|
John Hope (botanist)
Professor John Hope (10 May 1725 – 10 November 1786) was a Scottish physician and botanist. Although he did enormous work on plant classification and plant physiology, due to an absence of publications, he is now best known as an early supporter of Carl Linnaeus's system of classification. In 1783 he was a joint founder of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. In 1784 Hope was elected as president of the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh (1784-6). Early life Born in Edinburgh on 10 May 1725, John Hope was the son of surgeon Robert Hope and Marion Glas, and a grandson of Archibald Hope, Lord Rankeillor, a Senator of the College of Justice who was in turn the son of Sir John Hope, 2nd Baronet. He was the great-grandson of Sir Thomas Hope, 1st Baronet. He was educated at Dalkeith Grammar School, then studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh. He took leave to study botany under Bernard de Jussieu at the University of Paris, but returned to his studies in Scotland, gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal College Of Physicians Of Edinburgh
The Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh (RCPE) is a medical royal college in Scotland. It is one of three organisations that sets the specialty training standards for physicians in the United Kingdom. It was established by Royal charter in 1681. The college claims to have 12,000 fellows and members worldwide. History The RCPE was formed by a royal charter, granted in 1681, with Sir Robert Sibbald recognised as playing a key part in the negotiations. Three applications preceded this and had been unsuccessful. There were 21 original Fellows, eleven of whom were graduates or students of the University of Leiden. The Universities (Scotland) Act 1858 resulted in several items from the College's Charter becoming obsolete, and they obtained a further charter on 31 October 1861. In 1920 the College enacted changes that allowed women to be admitted on the same terms as men. The charter was amended on 7 May 2005. Edinburgh Pharmacopoeia In 1699 The College first published a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalkeith Grammar School
Dalkeith High School is a secondary state school located in Dalkeith, Midlothian, Scotland. History Dalkeith High School was previously the historic Dalkeith Grammar School. A list of masters of the Grammar School at Dalkeith (located on the High Street) commences at 1582. No other reference is made to the age of the school. An extract from the National Gazetteer, 1868 says: "The parish school, otherwise known as the grammar school, has long borne a high character among Scottish seminaries; beside the usual branches of a classical education, French, German, Italian, and mathematics are taught." Alexander Bower suggests in his History of the University of Edinburgh that "for upwards of a century, tmaintained a distinguished reputation, as being one of the best seminaries in Scotland for acquiring a knowledge of classical learning". Archibald Pitcairne (1652–1713), the physician, studied at Dalkeith Grammar School as did Alexander Wedderburn, 1st Earl of Rosslyn (1733–1805) wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Royal Society Of Edinburgh
The Royal Society of Edinburgh is Scotland's national academy of science and letters. It is a registered charity that operates on a wholly independent and non-partisan basis and provides public benefit throughout Scotland. It was established in 1783. , there are around 1,800 Fellows. The Society covers a broader selection of fields than the Royal Society of London, including literature and history. Fellowship includes people from a wide range of disciplines – science & technology, arts, humanities, medicine, social science, business, and public service. History At the start of the 18th century, Edinburgh's intellectual climate fostered many clubs and societies (see Scottish Enlightenment). Though there were several that treated the arts, sciences and medicine, the most prestigious was the Society for the Improvement of Medical Knowledge, commonly referred to as the Medical Society of Edinburgh, co-founded by the mathematician Colin Maclaurin in 1731. Maclaurin was unhappy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hopea
''Hopea'' is a genus of plants in the family Dipterocarpaceae. The genus was named after John Hope, 1725–1786, the first Regius Keeper of the Royal Botanic Garden, Edinburgh. It contains some 113 species, distributed from Sri Lanka and southern India to southern China, and southward throughout Malesia to New Guinea. They are mainly main and subcanopy trees of lowland rainforest, but some species can become also emergent trees, such as ''Hopea nutans''. Species accepted: Other species recently used, but now not accepted include: *'' Hopea exalata'', now a synonym of '' Hopea reticulata'' *''Hopea kitulgallensis'', not now accepted *''Hopea malabarica'', now a synonym of '' Hopea racophloea'' *'' Hopea quisumbingiana'', not now accepted *'' Hopea siamensis'', now a synonym of '' Hopea pierrei'' *'' Hopea wightiana'' Wall., now a synonym of '' Hopea ponga'' Gallery File:Hopea beccariana Base du tronc.JPG, ''Hopea beccariana'' File:A leaf of Hopea odorata.jpg, ''Hopea odora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greyfriars Kirkyard
Greyfriars Kirkyard is the graveyard surrounding Greyfriars Kirk in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is located at the southern edge of the Old Town, adjacent to George Heriot's School. Burials have been taking place since the late 16th century, and a number of notable Edinburgh residents are interred at Greyfriars. The Kirkyard is operated by City of Edinburgh Council in liaison with a charitable trust, which is linked to but separate from the church. The Kirkyard and its monuments are protected as a category A listed building. History Greyfriars takes its name from the Franciscan friary on the site (the friars of which wear grey habits), which was dissolved in 1560. The churchyard was founded in August 1562 after Royal sanction was granted to replace the churchyard at St Giles' Cathedral in Edinburgh. The latter burial ground was not used after around 1600. The Kirkyard was involved in the history of the Covenanters. The Covenanting movement began with signing of the National Cov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
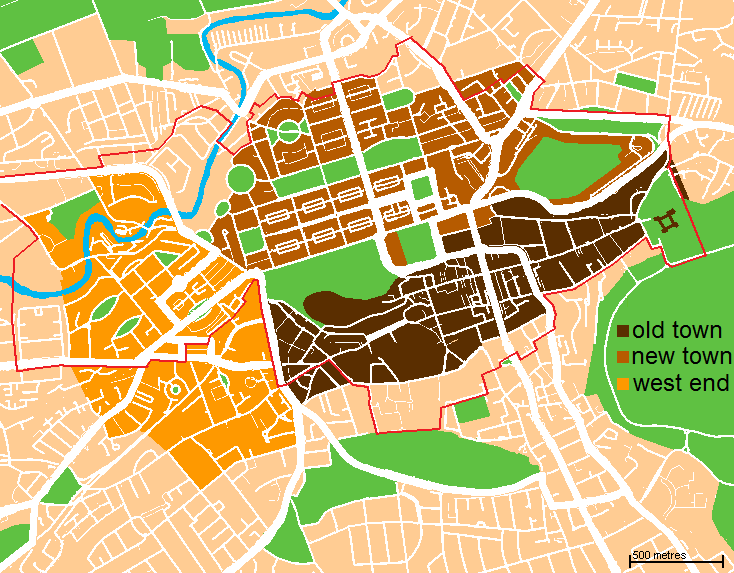
Old Town, Edinburgh
The Old Town ( sco, Auld Toun) is the name popularly given to the oldest part of Scotland's capital city of Edinburgh. The area has preserved much of its medieval street plan and many Reformation-era buildings. Together with the 18th/19th-century New Town, and West End, it forms part of a protected UNESCO World Heritage Site. Royal Mile The "Royal Mile" is a name coined in the early 20th century for the main street of the Old Town which runs on a downwards slope from Edinburgh Castle to Holyrood Palace and the ruined Holyrood Abbey. Narrow '' closes'' (alleyways), often no more than a few feet wide, lead steeply downhill to both north and south of the main spine which runs west to east. Significant buildings in the Old Town include St. Giles' Cathedral, the General Assembly Hall of the Church of Scotland, the National Museum of Scotland, the Old College of the University of Edinburgh and the Scottish Parliament Building. The area contains underground vaults and hidden pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Infirmary Of Edinburgh
The Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh, or RIE, often (but incorrectly) known as the Edinburgh Royal Infirmary, or ERI, was established in 1729 and is the oldest voluntary hospital in Scotland. The new buildings of 1879 were claimed to be the largest voluntary hospital in the United Kingdom, and later on, the Empire."In Coming Days" The Edinburgh Royal Infirmary Souvenir Brochure 1942 The hospital moved to a new 900 bed site in 2003 in Little France. It is the site of clinical medicine teaching as well as a teaching hospital for the University of Edinburgh Medical School. In 1960, the first successful kidney transplant performed in the UK was at this hospital. In 1964, the world's first coronary care unit was established at the hospital. It is the only site for liver, pancreas and pancreatic islet cell transplantation and one of two sites for kidney transplantation in Scotland. In 2012, the Emergency Department had 113,000 patient attendances, the highest number in Scotland. It is man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural science, natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Fellow, Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to many eminent scientists throughout history, including Isaac Newton (1672), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Winston Churchill (1941), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955) and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellowship has been awarded to Stephen Hawking (1974), David Attenborough (1983), Tim Hunt (1991), Elizabeth Blackburn (1992), Tim Berners-Lee (2001), Venki R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holyrood Palace
The Palace of Holyroodhouse ( or ), commonly referred to as Holyrood Palace or Holyroodhouse, is the official residence of the British monarch in Scotland. Located at the bottom of the Royal Mile in Edinburgh, at the opposite end to Edinburgh Castle, Holyroodhouse has served as the principal royal residence in Scotland since the 16th century, and is a setting for state occasions and official entertaining. The late Queen Elizabeth II spent one week in residence at Holyroodhouse at the beginning of each summer, where she carried out a range of official engagements and ceremonies. The 16th-century historic apartments of Mary, Queen of Scots, and the State Apartments, used for official and state entertaining, are open to the public throughout the year, except when members of the royal family are in residence. The Queen's Gallery was built at the western entrance to the Palace of Holyroodhouse and opened in 2002 to exhibit works of art from the Royal Collection. The gardens of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trinity College Kirk
Trinity College Kirk was a royal collegiate church in Edinburgh, Scotland. The kirk and its adjacent almshouse, Trinity Hospital, were founded in 1460 by Mary of Gueldres in memory of her husband, King James II who had been killed at the siege of Roxburgh Castle that year. Queen Mary was interred in the church, until her coffin was moved to Holyrood Abbey in 1848. The original concept was never completed. Only the apse, choir and transepts were completed. The church was originally located in the valley between the Old Town and Calton Hill, but was systematically dismantled in the 1840s (under the supervision of David Bryce) due to the construction of Waverley Station on its site. Its stones were numbered in anticipation of rebuilding and were stored in a yard on Calton Hill. Reconstruction did not begin until 1872, when it was moved to a site on Chalmers Close on the newly formed Jeffrey Street overlooking the original site. Early history The church and hospital of So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regius Keeper Of The Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh
The Royal status of the Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh (RBGE) is intrinsically linked to the issue of a Royal Warrant to the first Intendant of the Gardens in 1699. Since that date, the appointment of each new Director of RBGE has required the assent of the reigning monarch of the United Kingdom, the appointee receiving the unique title Regius (= royal) Keeper. Just 29 years after the original Physic Garden was founded, by Dr (later Sir) Robert Sibbald and Dr (later Sir) Andrew Balfour, their appointed Garden overseer - James Sutherland - was rewarded for his diverse contributions: to the care of the gardens, to medical and botanical teaching and perhaps crucially, to the restoration of the King’s Garden at the Palace of Holyroodhouse. The Royal Warrant was issued on 12 January 1699, at the close of the 17th century. Until 1956 the office of Regius Keeper was combined with the office of His/Her Majesty's Botanist (also established in 1699). Since then the office of HM Bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |