|
John Hope Franklin
John Hope Franklin (January 2, 1915 – March 25, 2009) was an American historian of the United States and former president of Phi Beta Kappa, the Organization of American Historians, the American Historical Association, and the Southern Historical Association. Franklin is best known for his work ''From Slavery to Freedom'', first published in 1947, and continually updated. More than three million copies have been sold. In 1995, he was awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the nation's highest civilian honor. Born in Oklahoma, Franklin attended Fisk University and then Harvard University, receiving his doctorate in 1941. He was a professor at Howard University, and in 1956 was named to head the history department at Brooklyn College, part of the City University of New York. Recruited to the University of Chicago in 1964, he eventually led the history department and was appointed to a named chair. He then moved to Duke University in 1983, as an appointee to a named c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rentiesville, Oklahoma
Rentiesville is a town in McIntosh County, Oklahoma, McIntosh County, Oklahoma, United States. It was founded in 1903 and named for William Rentie, a local landowner. It was one of 50 all-black towns in Oklahoma and one of 13 that still survives.O'Dell, Larry. ''Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture''. Rentiesville. Accessed August 27, 2012/ref> The population was 128 at the 2010 census, an increase of 25.5 percent from 102 in 2000 United States Census, 2000. History The Civil War Battle of Honey Springs was fought about a half mile east of present-day Rentiesville and south of Oktaha, Oklahoma, Oktaha, near the county line; the Honey Springs Battlefield is on the National Register of Historic Places listings in Muskogee County, Oklahoma. Honey Springs was Oklahoma's largest Civil War Engagement (military), engagement. Rentiesville was founded as an all-black town in 1903 on land owned by William Rentie and Phoebe McIntosh. The post office opened May 11, 1904, and the town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Historical Association
The American Historical Association (AHA) is the oldest professional association of historians in the United States and the largest such organization in the world. Founded in 1884, the AHA works to protect academic freedom, develop professional standards, and support scholarship and innovative teaching. It publishes ''The American Historical Review'' four times a year, with scholarly articles and book reviews. The AHA is the major organization for historians working in the United States, while the Organization of American Historians is the major organization for historians who study and teach about the United States. The group received a congressional charter in 1889, establishing it "for the promotion of historical studies, the collection and preservation of historical manuscripts, and for kindred purposes in the interest of American history, and of history in America." Current activities As an umbrella organization for the discipline, the AHA works with other major histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulsa Race Massacre
The Tulsa race massacre, also known as the Tulsa race riot or the Black Wall Street massacre, was a two-day-long massacre that took place between May 31 – June 1, 1921, when mobs of white residents, some of whom had been appointed as deputies and armed by city officials, attacked black residents and destroyed homes and businesses of the Greenwood District in Tulsa, Oklahoma. The event is considered one of "the single worst incident of racial violence in American history" and has been described as one of the deadliest terrorist attacks in the history of the United States. The attackers burned and destroyed more than 35 square blocks of the neighborhood—at the time one of the wealthiest black communities in the United States, colloquially known as "Black Wall Street." More than 800 people were admitted to hospitals, and as many as 6,000 black residents of Tulsa were interned in large facilities, many of them for several days. The Oklahoma Bureau of Vital Statistics offici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freedman
A freedman or freedwoman is a formerly enslaved person who has been released from slavery, usually by legal means. Historically, enslaved people were freed by manumission (granted freedom by their captor-owners), emancipation (granted freedom as part of a larger group), or self-purchase. A fugitive slave is a person who escaped enslavement by fleeing. Ancient Rome Rome differed from Greek city-states in allowing freed slaves to become plebeian citizens. The act of freeing a slave was called ''manumissio'', from ''manus'', "hand" (in the sense of holding or possessing something), and ''missio'', the act of releasing. After manumission, a slave who had belonged to a Roman citizen enjoyed not only passive freedom from ownership, but active political freedom ''(libertas)'', including the right to vote. A slave who had acquired ''libertas'' was known as a ''libertus'' ("freed person", feminine ''liberta'') in relation to his former master, who was called his or her patron ''( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Territory
The Indian Territory and the Indian Territories are terms that generally described an evolving land area set aside by the Federal government of the United States, United States Government for the relocation of Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans who held aboriginal title to their land as a sovereign independent state. In general, the tribes ceded land they occupied in exchange for Land grant#United States, land grants in 1803. The concept of an Indian Territory was an outcome of the US federal government's 18th- and 19th-century policy of Indian removal. After the Indian Territory in the American Civil War, American Civil War (1861–1865), the policy of the US government was one of Cultural assimilation of Native Americans#Americanization and assimilation (1857–1920), assimilation. The term ''Indian Reserve (1763), Indian Reserve'' describes lands the Kingdom of Great Britain, British set aside for Indigenous tribes between the Appalachian Mountains and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
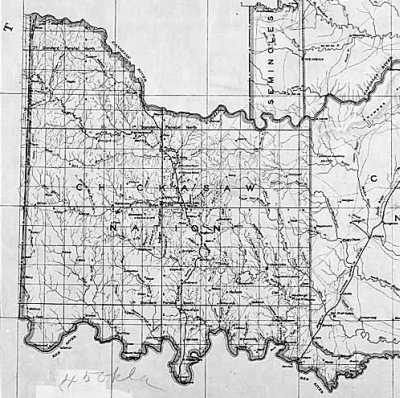
Chickasaw Nation
The Chickasaw Nation (Chickasaw language, Chickasaw: Chikashsha I̠yaakni) is a federally recognized tribes, federally recognized Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribe, with its headquarters located in Ada, Oklahoma in the United States. They are an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, originally from northern Mississippi, northernwestern Alabama, southwestern Kentucky, and western Tennessee. Today, the Chickasaw Nation is the 13th largest tribe in the United States. Currently, the nation's jurisdictional territory and Indian reservation, reservation includes about 7,648 square miles of south-central Oklahoma, including Bryan, Carter, Coal, Garvin, Grady, Jefferson, Johnston, Love, McClain, Marshall, Murray, Pontotoc, and Stephens counties. These counties are separated into four districts, the Pontotoc, Pickens, Tishomingo, and Panola, with relatively equal populations. Their population today is estimated to be 38,000, with the majority residin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Georgia Encyclopedia
The ''New Georgia Encyclopedia'' (NGE) is a web-based encyclopedia containing over 2,000 articles about the state of Georgia. It is a program of Georgia Humanities (GH), in partnership with the University of Georgia Press, the University System of Georgia/Georgia Library Learning Online (GALILEO), and the Office of the Governor. The NGE was launched in 2004. It was the first state encyclopedia to be conceived and designed exclusively for publication online. The idea for the project grew out of the 1996 joint publication of ''The New Georgia Guide'' by the Georgia Humanities Council and the University of Georgia Press. The guide, itself a spiritual successor to the New Deal-era American Guide Series, was a literary success. Georgia Humanities and UGA Press then convinced Governor Zell Miller, who commissioned the guide in the first place, to fund the planning and development of a comprehensive print and online state encyclopedia. The name "New Georgia Encyclopedia" was chosen as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlanta University
Clark Atlanta University (CAU or Clark Atlanta) is a private, Methodist, historically black research university in Atlanta, Georgia. Clark Atlanta is the first Historically Black College or University (HBCU) in the Southern United States. Founded on September 19, 1865, as Atlanta University, it consolidated with Clark College (established 1869) to form Clark Atlanta University in 1988. It is classified among "R2: Doctoral Universities – High research activity". History Atlanta University was founded on September 19, 1865, as the first HBCU in the Southern United States. Atlanta University was the nation's first graduate institution to award degrees to African Americans in the Nation and the first to award bachelor's degrees to African Americans in the South; Clark College (1869) was the nation's first four-year liberal arts college to serve African-American students. The two consolidated in 1988 to form Clark Atlanta University. Atlanta University In the city of Atlanta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hope (educator)
John Hope (June 2, 1868 – February 22, 1936), born in Augusta, Georgia, was an American educator and political activist, the first African-descended president of both Morehouse College in 1906 and of Atlanta University in 1929, where he worked to develop graduate programs. Both are historically Black colleges. Determined to finish his education after having had to leave school to help support his family after his father's death, Hope went North: graduating from Worcester Academy and Brown University. He returned to the South to teach, and in 1906 became the first African American president of Atlanta Baptist College. He served as president until his death in 1936. After the college's affiliation with Atlanta University, Hope was selected in 1929 as the university's first African-American president; he worked to develop that institution's graduate programs to ensure higher education for Blacks. Hope was active in national civil rights organizations, including the Niagara Moveme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Charlotte Observer
''The Charlotte Observer'' is an American English-language newspaper serving Charlotte, North Carolina, and its metro area. The Observer was founded in 1886. As of 2020, it has the second-largest circulation of any newspaper in the Carolinas. It is owned by Chatham Asset Management. Overview ''The Observer'' primarily serves Charlotte and Mecklenburg County and the surrounding counties of Iredell, Cabarrus, Union, Lancaster, York, Gaston, Catawba, and Lincoln. Home delivery service in outlying counties has declined in recent years, with delivery times growing later as the paper has outsourced circulation services outside the primary Charlotte area. Circulation at ''The Charlotte Observer'' has been declining for many years. The period of May 2011 showed that ''Charlotte Observer'' circulation totaled 155,497 daily and 212,318 Sunday. 2017 Print Circulation Daily: 69,987 and Sunday: 106,434. The newspaper has an online presence and its staff also oversees a NASCAR news we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buck Colbert Franklin
Buck Colbert Franklin (May 6, 1879September 24, 1960) was an African American lawyer best known for defending survivors of the 1921 Tulsa race massacre. Early life and education Buck Colbert Franklin was born on May 6, 1879, near Homer, in would later become Pontotoc County, Oklahoma. His father, David Franklin, was a Black man who had escaped from slavery and fought for the Union Army in 1864. His mother, Millie Colbert Franklin, was one-fourth Choctaw and had been raised in that nation's traditional culture. Millie and David were married in 1856 and moved from Mississippi to a 300-acre farm near Homer in the Indian Territory, on communal land of the Chickasaw Nation. Buck was the seventh of the couple's ten children, and was named for his grandfather, who had purchased his own freedom. Millie died in 1886 after a trip to Tuskahoma to prove her Choctaw citizenship. David was a successful rancher who used his wealth to build up his community. Franklin's childhood was shaped by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
