of the Collège des Écossais (Scots College), an international teaching establishment in Montpellier, France, and in the 1920s he bought the Château d'Assas to set up a centre for urban studies. Biography The son of Janet Stevenson and soldier Alexander Geddes, Patrick Geddes was born in Ballater, Aberdeenshire, and educated at Perth Academy. He studied at the Royal College ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabian Society
The Fabian Society is a British socialist organisation whose purpose is to advance the principles of social democracy and democratic socialism via gradualist and reformist effort in democracies, rather than by revolutionary overthrow. The Fabian Society was also historically related to radicalism, a left-wing liberal tradition. As one of the founding organisations of the Labour Representation Committee in 1900, and as an important influence upon the Labour Party which grew from it, the Fabian Society has had a powerful influence on British politics. Members of the Fabian Society have included political leaders from other countries, such as Jawaharlal Nehru, who adopted Fabian principles as part of their own political ideologies. The Fabian Society founded the London School of Economics in 1895. Today, the society functions primarily as a think tank and is one of twenty socialist societies affiliated with the Labour Party. Similar societies exist in Australia (the Australi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Democratic Federation
The Social Democratic Federation (SDF) was established as Britain's first organised socialist political party by H. M. Hyndman, and had its first meeting on 7 June 1881. Those joining the SDF included William Morris, George Lansbury, James Connolly and Eleanor Marx. However, Friedrich Engels, Karl Marx's long-term collaborator, refused to support Hyndman's venture. Many of its early leading members had previously been active in the Manhood Suffrage League. The SDF battled through defections of its right and left wings to other organisations in the first decade of the twentieth century before uniting with other radical groups in the Marxist British Socialist Party from 1911 until 1920. Organizational history Origins and early years The British Marxist movement effectively began in 1880 when a businessman named Henry M. Hyndman read Karl Marx's ''Communist Manifesto'' in French translation while crossing to America. Upon his return to London, Hyndman sought out Marx, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annie Besant
Annie Besant ( Wood; 1 October 1847 – 20 September 1933) was a British socialist, theosophist, freemason, women's rights activist, educationist, writer, orator, political party member and philanthropist. Regarded as a champion of human freedom, she was an ardent supporter of both Irish and Indian self-rule. She was also a prolific author with over three hundred books and pamphlets to her credit. As an educationist, her contributions included being one of the founders of the Banaras Hindu University. For fifteen years, Besant was a public proponent in England of atheism and scientific materialism. Besant's goal was to provide employment, better living conditions, and proper education for the poor. Besant then became a prominent speaker for the National Secular Society (NSS), as well as a writer, and a close friend of Charles Bradlaugh. In 1877 they were prosecuted for publishing a book by birth control campaigner Charles Knowlton. The scandal made them famous, and Bradla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trafalgar Square
Trafalgar Square ( ) is a public square in the City of Westminster, Central London, laid out in the early 19th century around the area formerly known as Charing Cross. At its centre is a high column bearing a statue of Admiral Nelson commemorating the victory at the Battle of Trafalgar. The battle of 21 October 1805, established the British navy's dominance at sea in the Napoleonic Wars over the fleets of France and Spain. The site around Trafalgar Square had been a significant landmark since the 1200s. For centuries, distances measured from Charing Cross have served as location markers. The site of the present square formerly contained the elaborately designed, enclosed courtyard of the King's Mews. After George IV moved the mews to Buckingham Palace, the area was redeveloped by John Nash, but progress was slow after his death, and the square did not open until 1844. The Nelson's Column at its centre is guarded by four lion statues. A number of commemorative statues and sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jane Wilde
Jane Francesca Agnes, Lady Wilde (née Elgee; 27 December 1821 – 3 February 1896) was an Irish poet under the pen name Speranza and supporter of the nationalist movement. Lady Wilde had a special interest in Irish folktales, which she helped to gather and was the mother of Oscar Wilde and Willie Wilde. Personal life Jane was the last of the four children of Charles Elgee (1783–1824), the son of Archdeacon John Elgee, a Wexford solicitor, and his wife Sarah (née Kingsbury, d. 1851). Her father died when she was three years old which meant she was largely self-educated. Even so, she is said to have mastered 10 languages by the age of 18. She claimed that her great-grandfather was an Italian who had come to Wexford in the 18th century; in fact, the Elgees descended from Durham labourers. On 12 November 1851 she married Sir William Wilde, an eye and ear surgeon (and also a researcher of folklore), in St. Peter's church in Dublin, and they had three children: William Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)