|
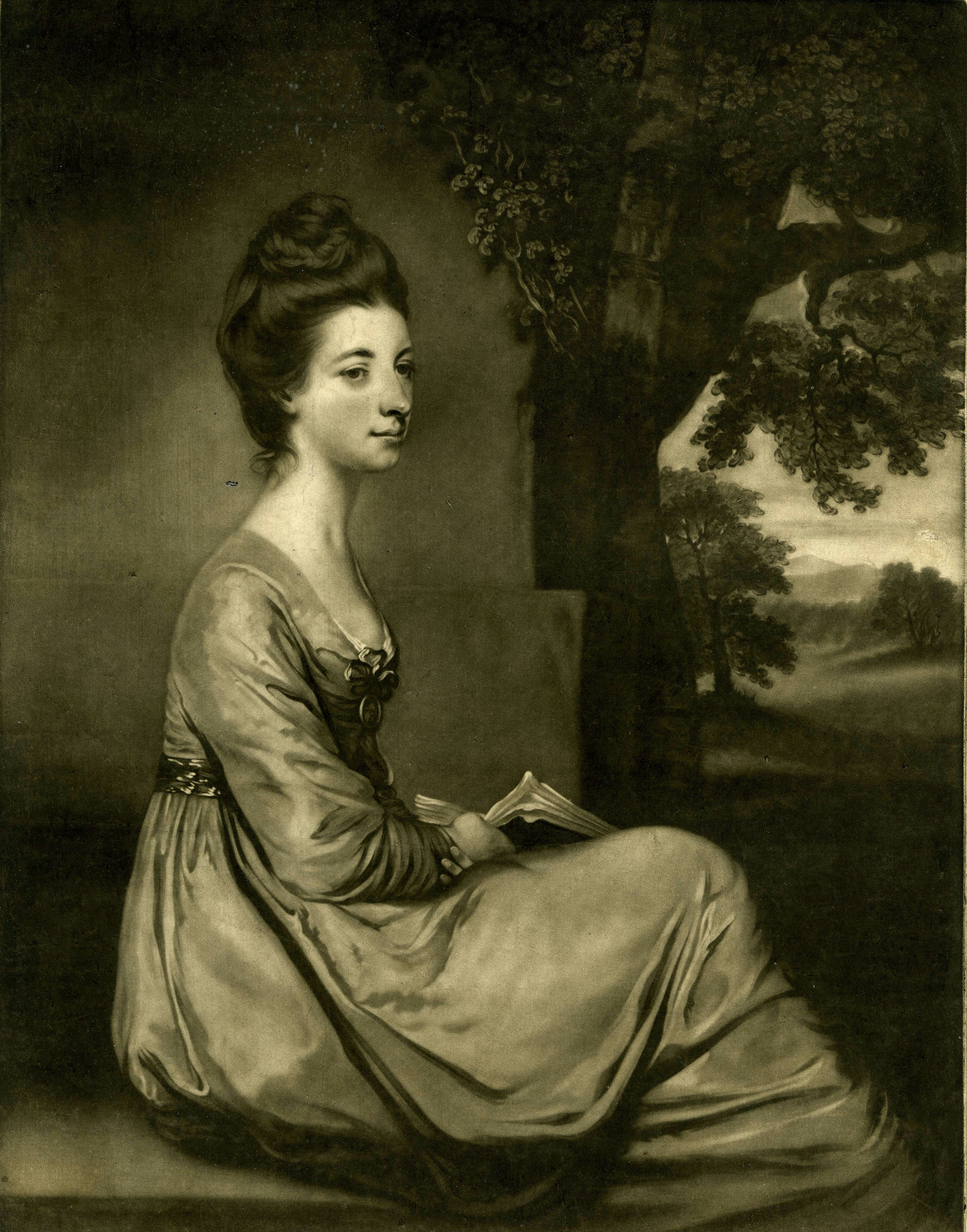
John Russell (English Painter)
John Russell RA (29 March 1745 – 20 April 1806) was an English painter renowned for his portrait work in oils and pastels, and as a writer and teacher of painting techniques. Life and work Russell was born in Guildford, Surrey, the son of John Russell Snr., book and print seller and four times mayor of the town; his father was something of an artist, and drew and published two views of Guildford. Russell was educated at the Royal Grammar School, Guildford, and soon showed a strong inclination for art. He trained under Francis Cotes RA (of Cavendish Square, London), one of the pioneers of English pastel painting, and, like Cotes, was an admirer of the pastel drawings of Rosalba Carriera whose methods influenced his technique of "sweetening". At the age of 19 he converted to Methodism, which was the cause of tension with his family and with his teacher; he made no secret of his strong evangelical leanings and would attempt to preach and convert at every opportunity. Russel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Russell - National Portrait Gallery
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortimer Street
Mortimer Street is a street in the City of Westminster. It runs from the junction of Cavendish Place, Langham Place, and Regent Street in the west, to the junction of Cleveland Street, Goodge Street, and Newman Street in the east. It is joined by Great Portland Street, Great Titchfield Street, Wells Street, Nassau Street, Berners Street Berners Street is a thoroughfare located to the north of Oxford Street in the City of Westminster in the West End of London, originally developed as a residential street in the mid-18th century by property developer William Berners, and later ..., and Berners Mews. Notable buildings It contains a number of listed buildings: *No. 10, Arts and crafts influenced offices. *Nos. 34–38, Radiant House. * Nos. 42 & 44, an arts and crafts influenced former youth hostel by Beresford Pite. * The George public house. *No. 82, c.1900, shop with offices above by Beresford Pite. *No. 93, c.1906-10 office block by W. and E. Hunt. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face Of The Moon Russell
The face is the front of an animal's head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may affect the psyche adversely. Structure The front of the human head is called the face. It includes several distinct areas, of which the main features are: *The forehead, comprising the skin beneath the hairline, bordered laterally by the temples and inferiorly by eyebrows and ears *The eyes, sitting in the orbit and protected by eyelids and eyelashes * The distinctive human nose shape, nostrils, and nasal septum *The cheeks, covering the maxilla and mandibula (or jaw), the extremity of which is the chin *The mouth, with the upper lip divided by the philtrum, sometimes revealing the teeth Facial appearance is vital for human recognition and communication. Facial muscles in humans allow expression of emotions. The face is itself a highl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlotte Of Mecklenburg-Strelitz
Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz (Sophia Charlotte; 19 May 1744 – 17 November 1818) was Queen of Great Britain and of Ireland as the wife of King George III from their marriage on 8 September 1761 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which she was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until her death in 1818. As George's wife, she was also Electress of Hanover until becoming Queen of Hanover on 12 October 1814, when the electorate became a kingdom. Charlotte was Britain's longest-serving queen consort. Charlotte was born into the royal family of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, a duchy in northern Germany. In 1760, the young and unmarried George III inherited the British throne. As Charlotte was a minor German princess with no interest in politics, George considered her a suitable consort, and they married in 1761. The marriage lasted 57 years, and produced 15 children, 13 of whom survived to adulthood. They included two fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George III Of The United Kingdom
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Monarchy of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until Acts of Union 1800, the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until his death in 1820. He was the longest-lived and longest-reigning king in British history. He was concurrently Duke and Prince-elector of Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Brunswick-Lüneburg ("Hanover") in the Holy Roman Empire before becoming King of Hanover on 12 October 1814. He was a monarch of the House of Hanover but, unlike his two predecessors, he was born in Great Britain, spoke English as his first language and never visited Hanover. George's life and reign were marked by a series of military conflicts involving his kingdoms, much of the rest of Europe, and places farther afield in Africa, the Americas and Asia. Early in his reign, Great Britain defeated France in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis Willis (physician)
Francis Willis (17 August 1718 – 5 December 1807) was a Lincolnshire physician and clergyman, famous for his treatment of George III. Early career Willis was the third son of the Rev. John Willis of Lincoln. He claimed to be a descendant of the Willis family of Fenny Compton, Warwickshire, a kinsman of the George Wyllys who became Governor of Connecticut, New England, and the Willis baronets of Fen Ditton, Cambridgeshire. After an undergraduate career at Lincoln College, Oxford and St Alban Hall he was elected a Fellow of Brasenose College, Oxford in 1740 and was ordained as a priest. Willis was Rector of the college living of Wapping 1748–1750. He resigned his Fellowship in 1750, as he was required to do on his marriage, and he and his wife took up residence at Dunston, Lincolnshire, where he looked after the local interests of Sir Francis Dashwood whilst apparently practising medicine. In 1755 he published 'The Case of a Shepherd near Lincoln' in the London Gazette, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir Joseph Banks
Sir Joseph Banks, 1st Baronet, (19 June 1820) was an English naturalist, botanist, and patron of the natural sciences. Banks made his name on the 1766 natural-history expedition to Newfoundland and Labrador. He took part in Captain James Cook's first great voyage (1768–1771), visiting Brazil, Tahiti, and after 6 months in New Zealand, Australia, returning to immediate fame. He held the position of president of the Royal Society for over 41 years. He advised King George III on the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, and by sending botanists around the world to Botanical expedition, collect plants, he made Kew the world's leading botanical garden. He is credited for bringing 30,000 plant specimens home with him; amongst them, he was the first European to document 1,400. Banks advocated Colony of New South Wales, British settlement in New South Wales and the colonisation of Australia, as well as the establishment of Botany Bay as a place for the Penal transportation, reception of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Wesley
John Wesley (; 2 March 1791) was an English people, English cleric, Christian theology, theologian, and Evangelism, evangelist who was a leader of a Christian revival, revival movement within the Church of England known as Methodism. The societies he founded became the dominant form of the independent Methodist movement that continues to this day. Educated at Charterhouse School, Charterhouse and Christ Church, Oxford, Wesley was elected a fellow of Lincoln College, Oxford, in 1726 and ordination, ordained as an Anglican priest two years later. At Oxford, he led the "Holy Club", a society formed for the purpose of the study and the pursuit of a devout Christian life; it had been founded by his brother Charles Wesley, Charles and counted George Whitefield among its members. After an unsuccessful ministry of two years, serving at Christ Church (Savannah, Georgia), Christ Church, in the Georgia colony of Savannah, Georgia, Savannah, he returned to London and joined a religious so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Wesley
Charles Wesley (18 December 1707 – 29 March 1788) was an English leader of the Methodist movement. Wesley was a prolific hymnwriter who wrote over 6,500 hymns during his lifetime. His works include " And Can It Be", " Christ the Lord Is Risen Today", the carol "Hark! The Herald Angels Sing", and " Lo! He Comes With Clouds Descending". Charles Wesley was born in Epworth, Lincolnshire, the son of Anglican cleric and poet Samuel Wesley and his wife Susanna. He was a younger brother of Methodist founder John Wesley and Anglican cleric Samuel Wesley the Younger, and he became the father of musician Samuel Wesley and grandfather of musician Samuel Sebastian Wesley. He was educated at Oxford University, where his brothers had also studied, and he formed the "Holy Club" among his fellow students in 1729. John Wesley later joined this group, as did George Whitefield. Charles followed his father and brother into the church in 1735, and he travelled with John to Georgia in America, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Wilberforce
William Wilberforce (24 August 175929 July 1833) was a British politician, philanthropist and leader of the movement to abolish the slave trade. A native of Kingston upon Hull, Yorkshire, he began his political career in 1780, eventually becoming an independent Member of Parliament (MP) for Yorkshire (1784–1812). In 1785, he became an evangelical Christian, which resulted in major changes to his lifestyle and a lifelong concern for reform. In 1787, Wilberforce came into contact with Thomas Clarkson and a group of activists against the slave trade, including Granville Sharp, Hannah More and Charles Middleton. They persuaded Wilberforce to take on the cause of abolition, and he soon became the leading English abolitionist. He headed the parliamentary campaign against the British Slave Trade for 20 years until the passage of the Slave Trade Act of 1807. Wilberforce was convinced of the importance of religion, morality and education. He championed causes and campaigns such as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
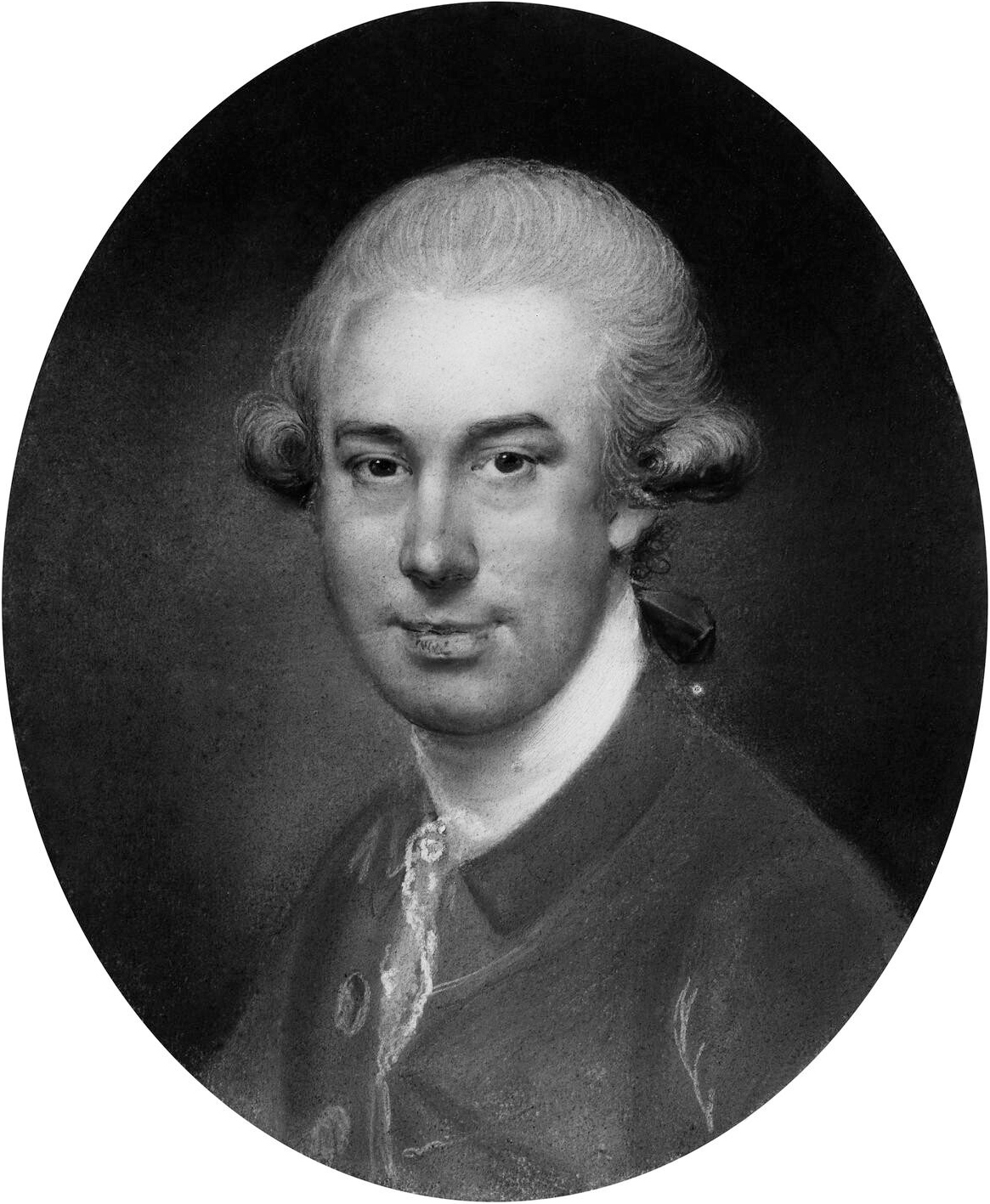
James Watson (engraver)
James Watson (c. 1739 – 1790) was an Irish engraver. Life He came while young to London, where he is supposed to have been a pupil of James Macardell. He became a leading mezzotint engraver. Watson published some of his works himself at his house in Little Queen Anne Street, Portland Chapel; but the majority were done for Sayer, Boydell, and other printsellers. He exhibited engravings with the Incorporated Society of Artists between 1762 and 1775. Watson died in Fitzroy Street, London, on 20 May 1790. The engraver Caroline Watson (1761?–1814) was his daughter and pupil. Works Watson produced plates from pictures by Joshua Reynolds, Thomas Gainsborough, Francis Cotes, Catherine Read, Anthony van Dyck, Gabriel Metzu, Godfried Schalcken, Peter Paul Rubens, and others. He engraved about fifty portraits after Reynolds, among them those of the Duchess of Cumberland; the Duchess of Manchester, with her son; Countess Spencer and her daughter; Barbara, Countess of Coventry; Ann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Whitefield
George Whitefield (; 30 September 1770), also known as George Whitfield, was an Anglican cleric and evangelist who was one of the founders of Methodism and the evangelical movement. Born in Gloucester, he matriculated at Pembroke College at the University of Oxford in 1732. There he joined the "Holy Club" and was introduced to the Wesley brothers, John and Charles, with whom he would work closely in his later ministry. Whitefield was ordained after receiving his Bachelor of Arts degree. He immediately began preaching, but he did not settle as the minister of any parish. Rather he became an itinerant preacher and evangelist. In 1740, Whitefield traveled to North America, where he preached a series of revivals that became part of the " Great Awakening". His methods were controversial and he engaged in numerous debates and disputes with other clergymen. Whitefield received widespread recognition during his ministry; he preached at least 18,000 times to perhaps 10 million listeners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)






