|
John Perry (engineer)
John Perry (14 February 1850 – 4 August 1920) was a pioneering engineer and mathematician from Ireland. Life He was born on 14 February 1850 at Garvagh, County Londonderry, the second son of Samuel Perry and a Scottish-born wife. John's brother James was the County Surveyor in Galway West and co-founded the Galway Electric Light Company. One of his daughters, Alice, was the one of the first women in the world with an engineering degree. Perry worked as Lord Kelvin's assistant at the University of Glasgow, and later became professor of mechanical engineering at Finsbury Technical College. He was a colleague of William Edward Ayrton and John Milne at the Imperial College of Engineering in Tokyo, 1875–79, and was also a Fellow of the Royal Society. He was professor of mathematics at Imperial College in London from 1896 to 1913. In 1900 he was elected president of the Institution of Electrical Engineers, and from 1906–08 served as president of the Physical Society of London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garvagh
Garvagh ( or ''Garbhachadh'' meaning "rough field") is a village in County Londonderry, Northern Ireland. It is on the banks of the Agivey River, south of Coleraine on the A29 route. In the 2001 Census it had a population of 1,288. It is situated within Causeway Coast and Glens district. History Garvagh was important from very early times, and later rebuilt as a Plantation town, as its broad main street and neatly planned buildings evidence. It was founded in the early 17th century by George Canning from Warwickshire, agent for the Ironmonger's Company of London, it was later grown into a middling-size market town by the Cannings. A striking feature of the town is the stone clock tower with an attractive clock and castellations, which dominates the main route through the town and also serves as the district cenotaph. On 26 July 1813 the Battle of Garvagh took place. The town has been immortalised in the famous Protestant folk-song " The Battle of Garvagh". The Troubles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Schuler
Maximilian Joseph Johannes Eduard Schuler (5 February 1882 in Zweibrücken – 30 July 1972) was a German engineer and is best known for discovering the principle known as Schuler tuning which is fundamental to the operation of a gyrocompass or inertial guidance system that will be operated near the surface of the earth. Schuler's cousin Hermann Anschütz-Kaempfe founded a firm near Kiel, Germany, to manufacture navigational devices using gyroscopes in 1905, and Schuler joined the firm in 1906. For many years they struggled with the problem of maintaining a vertical reference as a craft moved around on the surface of the earth. In 1923 Schuler published his discovery that if the gyrocompass was tuned to have an 84.4 minute period of oscillation (the ''Schuler period'') then it would resist errors due to sideways acceleration of the ship or aircraft in which it was installed. Later, Schuler served as a professor of dynamics at the University of Göttingen. According to the Mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Engineers
Irish may refer to: Common meanings * Someone or something of, from, or related to: ** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe ***Éire, Irish language name for the isle ** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland ** Republic of Ireland, a sovereign state * Irish language, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family spoken in Ireland * Irish people, people of Irish ethnicity, people born in Ireland and people who hold Irish citizenship Places * Irish Creek (Kansas), a stream in Kansas * Irish Creek (South Dakota), a stream in South Dakota * Irish Lake, Watonwan County, Minnesota * Irish Sea, the body of water which separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain People * Irish (surname), a list of people * William Irish, pseudonym of American writer Cornell Woolrich (1903–1968) * Irish Bob Murphy, Irish-American boxer Edwin Lee Conarty (1922–1961) * Irish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' sometimes refers only to solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets. Gutenberg, B., 1929, Lehrbuch der Geophysik. Leipzig. Berlin (Gebruder Borntraeger). Runcorn, S.K, (editor-in-chief), 1967, International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
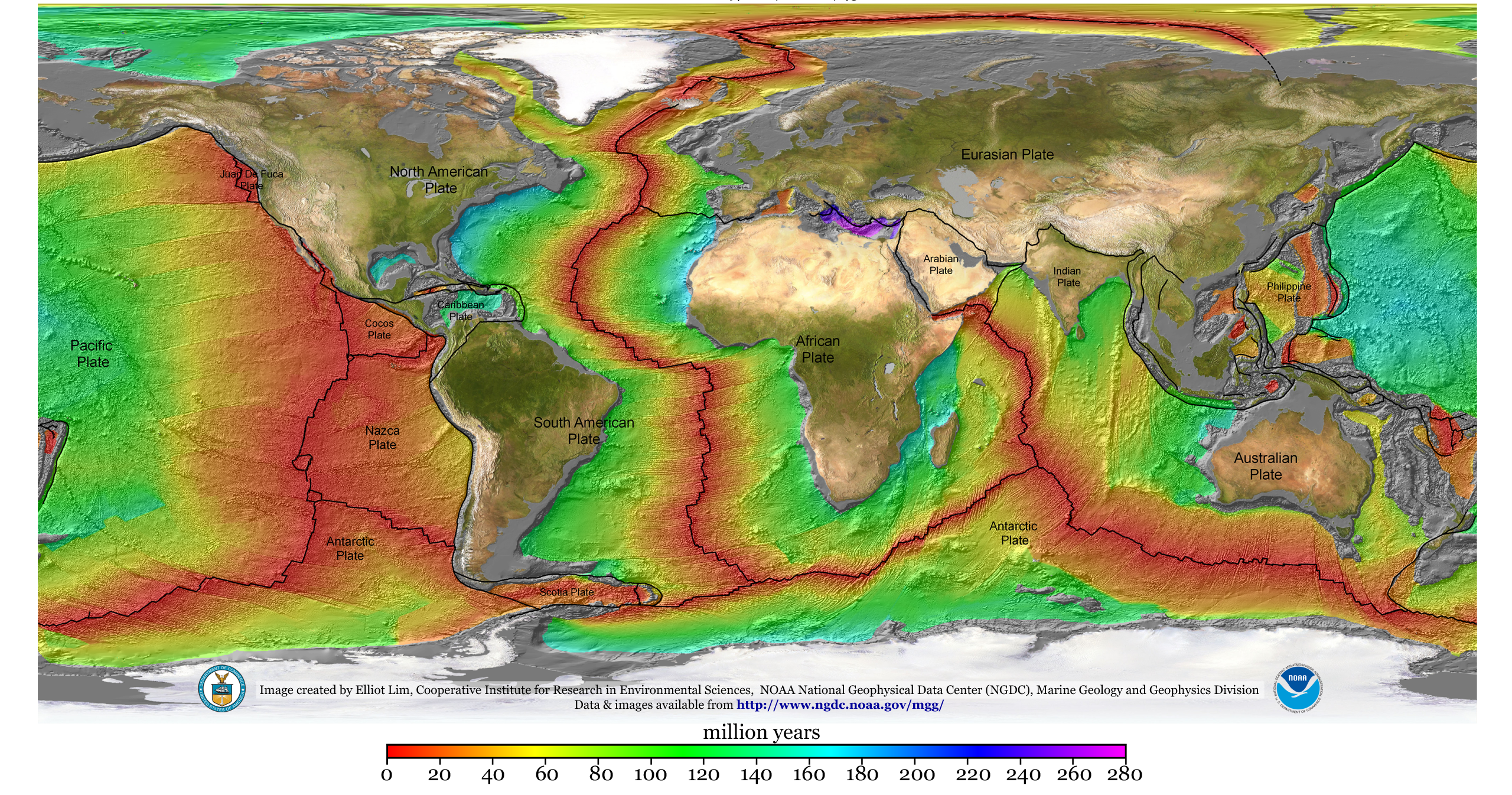
Continental Drift
Continental drift is the hypothesis that the Earth's continents have moved over geologic time relative to each other, thus appearing to have "drifted" across the ocean bed. The idea of continental drift has been subsumed into the science of plate tectonics, which studies the movement of the continents as they ride on plates of the Earth's lithosphere. The speculation that continents might have 'drifted' was first put forward by Abraham Ortelius in 1596. A pioneer of the modern view of mobilism was the Austrian geologist Otto Ampferer.Helmut W. Flügel: Die virtuelle Welt des Otto Ampferer und die Realität seiner Zeit'. In: Geo. Alp., Vol. 1, 2004. The concept was independently and more fully developed by Alfred Wegener in 1912, but the hypothesis was rejected by many for lack of any motive mechanism. The English geologist Arthur Holmes later proposed mantle convection for that mechanism. History Early history Abraham Ortelius , Theodor Christoph Lilienthal (1756), A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Community
The scientific community is a diverse network of interacting scientists. It includes many " sub-communities" working on particular scientific fields, and within particular institutions; interdisciplinary and cross-institutional activities are also significant. Objectivity is expected to be achieved by the scientific method. Peer review, through discussion and debate within journals and conferences, assists in this objectivity by maintaining the quality of research methodology and interpretation of results. History of scientific communities The eighteenth century had some societies made up of men who studied nature, also known as natural philosophers and natural historians, which included even amateurs. As such these societies were more like local clubs and groups with diverse interests than actual scientific communities, which usually had interests on specialized disciplines. Though there were a few older societies of men who studied nature such as the Royal Society of London, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
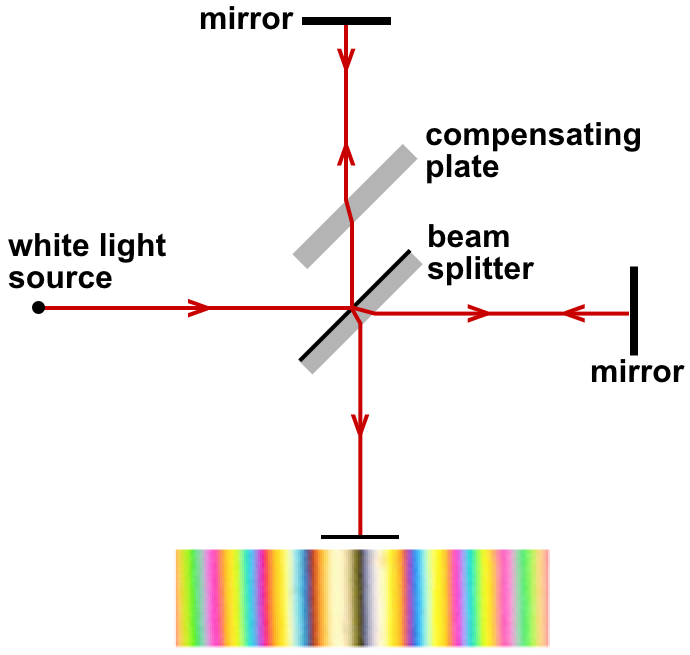
Luminiferous Aether
Luminiferous aether or ether ("luminiferous", meaning "light-bearing") was the postulated medium for the propagation of light. It was invoked to explain the ability of the apparently wave-based light to propagate through empty space (a vacuum), something that waves should not be able to do. The assumption of a spatial plenum of luminiferous aether, rather than a spatial vacuum, provided the theoretical medium that was required by wave theories of light. The aether hypothesis was the topic of considerable debate throughout its history, as it required the existence of an invisible and infinite material with no interaction with physical objects. As the nature of light was explored, especially in the 19th century, the physical qualities required of an aether became increasingly contradictory. By the late 1800s, the existence of the aether was being questioned, although there was no physical theory to replace it. The negative outcome of the Michelson–Morley experiment (1887) suggeste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Age Of Earth
The age of Earth is estimated to be 4.54 ± 0.05 billion years This age may represent the age of Earth's accretion, or core formation, or of the material from which Earth formed. This dating is based on evidence from radiometric age-dating of meteorite material and is consistent with the radiometric ages of the oldest-known terrestrial and lunar samples. Following the development of radiometric age-dating in the early 20th century, measurements of lead in uranium-rich minerals showed that some were in excess of a billion years old.For the abstract, see: The oldest such minerals analyzed to date—small crystals of zircon from the Jack Hills of Western Australia—are at least 4.404 billion years old. Calcium–aluminium-rich inclusions—the oldest known solid constituents within meteorites that are formed within the Solar System—are 4.567 billion years old, giving a lower limit for the age of the Solar System. It is hypothesised that the accretion of Earth began soon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiometric Dating
Radiometric dating, radioactive dating or radioisotope dating is a technique which is used to date materials such as rocks or carbon, in which trace radioactive impurities were selectively incorporated when they were formed. The method compares the abundance of a naturally occurring radioactive isotope within the material to the abundance of its decay products, which form at a known constant rate of decay. The use of radiometric dating was first published in 1907 by Bertram Boltwood and is now the principal source of information about the absolute age of rocks and other geological features, including the age of fossilized life forms or the age of Earth itself, and can also be used to date a wide range of natural and man-made materials. Together with stratigraphic principles, radiometric dating methods are used in geochronology to establish the geologic time scale. Among the best-known techniques are radiocarbon dating, potassium–argon dating and uranium–lead dating. By al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha decay ( ), beta decay ( ), and gamma decay ( ), all of which involve emitting one or more particles. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force. A fourth type of common decay is electron capture, in which an unstable nucleus captures an inner electron from one of the electron shells. The loss of that electron from the shell results in a cascade of electrons dropping down to that lower shell resulting in emission of discrete X-rays from the transitions. A common example is iodine-125 commonly used in medical settings. Radioactive decay is a stochastic (i.e. random) proce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermal Conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is a measure of its ability to conduct heat. It is commonly denoted by k, \lambda, or \kappa. Heat transfer occurs at a lower rate in materials of low thermal conductivity than in materials of high thermal conductivity. For instance, metals typically have high thermal conductivity and are very efficient at conducting heat, while the opposite is true for insulating materials like Rockwool or Styrofoam. Correspondingly, materials of high thermal conductivity are widely used in heat sink applications, and materials of low thermal conductivity are used as thermal insulation. The reciprocal of thermal conductivity is called thermal resistivity. The defining equation for thermal conductivity is \mathbf = - k \nabla T, where \mathbf is the heat flux, k is the thermal conductivity, and \nabla T is the temperature gradient. This is known as Fourier's Law for heat conduction. Although commonly expressed as a scalar, the most general form of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legum Doctor
Legum Doctor (Latin: “teacher of the laws”) (LL.D.) or, in English, Doctor of Laws, is a doctorate-level academic degree in law or an honorary degree, depending on the jurisdiction. The double “L” in the abbreviation refers to the early practice in the University of Cambridge to teach both canon law and civil law (Doctor of both laws), with the double “L” itself indicating the plural, although Cambridge now gives the degree the name Doctor of Law in English. This contrasts with the practice of the University of Oxford, where the degree that survived from the Middle Ages is the DCL or Doctor of Civil Law (only). European and Commonwealth usage In the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, and a number of European countries, the LL.D. is a higher doctorate usually awarded on the basis of exceptionally insightful and distinctive publications that contain significant and original contributions to the study of law. In South Africa, the LL.D. is awarded by many unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)