|
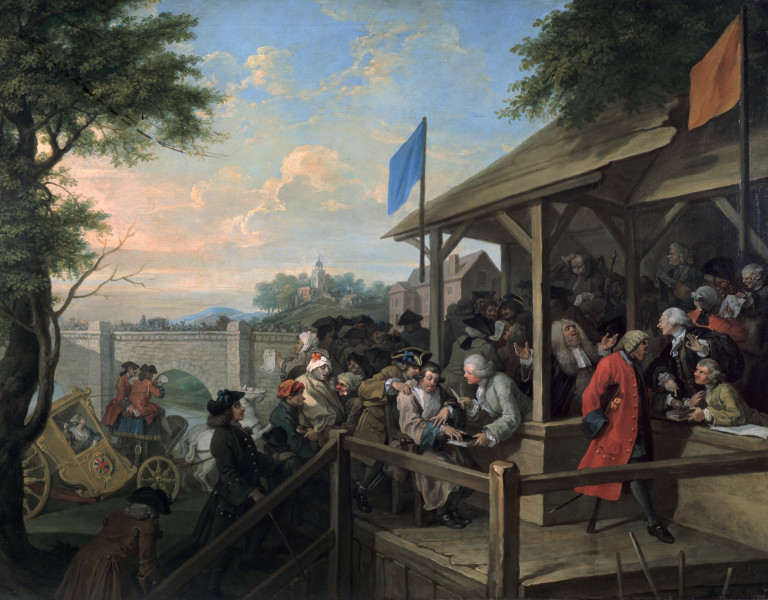
John Shebbeare
John Shebbeare (1709–1788) was a British Tory political satirist. Life He was the eldest son of an attorney and corn-factor of Bideford, Devonshire. A hundred and a village in Devon, where the family had owned land, bear their name. Shebbeare was educated at the free school, Exeter, under Zachariah Mudge, and there, it is said, "gave evidence of his future eminence in misanthropy and literature." In his sixteenth year he was apprenticed to a surgeon, and afterwards set up for himself. Having, however, lampooned both his master and the members of the Exeter corporation, he in 1736 removed to Bristol, where in 1750 he was listed in land tax records as being at 10, Guinea Street, a house which is extant. He entered into partnership with a chemist in the city. In 1740 he published ''A new Analysis of the Bristol Waters; together with the Cause of Diabetes and Hectic, and their Cure, as it results from those Waters'', which was reissued in 1760. The Shebbeare family had left Guinea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Template:Infobox Writer/doc
Infobox writer may be used to summarize information about a person who is a writer/author (includes screenwriters). If the writer-specific fields here are not needed, consider using the more general ; other infoboxes there can be found in :People and person infobox templates. This template may also be used as a module (or sub-template) of ; see WikiProject Infoboxes/embed for guidance on such usage. Syntax The infobox may be added by pasting the template as shown below into an article. All fields are optional. Any unused parameter names can be left blank or omitted. Parameters Please remove any parameters from an article's infobox that are unlikely to be used. All parameters are optional. Unless otherwise specified, if a parameter has multiple values, they should be comma-separated using the template: : which produces: : , language= If any of the individual values contain commas already, add to use semi-colons as separators: : which produces: : , ps ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Boswell
James Boswell, 9th Laird of Auchinleck (; 29 October 1740 (New Style, N.S.) – 19 May 1795), was a Scottish biographer, diarist, and lawyer, born in Edinburgh. He is best known for his biography of his friend and older contemporary the English writer Samuel Johnson, which is commonly said to be the greatest biography written in the English language. A great mass of Boswell's diaries, letters and private papers were recovered from the 1920s to the 1950s, and their ongoing publication by Yale University has transformed his reputation. Early life Boswell was born in Blair's Land on the east side of Parliament Close behind St Giles' Cathedral in Edinburgh on 29 October 1740 (New Style, N.S.). He was the eldest son of a judge, Alexander Boswell, Lord Auchinleck, and his wife Euphemia Erskine. As the eldest son, he was heir to his family's estate of Auchinleck in Ayrshire. Boswell's mother was a strict Calvinist, and he felt that his father was cold to him. As a child, he was delica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tories (British Political Party)
The Tories were a loosely organised political faction and later a political party, in the Parliaments of England, Scotland, Ireland, Great Britain and the United Kingdom. They first emerged during the 1679 Exclusion Crisis, when they opposed Whig efforts to exclude James, Duke of York from the succession on the grounds of his Catholicism. Despite their fervent opposition to state-sponsored Catholicism, Tories opposed exclusion in the belief inheritance based on birth was the foundation of a stable society. After the succession of George I in 1714, the Tories were excluded from government for nearly 50 years and ceased to exist as an organised political entity in the early 1760s, although it was used as a term of self-description by some political writers. A few decades later, a new Tory party would rise to establish a hold on government between 1783 and 1830, with William Pitt the Younger followed by Robert Jenkinson, 2nd Earl of Liverpool. The Whigs won control of Parl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Clarendon
Earl of Clarendon is a title that has been created twice in British history, in 1661 and 1776. The family seat is Holywell House, near Swanmore, Hampshire. First creation of the title The title was created for the first time in the Peerage of England in 1661 for the statesman Edward Hyde, 1st Baron Hyde. He was Chancellor of the Exchequer from 1643 to 1646 and Lord Chancellor from 1658 to 1667 and a close political adviser to Charles II, although he later fell out of favour and was forced into exile. Hyde had already been created Baron Hyde, of Hindon in the County of Wiltshire, in 1660, and was made Viscount Cornbury, in the County of Oxford, at the same time he was given the earldom. These titles were also in the Peerage of England. His second son Laurence Hyde was also a politician and was created Earl of Rochester in 1682. Lord Clarendon's daughter Anne Hyde married the future King James II and was the mother of Queen Mary II and Queen Anne. Lord Clarendon was su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Gwyn
Francis Gwyn PC (1648 – 14 June 1734), of Llansannor Court, was a Welsh Tory politician who sat in the English and House of Commons at various times between 1673 and 1727. Background Gwyn was the son and heir of Edward Gwyn of Llansannor, Glamorganshire, who married Eleanor, youngest daughter of Sir Francis Popham of Littlecott, Wiltshire. He was born at Combe Florey in Somerset about 1648. He matriculated at Christ Church, Oxford, on 1 June 1666, aged 17 and was admitted at Middle Temple in 1667. Although he trained as a lawyer, he had ample means and went into politics. Member of Parliament Gwyn was elected as Member of Parliament for Chippenham at the general election of 1673 and although his election was voided on 6 February, he was returned at a by-election on 11 February 1673. He was defeated at Chippenham at the 1679 general election and remained outside the House of Commons discharging his official duties. At the 1685 general election he was returned unopposed as MP f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
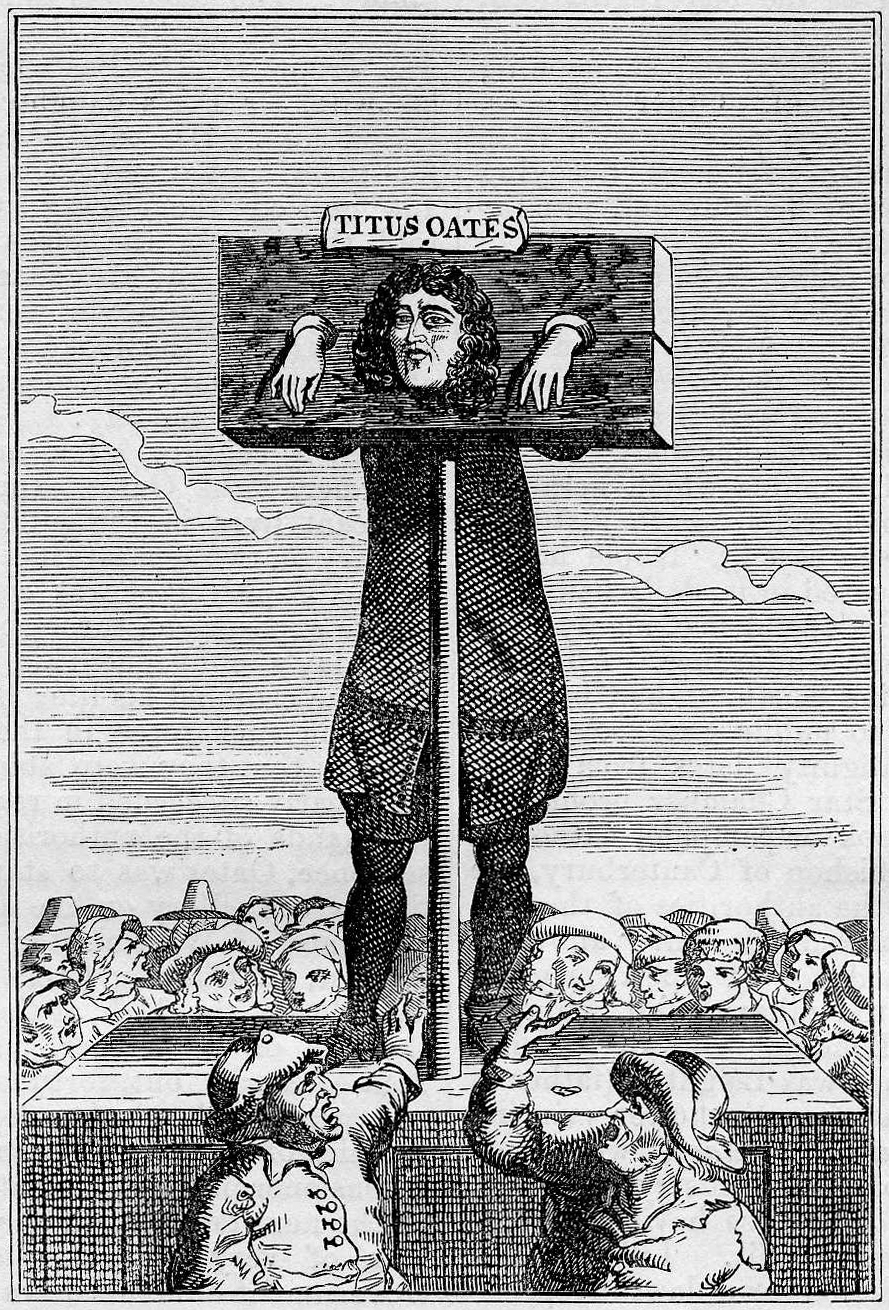
Arthur Beardmore
Arthur Beardmore (died 1771) was an English lawyer and a friend of John Wilkes. Beardmore was an editor of the ''Monitor''. On 6 November 1762 the Secretary of State for the Southern Department, Lord Halifax, issued warrants for the arrest of Beardmore. He was arrested on 11 November for publishing an article on the Princess Dowager and Lord Bute. He made sure he was arrested when he was teaching his son ''Magna Carta (Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...'', an act which was commemorated in a popular print in 1764 after he won £1,000 in damages in May of that year.Anne Pallister, ''Magna Carta. The Heritage of Liberty'' (Oxford University Press, 1971), p. 60, n. 3. Notes {{DEFAULTSORT:Beardmore, Arthur 1771 deaths Year of birth unknown English lawyers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
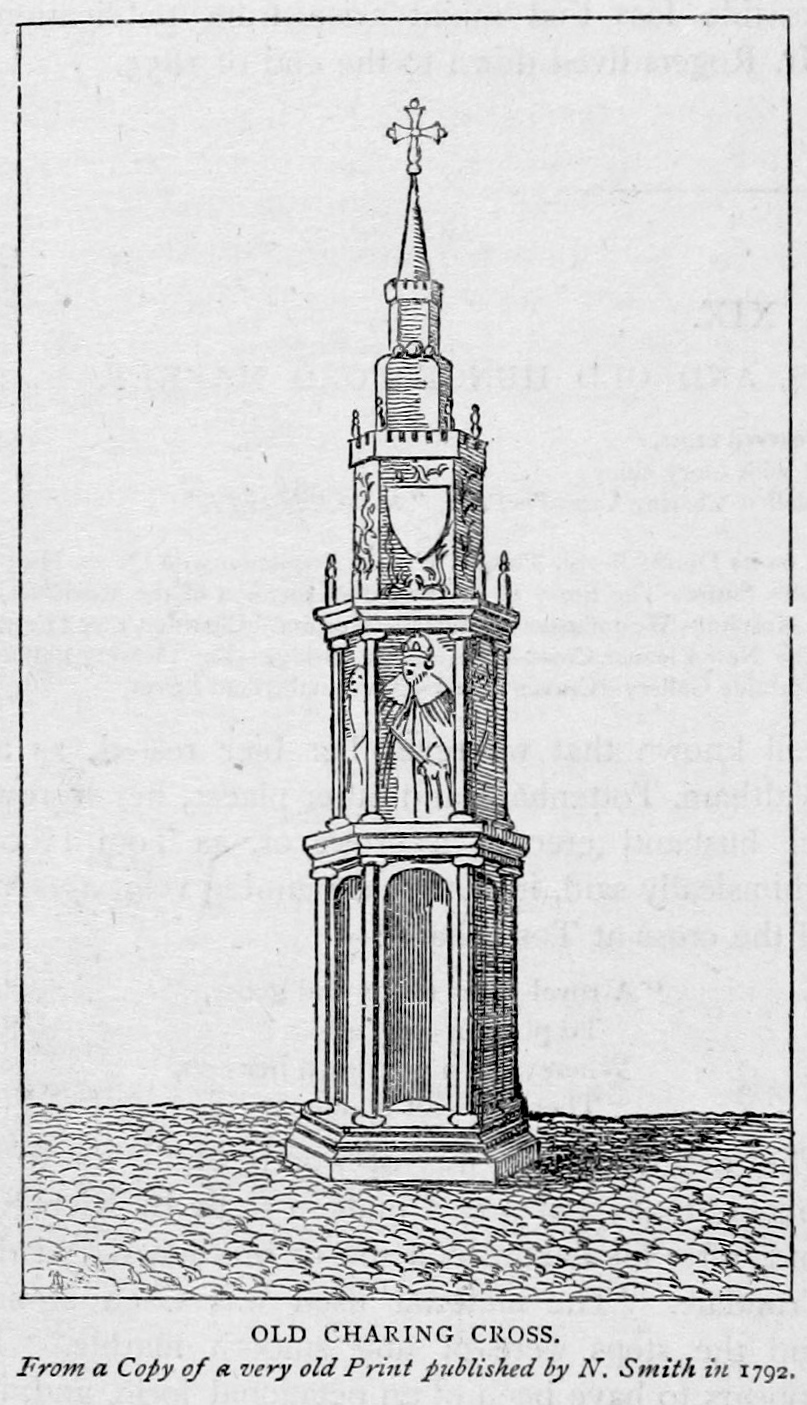
Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Clockwise from north these are: the east side of Trafalgar Square leading to St Martin's Place and then Charing Cross Road; the Strand leading to the City; Northumberland Avenue leading to the Thames Embankment; Whitehall leading to Parliament Square; The Mall leading to Admiralty Arch and Buckingham Palace; and two short roads leading to Pall Mall. The name also commonly refers to the Queen Eleanor Memorial Cross at Charing Cross station. A bronze equestrian statue of Charles I, erected in 1675, stands on a high plinth, situated roughly where a medieval monumental cross had previously stood for 353 years (since its construction in 1294) until destroyed in 1647 by Cromwell and his revolutionary government. The famously beheaded King, appearing ascendant, is the work of French sculptor Hubert Le Sueur. The aforementioned eponymous monument, the "Charing Cross", was the largest and most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pillory
The pillory is a device made of a wooden or metal framework erected on a post, with holes for securing the head and hands, formerly used for punishment by public humiliation and often further physical abuse. The pillory is related to the stocks. Etymology The word is documented in English since 1274 (attested in Anglo-Latin from ), and stems from Old French (1168; modern French , see below), itself from medieval Latin , of uncertain origin, perhaps a diminutive of Latin 'pillar, stone barrier'. Description Rather like the lesser punishment called the stocks, the pillory consisted of hinged wooden boards forming holes through which the head and/or various limbs were inserted; then the boards were locked together to secure the captive. Pillories were set up to hold people in marketplaces, crossroads, and other public places. They were often placed on platforms to increase public visibility of the person. Often a placard detailing the crime was placed nearby; these punishment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitehall Evening Post
The ''Whitehall Evening Post'' was a London newspaper, founded in September 1718 by Daniel Defoe. The newspaper was initially published on Tuesdays, Thursdays, and Saturdays. Defoe left it in June 1720, but it continued to exist until the end of the century. It closed in 1801, with issue 8487 and was merged with the ''English Chronicle ''The English Chronicle'' was a thrice-weekly evening newspaper founded in London in 1779. History and profile ''The Chronicle'' was founded in 1779 although the founders are not known. In 1781 it was given the supplementary title ''Or, Universal ...''. Its editors included Thomas Leach, and finally Stephen Jones. References {{Defunct newspapers of the United Kingdom Defunct newspapers published in the United Kingdom Daniel Defoe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King's Bench Prison
The King's Bench Prison was a prison in Southwark, south London, England, from medieval times until it closed in 1880. It took its name from the King's Bench court of law in which cases of defamation, bankruptcy and other misdemeanours were heard; as such, the prison was often used as a debtor's prison until the practice was abolished in the 1860s. In 1842, it was renamed the Queen's Bench Prison, and became the Southwark Convict Prison in 1872. Origins The first prison was originally constructed from two houses and was situated in Angel Place, off Borough High Street, Southwark – as with other judicial buildings it was often targeted during uprisings, being burned in 1381 and 1450. During the reign of King Henry VIII, new prison buildings were constructed within an enclosing brick wall. This was eventually demolished in 1761. New building Its 1758 replacement was built at a cost of £7,800 on a site close to St George's Fields (south of Borough Road, close to its junction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Murray, 1st Earl Of Mansfield
William Murray, 1st Earl of Mansfield, PC, SL (2 March 170520 March 1793) was a British barrister, politician and judge noted for his reform of English law. Born to Scottish nobility, he was educated in Perth, Scotland, before moving to London at the age of 13 to take up a place at Westminster School. He was accepted into Christ Church, Oxford, in May 1723, and graduated four years later. Returning to London from Oxford, he was called to the Bar by Lincoln's Inn on 23 November 1730, and quickly gained a reputation as an excellent barrister. He became involved in politics in 1742, beginning with his election as a Member of Parliament for Boroughbridge, now in North Yorkshire, and appointment as Solicitor General. In the absence of a strong Attorney General, he became the main spokesman for the government in the House of Commons, and was noted for his "great powers of eloquence" and described as "beyond comparison the best speaker" in the House of Commons. With the promotion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
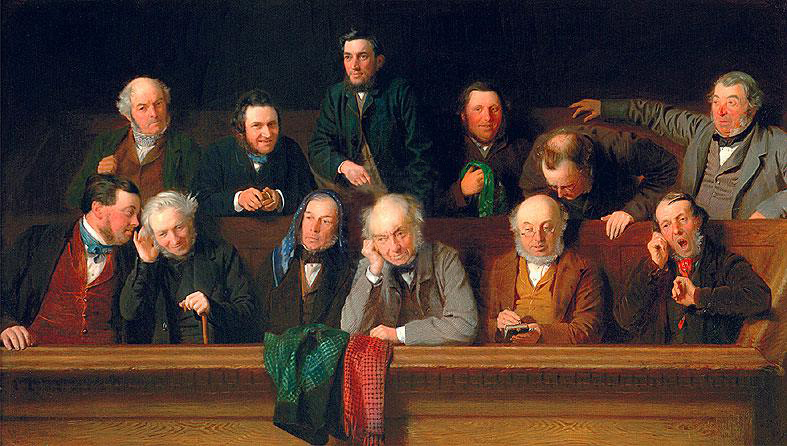
Jury Nullification
Jury nullification (US/UK), jury equity (UK), or a perverse verdict (UK) occurs when the jury in a criminal trial gives a not guilty verdict despite a defendant having clearly broken the law. The jury's reasons may include the belief that the law itself is unjust, that the prosecutor has misapplied the law in the defendant's case, that the punishment for breaking the law is too harsh, or general frustrations with the criminal justice system. Some juries have also refused to convict due to their own prejudices in favor of the defendant. Such verdicts are possible because a jury has an absolute right to return any verdict it chooses. Nullification is not an official part of criminal procedure, but is the logical consequence of two rules governing the systems in which it exists: # Jurors cannot be punished for passing an incorrect verdict. # A defendant who is acquitted can, in many jurisdictions, not be tried a second time for the same offence. A jury verdict that is contrary t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |