|
John Stewart Of Methven
Sir John Stewart of Methven (died 1628) was governor of Dumbarton Castle and Admiral of the Western Seas Family and marriage Sir John Stewart of Methven was an illegitimate son of Ludovic Stewart, 2nd Duke of Lennox. Stewart married Margaret Hamilton, a daughter of Sir Claud Hamilton of Shawfield, Rutherglen, and Illieston (d. 1614). He was made keeper of Dumbarton Castle in 1620, the position was in the gift of the Lennox family. Life Prisoners Margaret was a Catholic, and she was converted from her Catholicism by a prisoner in the castle, Alexander Simpson (1570-1639), minister of Dryburgh and Merton, in 1621. John Stewart was said to have treated Simpson and another minister, Andrew Duncan, very courteously and paid for their food and lodging. Prisoners at Dumbarton were usually expected to pay for their food. Garrison at Dumbarton, duties unfulfilled In 1625, Sir John Stewart of Methven undertook to have 16 "fensible men in ordinary" in the castle, as a garrison to keep wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
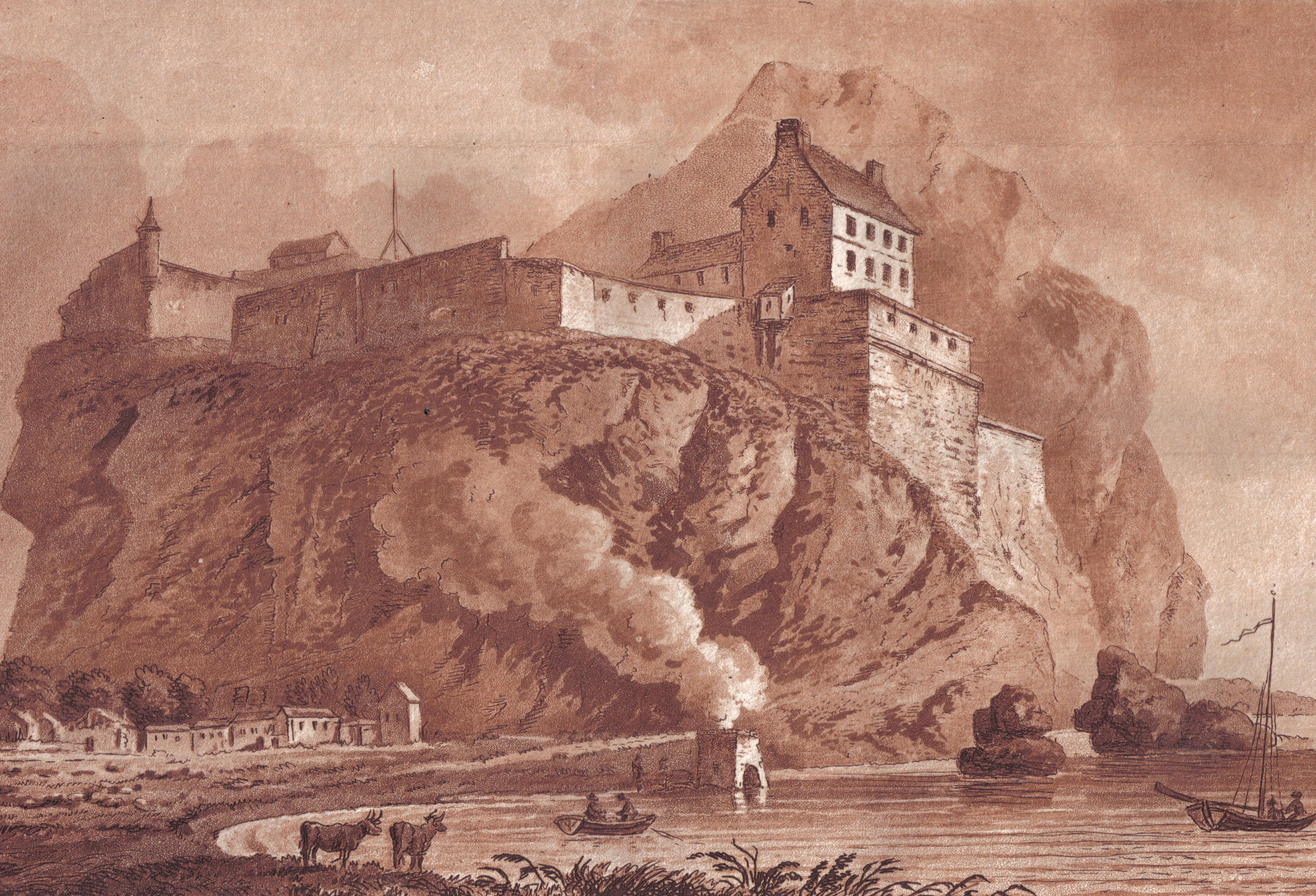
Dumbarton Castle
Dumbarton Castle ( gd, Dùn Breatainn, ; ) has the longest recorded history of any stronghold in Scotland. It sits on a volcanic plug of basalt known as Dumbarton Rock which is high and overlooks the Scottish town of Dumbarton. History Dumbarton Rock was formed between 330 and 340 million years ago, during the Early Carboniferous period, a time of widespread volcanic activity in the area where Glasgow is now situated; over time, the softer exterior of the volcano weathered away, leaving behind a volcanic plug of basalt. Iron Age At least as far back as the Iron Age, this has been the site of a strategically important settlement, as evidenced by archaeological finds. The people that came to reside there in the era of Roman Britain were known to have traded with the Romans. However the first written record about a settlement there was in a letter that Saint Patrick wrote to King Ceretic of Alt Clut in the late 5th century. Early Medieval era David Nash Ford has proposed tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludovic Stewart, 2nd Duke Of Lennox
Ludovic Stewart, 2nd Duke of Lennox and 1st Duke of Richmond (29 September 157416 February 1624), lord of the manor, lord of the Manor of Cobham, Kent, was a Scotland, Scottish nobleman who through their paternal lines was a second cousin of King James VI and I, James VI of Scotland and I of England. He was involved in the Plantation of Ulster in Ireland and the colonization of Maine in New England. Cape Elizabeth, Maine, Richmond's Island and Cape Richmond as well as Richmond, Maine (formerly Fort Richmond), are named after him. His magnificent monument with effigies survives in Westminster Abbey. Origins He was the eldest son of Esmé Stewart, 1st Duke of Lennox (1542-1583), a Frenchman of Scottish ancestry, by his wife Catherine de Balsac (d.post-1630), a daughter of Guillaume de Balsac, Sieur d'Entragues, by his wife Louise d'Humières. Ludovic's father was a favourite and first cousin once removed of King James VI and I, James VI of Scotland I of England (the King's f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claud Hamilton Of Shawfield
Sir Claud Hamilton of Shawfield, PC (Ire) (died 1614), also called of Leckprevick, a younger son of Claud Hamilton, 1st Lord Paisley in Scotland, was a gentleman of the privy chamber of King James VI and I, an undertaker in the Plantation of Ulster, and a privy counsellor in Ireland. Birth and origins Claud was born between 1575 and 1585, probably at Paisley, near Glasgow, Scotland, his parents' habitual residence. He was the third son of Claud Hamilton and his wife Margaret Seton. His father was at that time only a younger brother of James Hamilton, 3rd Earl of Arran but would later be created 1st Lord Paisley. His father's family descended from Walter FitzGilbert, the founder of the House of Hamilton, who had received the barony of Cadzow from Robert the Bruce. Claud's mother was a daughter of George Seton, 7th Lord Seton, by his wife Isobel Hamilton. Both parents were Scottish and seem to have been both Catholic. They had married in 1574 at Niddry Castle, West Lothia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
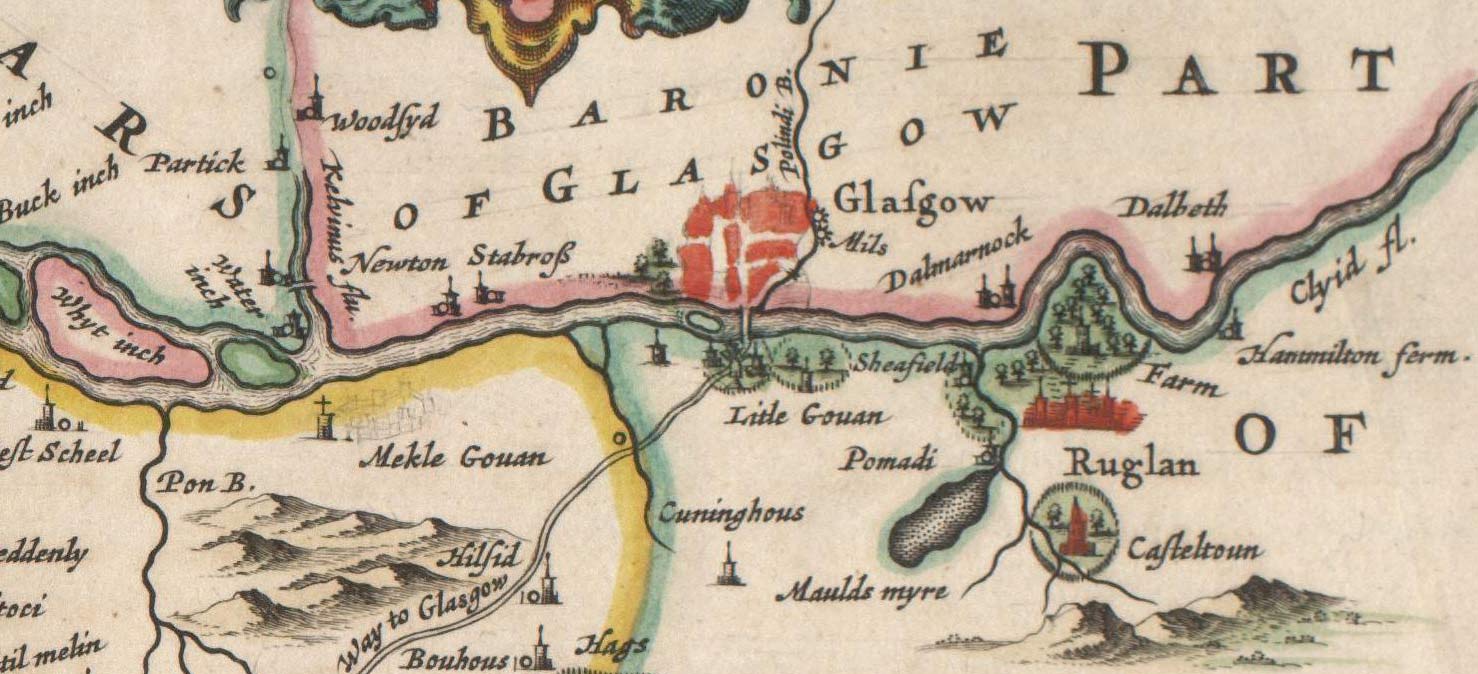
Shawfield
Shawfield is an industrial/commercial area of the Royal Burgh of Rutherglen in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, located to the north of the town centre. It is bordered to the east by the River Clyde, to the north by the Glasgow neighbourhood of Oatlands and the adjacent Richmond Park, to the south-west by Glasgow's Polmadie and Toryglen districts, and to the south-east by Rutherglen's historic Main Street and its Burnhill neighbourhood, although it is separated from these southerly areas by the West Coast Main Line railway tracks and the M74 motorway. A road bridge connects Shawfield to the Dalmarnock, Bridgeton and Glasgow Green areas. Shawfield is a familiar name to many Scottish sports fans, as the stadium of that name is the national venue for greyhound racing and the former home of Clyde F.C. Early history Documentation states that in 1611 the estate of Shawfield was in the hands of the family of Claud Hamilton. His grandson James Hamilton was forced to sell the estate and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutherglen
Rutherglen (, sco, Ruglen, gd, An Ruadh-Ghleann) is a town in South Lanarkshire, Scotland, immediately south-east of the city of Glasgow, from its centre and directly south of the River Clyde. Having existed as a Lanarkshire burgh in its own right for more than 800 years, in 1975 Rutherglen lost its own local council and administratively became a component of the City of Glasgow (1975–1996), City of Glasgow District within the Strathclyde Local government areas of Scotland 1973–96, region (along with neighbouring Cambuslang). In 1996 the towns were reallocated to the South Lanarkshire Subdivisions of Scotland, council area.From a pawnbrokers to Parliament - Tommy McAvoy looks back on a career that too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illieston House
Illieston House, also known as Illieston Castle, is a castle located in West Lothian, Scotland, by the River Almond near Broxburn. Description The castle is a T-plan design, 2 storeys tall, with an attic, slated roof, and an additional kitchen wing. It has gabled dormers, and a stair-tower on the south side. There is an additional 2nd stair-turret from the 2nd storey leading to a watch-chamber at the top of the main stair-tower. The modern interior includes four bedrooms and three reception rooms over three levels, plus a "turret room". The kitchen wing includes a separate laundry room and small lobby, beside a walled garden. History Origins to 18th century The Stewart kings James II and James IV are said to have had a hunting lodge at Illieston. The castle was built on the slopes of the River Almond some time around 1600 for a branch of the Hamilton family. It was acquired by John Ellis in 1663 or 1664, who added a gateway inscribed with his initials in 1665. The name Il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dryburgh
Dryburgh is a village in the Borders region of Scotland, within the county of Berwickshire. It is most famous for the ruined Dryburgh Abbey. Dryburgh Abbey Hotel lies on the edge of the village. The village K6 red telephone box outside the former post office is Category B listed. Dryburgh Abbey Dryburgh Abbey was founded in the 12th century, and burned by English troops in 1322, and again in 1385. It was restored in the 15th century, before being destroyed in 1544. The ruined site is now a scheduled monument, and its grounds are listed in the Inventory of Gardens and Designed Landscapes in Scotland. Orchard Gate Orchard Gate is a 19th century, Category B listed Gothic arched gateway. It has battlemented parapet and piers with incised crosses. The Temple of the Muses This circular nine columned gazebo stands since 1817 on Bass Hill, a mound overlooking the River Tweed at the west end of the village. It is dedicated to the poet James Thomson, the Ednam poet and author of " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
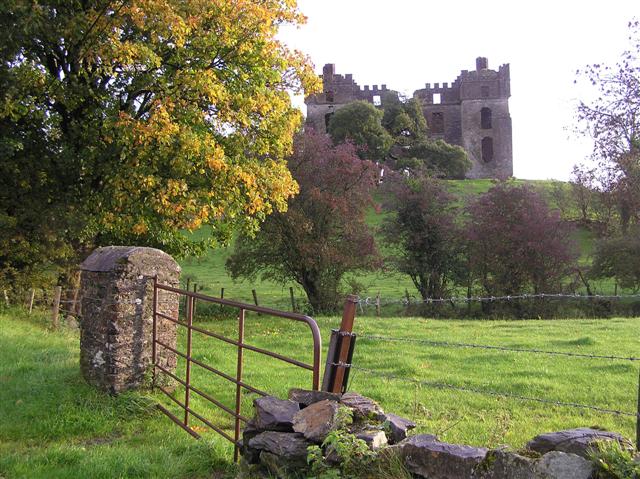
Mongavlin Castle
Mongavlin Castle also known as Mongevlin Castle is a ruined castle on the west bank of the River Foyle, approx 3 km south of St Johnston, County Donegal, Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It was once a stronghold of the O'Donnell dynasty, O'Donnell's, Lords of Tyrconnell. History In the sixteenth century Mongevlin was the chief residence of Ineen Dubh, who was the daughter of James MacDonald, 6th of Dunnyveg, and mother of Red Hugh O'Donnell. The State Paper recording her possession of the castle: ''" From Cul-Mac-Tryan runs a bogg three myles in length to the side of Lough Foyle in the midst of the bog is a standing loughe called Bunaber here at Bunaber dwells O'Donnell's mother (Ineen Dubh M'Donnell). Three miles above Cargan stands a fort called McGevyvelin (Mongivlin) upon the river of Lough Foyle O'Donnell's mother's chief house."'' When Ineen Dubh came to Ireland to marry Aodh mac Maghnusa Ó Domhnaill (Anglicized: Sir Hugh O'Donnell), she brought a force of 100 of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raphoe
Raphoe ( ; ) is a historical village in County Donegal, Ireland. It is the main town in the fertile district of East Donegal known as the Laggan, as well as giving its name to the Barony of Raphoe, which was later divided into the baronies of Raphoe North and Raphoe South, as well as to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Raphoe and the Church of Ireland (Anglican) Diocese of Derry and Raphoe. The Burn Dale (also known in English as the Burn Deele) is a ''burn (landform), burn'' (a small river) that flows a short distance to the south of Raphoe. The Burn Dale eventually flows, via the village of Ballindrait, into the River Foyle just north of Lifford. Name ''Raphoe'', historically ''Raffoe'',Placenames Database of Ireland (see archival records) comes from the Irish Language, Irish ''Ráth Bhoth'', which is made up of the words ''ráth'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantation Of Ulster
The Plantation of Ulster ( gle, Plandáil Uladh; Ulster-Scots: ''Plantin o Ulstèr'') was the organised colonisation (''plantation'') of Ulstera province of Irelandby people from Great Britain during the reign of King James I. Most of the settlers (or ''planters'') came from southern Scotland and northern England; their culture differed from that of the native Irish. Small privately funded plantations by wealthy landowners began in 1606, while the official plantation began in 1609. Most of the colonised land had been confiscated from the native Gaelic chiefs, several of whom had fled Ireland for mainland Europe in 1607 following the Nine Years' War against English rule. The official plantation comprised an estimated half a million acres (2,000 km2) of arable land in counties Armagh, Cavan, Fermanagh, Tyrone, Donegal, and Londonderry. Land in counties Antrim, Down, and Monaghan was privately colonised with the king's support. Among those involved in planning and ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privy Council Of Scotland
The Privy Council of Scotland ( — 1 May 1708) was a body that advised the Scottish monarch. In the range of its functions the council was often more important than the Estates in the running the country. Its registers include a wide range of material on the political, administrative, economic and social affairs of the Kingdom of Scotland. The council supervised the administration of the law, regulated trade and shipping, took emergency measures against the plague, granted licences to travel, administered oaths of allegiance, banished beggars and gypsies, dealt with witches, recusants, Covenanters and Jacobites and tackled the problem of lawlessness in the Highlands and the Borders. History Like the Parliament, the council was a development of the King's Council. The King's Council, or ''curia regis'', was the court of the monarch surrounded by his royal officers and others upon whom he relied for advice. It is known to have existed in the thirteenth century, if not earlier, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |