|
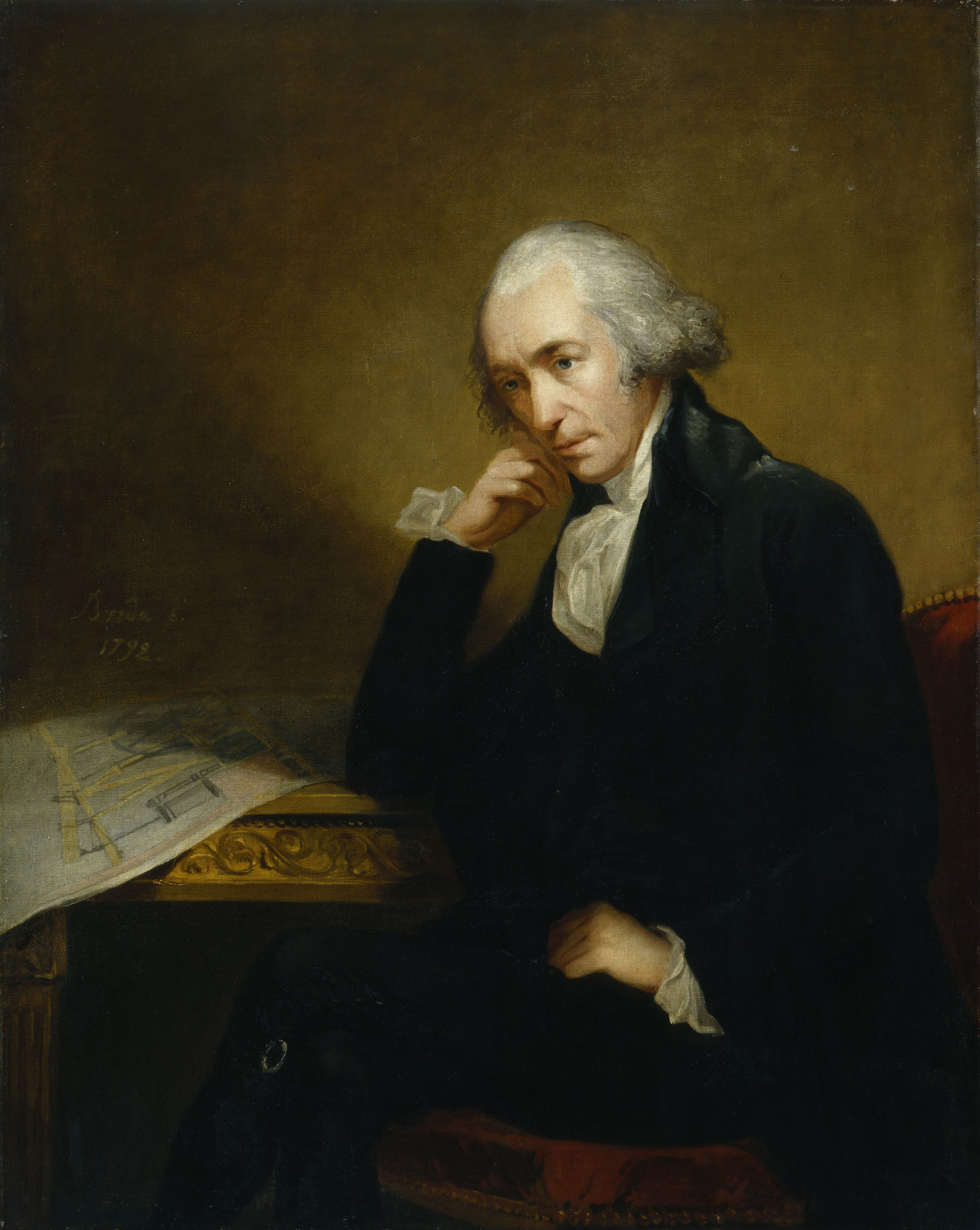
John Smeaton
John Smeaton (8 June 1724 – 28 October 1792) was a British civil engineer responsible for the design of bridges, canals, harbours and lighthouses. He was also a capable mechanical engineer and an eminent physicist. Smeaton was the first self-proclaimed "civil engineer", and is often regarded as the "father of civil engineering".Mark Denny (2007). "Ingenium: Five Machines That Changed the World". p. 34. JHU Press. He pioneered the use of hydraulic lime in concrete, using pebbles and powdered brick as aggregate. Smeaton was associated with the Lunar Society. Law and physics Smeaton was born in Austhorpe, Leeds, England. After studying at Leeds Grammar School he joined his father's law firm, but left to become a mathematical instrument maker (working with Henry Hindley), developing, among other instruments, a pyrometer to study material expansion. In 1750, his premises were in the Great Turnstile in Holborn. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1753 and in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eddystone Lighthouse
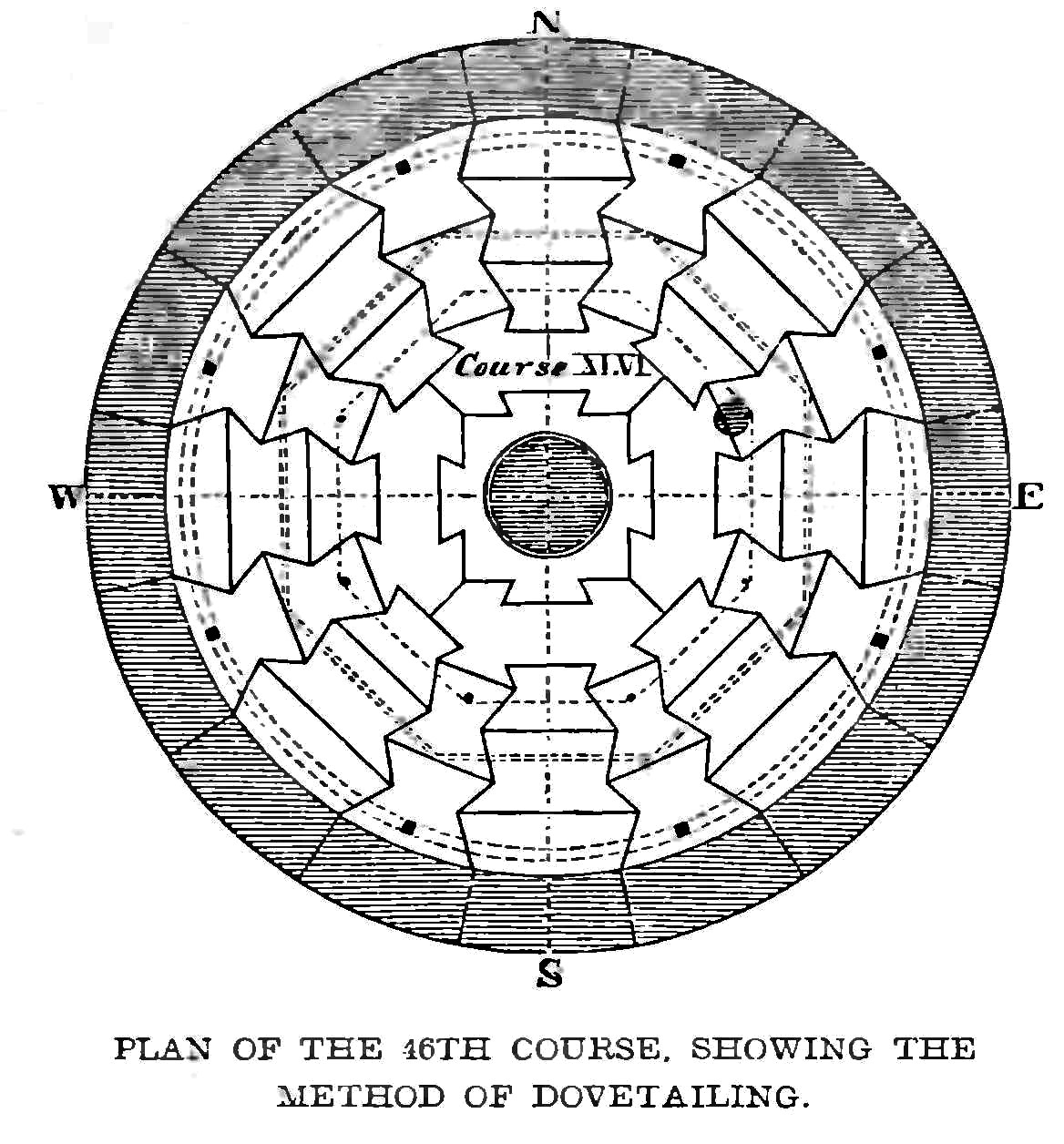
The Eddystone Lighthouse is a lighthouse that is located on the dangerous Eddystone Rocks, south of Rame Head in Cornwall, England. The rocks are submerged below the surface of the sea and are composed of Precambrian gneiss. View at 1:50000 scale The current structure is the fourth to be built on the site. The first lighthouse (Winstanley's) was swept away in a powerful storm, killing its architect and five other men in the process. The second (Rudyard's) stood for fifty years before it burned down. The third (Smeaton's) is renowned because of its influence on lighthouse design and its importance in the development of concrete for building; its upper portions were re-erected in Plymouth as a monument. The first lighthouse, completed in 1699, was the world's first open ocean lighthouse, although the Cordouan Lighthouse off the western French coast preceded it as the first offshore lighthouse. The need for a light The Eddystone Rocks are an extensive reef approximately 12 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrometer
A pyrometer is a type of remote-sensing thermometer used to measure the temperature of distant objects. Various forms of pyrometers have historically existed. In the modern usage, it is a device that from a distance determines the temperature of a surface from the amount of the thermal radiation it emits, a process known as pyrometry and sometimes radiometry. The word pyrometer comes from the Greek word for fire, "πῦρ" (''pyr''), and ''meter'', meaning to measure. The word pyrometer was originally coined to denote a device capable of measuring the temperature of an object by its incandescence, visible light emitted by a body which is at least red-hot. Modern pyrometers or infrared thermometers also measure the temperature of cooler objects, down to room temperature, by detecting their infrared radiation flux. Principle It is based on the principle that the intensity of light received by the observer depends upon distance of observer from source and temperature of dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. If is an object's mass and is its velocity (also a vector quantity), then the object's momentum is : \mathbf = m \mathbf. In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of measurement of momentum is the kilogram metre per second (kg⋅m/s), which is equivalent to the newton-second. Newton's second law of motion states that the rate of change of a body's momentum is equal to the net force acting on it. Momentum depends on the frame of reference, but in any inertial frame it is a ''conserved'' quantity, meaning that if a closed system is not affected by external forces, its total linear momentum does not change. Momentum is also conserved in special relativity (with a modified formula) and, in a modified form, in electrodynamics, quantum mechanics, qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the greatest mathematicians and physicists and among the most influential scientists of all time. He was a key figure in the philosophical revolution known as the Enlightenment. His book (''Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy''), first published in 1687, established classical mechanics. Newton also made seminal contributions to optics, and shares credit with German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz for developing infinitesimal calculus. In the , Newton formulated the laws of motion and universal gravitation that formed the dominant scientific viewpoint for centuries until it was superseded by the theory of relativity. Newton used his mathematical description of gravity to derive Kepler's laws of planetary motion, account for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation Of Energy
In physics and chemistry, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant; it is said to be ''conserved'' over time. This law, first proposed and tested by Émilie du Châtelet, means that energy can neither be created nor destroyed; rather, it can only be transformed or transferred from one form to another. For instance, chemical energy is converted to kinetic energy when a stick of dynamite explodes. If one adds up all forms of energy that were released in the explosion, such as the kinetic energy and potential energy of the pieces, as well as heat and sound, one will get the exact decrease of chemical energy in the combustion of the dynamite. Classically, conservation of energy was distinct from conservation of mass. However, special relativity shows that mass is related to energy and vice versa by ''E = mc2'', and science now takes the view that mass-energy as a whole is conserved. Theoretically, this implies that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gottfried Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm (von) Leibniz . ( – 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat. He is one of the most prominent figures in both the history of philosophy and the history of mathematics. He wrote works on philosophy, theology, ethics, politics, law, history and philology. Leibniz also made major contributions to physics and technology, and anticipated notions that surfaced much later in probability theory, biology, medicine, geology, psychology, linguistics and computer science. In addition, he contributed to the field of library science: while serving as overseer of the Wolfenbüttel library in Germany, he devised a cataloging system that would have served as a guide for many of Europe's largest libraries. Leibniz's contributions to this vast array of subjects were scattered in various learned journals, in tens of thousands of letters and in unpublished manuscripts. He wrote in several languages, primarily in Latin, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vis Viva
''Vis viva'' (from the Latin for "living force") is a historical term used for the first recorded description of what we now call kinetic energy in an early formulation of the principle of conservation of energy. Overview Proposed by Gottfried Leibniz over the period 1676–1689, the theory was controversial as it seemed to oppose the theory of conservation of quantity of motion advocated by René Descartes. Quantity of motion is different from momentum. However, Newton defined quantity of motion as the conjunction of the quantity of matter and velocity (see Definition II in Principia). In Definition III he defines the force which resists a change in motion as the vis inertia of Descartes. His Third Law of Motion is a statement of what becomes known as the conservation of momentum as he demonstrates in the related Scholium. Leibniz accepted the principle of conservation of momentum, but rejected the Cartesian version of it. The difference between Newton and Descartes and Leibniz w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, the increasing use of steam power and water power, the development of machine tools and the rise of the mechanized factory system. Output greatly increased, and a result was an unprecedented rise in population and in the rate of population growth. Textiles were the dominant industry of the Industrial Revolution in terms of employment, value of output and capital invested. The textile industry was also the first to use modern production methods. The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain, and many of the technological and architectural innovations were of British origin. By the mid-18th century, Britain was the world's leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Wheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with a number of blades or buckets arranged on the outside rim forming the driving car. Water wheels were still in commercial use well into the 20th century but they are no longer in common use. Uses included milling flour in gristmills, grinding wood into pulp for papermaking, hammering wrought iron, machining, ore crushing and pounding fibre for use in the manufacture of cloth. Some water wheels are fed by water from a mill pond, which is formed when a flowing stream is dammed. A channel for the water flowing to or from a water wheel is called a mill race. The race bringing water from the mill pond to the water wheel is a headrace; the one carrying water after it has left the wheel is commonly referred to as a tailrace. Waterwheels were used for various purposes from ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windmill
A windmill is a structure that converts wind power into rotational energy using vanes called windmill sail, sails or blades, specifically to mill (grinding), mill grain (gristmills), but the term is also extended to windpumps, wind turbines, and other applications, in some parts of the English speaking world. The term wind engine is sometimes used to describe such devices. Windmills were used throughout the High Middle Ages, high medieval and early modern periods; the horizontal or panemone windmill first appeared in Persia during the 9th century, and the vertical windmill first appeared in northwestern Europe in the 12th century. Regarded as an icon of Culture of the Netherlands, Dutch culture, there are approximately 1,000 windmills in the Netherlands today. Forerunners Wind-powered machines may have been known earlier, but there is no clear evidence of windmills before the 9th century. Hero of Alexandria (Heron) in first-century Roman Egypt described what appears to be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waterwheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with a number of blades or buckets arranged on the outside rim forming the driving car. Water wheels were still in commercial use well into the 20th century but they are no longer in common use. Uses included milling flour in gristmills, grinding wood into pulp for papermaking, hammering wrought iron, machining, ore crushing and pounding fibre for use in the manufacture of cloth. Some water wheels are fed by water from a mill pond, which is formed when a flowing stream is dammed. A channel for the water flowing to or from a water wheel is called a mill race. The race bringing water from the mill pond to the water wheel is a headrace; the one carrying water after it has left the wheel is commonly referred to as a tailrace. Waterwheels were used for various purposes from ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.gif)

