|
John DeCou
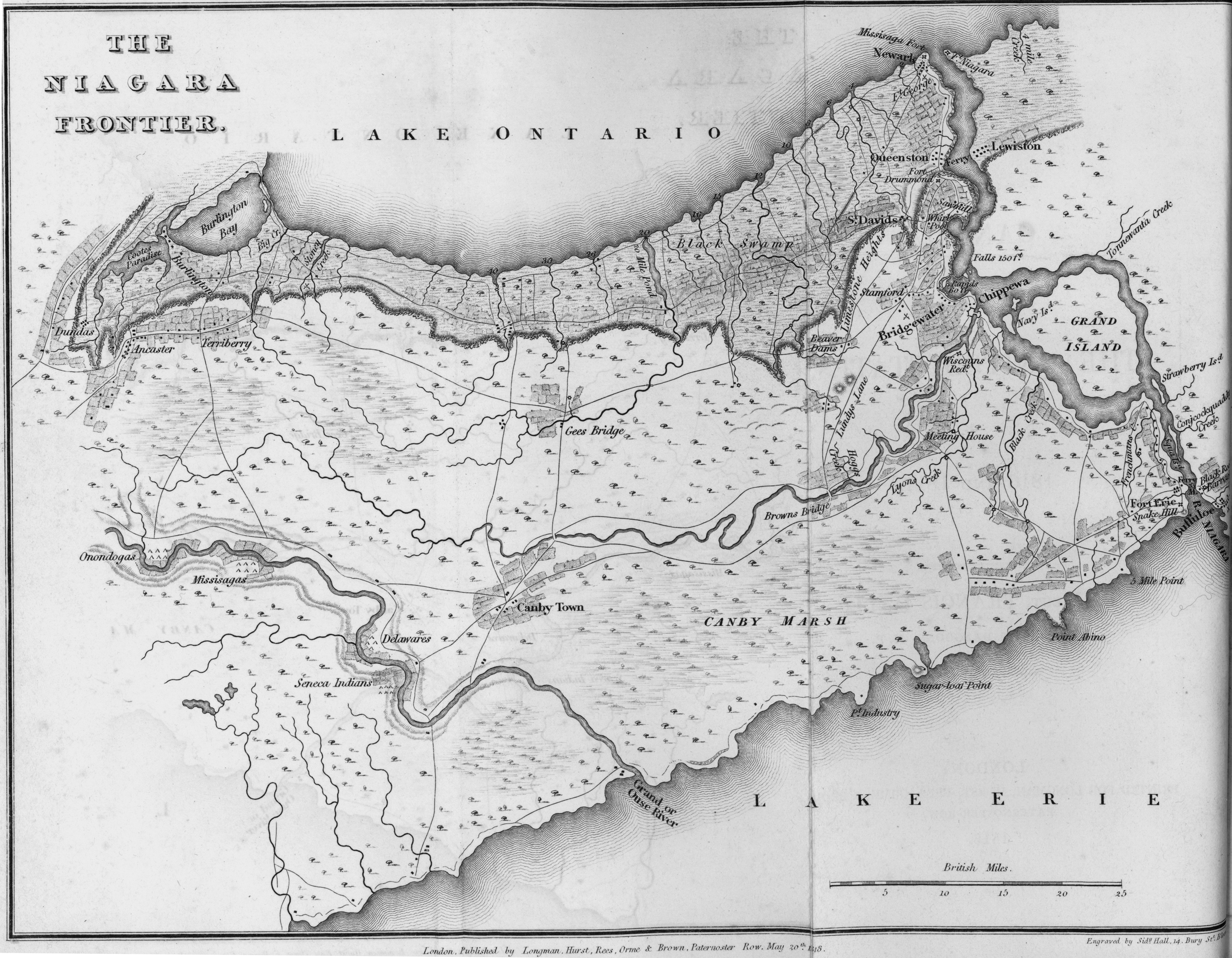
John DeCew (1766–1855), (variably spelt DeCou, Du Coo or DeCow, and sometimes with the "C" not capitalized) was a United Empire Loyalist, an early settler in the Niagara Peninsula of Upper Canada, a commissioned militia officer in the War of 1812, and a founding member of the Welland Canal Company. Early life DeCew was born in 1766 in the British colonies which would, after the War of American Independence, become the United States. The Dictionary of Canadian Biography Online indicates that he was born in New Jersey, whereas a plaque located in Thorold, Ontario, indicates that he was born in Vermont. He was the eldest son of Jacob DeCew and Elizabeth Bloome. With his family, who remained loyal to Britain after American independence, he immigrated to Upper Canada in 1787. In 1788, he served on a survey crew, and around the same time, acquired a site for a mill at what is currently known as DeCew Falls on Beaverdams Creek. He constructed one of the first sawmills in the region, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Empire Loyalist
United Empire Loyalists (or simply Loyalists) is an honorific title which was first given by the 1st Lord Dorchester, the Governor of Quebec, and Governor General of The Canadas, to American Loyalists who resettled in British North America during or after the American Revolution. At the time, the demonym ''Canadian'' or ''Canadien'' was used to refer to the indigenous First Nations groups and the descendants of New France settlers inhabiting the Province of Quebec. They settled primarily in Nova Scotia and the Province of Quebec. The influx of loyalist settlers resulted in the creation of several new colonies. In 1784, New Brunswick was partitioned from the Colony of Nova Scotia after significant loyalist resettlement around the Bay of Fundy. The influx of loyalist refugees also resulted in the Province of Quebec's division into Lower Canada (present-day Quebec), and Upper Canada (present-day Ontario) in 1791. The Crown gave them land grants of one lot. One lot consisted of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DeCou House
DeCew House (variably spelt DeCow, Du Coo or DeCou) was built c.1808 in Thorold Township, Upper Canada. The two-story house had limestone walls thick. Early history DeCew was a captain in the 2nd Lincoln Militia during the War of 1812, and also spent almost a year as a prisoner of war. During his absence, his house was used by the British army as a detachment headquarters under the command of Lieutenant James FitzGibbon. The house is remembered as the destination of Laura Secord's celebrated journey to warn the British of a planned American attack. Thanks to her warning, FitzGibbon was prepared for the attack, and in the ensuing Battle of Beaver Dams was able to secure the surrender of an American force of approximately 500 men. Following the war, DeCew lived in the house with his wife Katharine, raising eleven children and operating a mill (a predecessor of the Morningstar Mill) a short distance away. He sold the house when he relocated to Haldimand County in 1834. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lime Kiln
A lime kiln is a kiln used for the calcination of limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce the form of lime (material), lime called quicklime (calcium oxide). The chemical equation for this chemical reaction, reaction is :Calcium carbonate, CaCO3 + heat → Calcium oxide, CaO + Carbon dioxide, CO2 This reaction can take place at anywhere above 840 °C (1544 °F), but is generally considered to occur at 900 °C(1655 °F) (at which temperature the partial pressure of CO2 is 1 atmosphere (unit), atmosphere), but a temperature around 1000 °C (1832 °F) (at which temperature the partial pressure of CO2 is 3.8 atmospheres) is usually used to make the reaction proceed quickly.Parkes, G.D. and Mellor, J.W. (1939). ''Mellor's Modern Inorganic Chemistry'' London: Longmans, Green and Co. Excessive temperature is avoided because it produces unreactive, "dead-burned" lime. Slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) can be formed by mixing quicklime with water. Early li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand River (Ontario)
The Grand River, formerly known as The River Ouse, is a large river in Ontario, Canada. It lies along the western fringe of the Greater Golden Horseshoe region of Ontario which overlaps the eastern portion of southwestern Ontario, sometimes referred to as Midwestern Ontario, along the length of this river. From its source near Wareham, Ontario, it flows south through Grand Valley, Fergus, Elora, Waterloo, Kitchener, Cambridge, Paris, Brantford, Caledonia, and Cayuga before emptying into the north shore of Lake Erie south of Dunnville at Port Maitland. One of the scenic and spectacular features of the river is the falls and Gorge at Elora. The Grand River is the largest river that is entirely within southern Ontario's boundaries. The river owes its size to the unusual fact that its source is relatively close to the Georgian Bay of Lake Huron, yet it flows southwards to Lake Erie, rather than westward to the closer Lake Huron or northward to Georgian Bay (most southern Onta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haldimand County
Haldimand County is a rural city-status single-tier municipality on the Niagara Peninsula in Southern Ontario, Canada, on the north shore of Lake Erie, and on the Grand River. Despite its name, it is no longer a county by definition, as all municipal services are handled by a single level of government. Municipal offices are located in Cayuga. The county is adjacent to Norfolk County, the County of Brant, the City of Hamilton, and the Regional Municipality of Niagara. History Haldimand's history has been closely associated with that of neighbouring Norfolk County. Upper Canada was created in 1791 by being separated from the old Province of Quebec, Haldimand was created in 1798 as part of the Niagara District. It was named after Sir Frederick Haldimand, the governor of the Province of Quebec from 1778 to 1785. In 1844, the land was surrendered by the Six Nations to the Crown in an agreement that was signed by the vast majority of Chiefs in the Haldimand tract. From 1974 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebellions Of 1837
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority. A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and then manifests itself by the refusal to submit or to obey the authority responsible for this situation. Rebellion can be individual or collective, peaceful ( civil disobedience, civil resistance, and nonviolent resistance) or violent (terrorism, sabotage and guerrilla warfare). In political terms, rebellion and revolt are often distinguished by their different aims. While rebellion generally seeks to evade and/or gain concessions from an oppressive power, a revolt seeks to overthrow and destroy that power, as well as its accompanying laws. The goal of rebellion is resistance while a revolt seeks a revolution. As power shifts relative to the external adversary, or power shifts within a mixed coalition, or positions harden or soften on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Lyon Mackenzie
William Lyon Mackenzie (March12, 1795 August28, 1861) was a Scottish Canadian-American journalist and politician. He founded newspapers critical of the Family Compact, a term used to identify elite members of Upper Canada. He represented York County in the Legislative Assembly of Upper Canada and aligned with Reformers. He led the rebels in the Upper Canada Rebellion; after its defeat, he unsuccessfully rallied American support for an invasion of Upper Canada as part of the Patriot War. Although popular for criticising government officials, he failed to implement most of his policy objectives. He is one of the most recognizable Reformers of the early 19th century. Raised in Dundee, Scotland, Mackenzie emigrated to York, Upper Canada, in 1820. He published his first newspaper, the ''Colonial Advocate'' in 1824, and was elected a York County representative to the Legislative Assembly in 1827. York became the city of Toronto in 1834 and Mackenzie was elected its first mayor; h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legislative Assembly Of Upper Canada
The Legislative Assembly of Upper Canada was the elected part of the legislature for the province of Upper Canada, functioning as the lower house in the Parliament of Upper Canada. Its legislative power was subject to veto by the appointed List of lieutenant governors of Ontario, Lieutenant Governor, Executive Council of Upper Canada, Executive Council, and Legislative Council of Upper Canada, Legislative Council. The first elections in Upper Canada, in which only land-owning males were permitted to vote, were held in August 1792. The first session of the Assembly's sixteen members occurred in Newark, Upper Canada on 17 September 1792. Shortly before the capital of Upper Canada was moved to York, Upper Canada, York in 1796 the Assembly was dissolved and reconvened for twelve more sessions between 1797 and 1840 in modest buildings in the new capital. Members continued to be elected by land-owning males to represent counties and the larger towns. During the War of 1812, United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niagara Escarpment
The Niagara Escarpment is a long escarpment, or cuesta, in Canada and the United States that runs predominantly east–west from New York through Ontario, Michigan, Wisconsin, and into Illinois. The escarpment is most famous as the cliff over which the Niagara River plunges at Niagara Falls, for which it is named. The escarpment is a UNESCO World Biosphere Reserve. The reserve has the oldest forest ecosystem and trees in eastern North America. The escarpment is not a fault line but the result of unequal erosion. It is composed of an outcrop belt of the Lockport Formation of Silurian age, and is similar to the Onondaga Formation, which runs in a parallel outcrop belt just to the south, through western New York and southern Ontario. The escarpment is the most prominent of several escarpments formed in the bedrock of the Great Lakes Basin. From its easternmost point near Watertown, New York, the escarpment shapes in part the individual basins and landforms of Lake Ontario, Lak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welland River
The Welland River (originally called the Chippawa Creek) is a river in the Golden Horseshoe that passes through the Southern Ontario cities of Welland and Niagara Falls. It flows from its source just south of Hamilton, Ontario to meet the Niagara River. History The river was originally called the Chippawa Creek since it drained into the Niagara River at Chippawa. Like many other places in Niagara, it was renamed by John Graves Simcoe, the first lieutenant governor of Upper Canada in 1792. The present name was taken from the river of the same name in Lincolnshire, Eastern England. The Welland River is occasionally referred to as Chippawa Creek, especially by those in the Chippawa area itself. The Welland Canal was named after the river since it originally was planned to link Lake Ontario to Welland River. The city of Welland was later named after both waterways which crossed in the city. O'Reilly's Bridge The oldest structure spanning the Welland River was O'Reilly's Bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Hamilton Merritt
William Hamilton Merritt (July 3, 1793July 5, 1862) was a businessman and politician in the Niagara Peninsula of Upper Canada in the early 19th century. Although he was born in the United States, his family was Loyalist and eventually settled in Upper Canada. Merritt fought in the War of 1812, was captured by the invading American forces, and held as a prisoner of war. After the war, he returned to the Niagara region and began a career in business. He was one of the founders of the Welland Canal. Family and early life Merritt was born in Bedford in Westchester County, New York on July 3, 1793. His father, Thomas, fought as a United Empire Loyalist in the American Revolutionary War. After the revolution, the family resided in New Brunswick before returning to the U.S. In 1795, they moved to Upper Canada, settling on the Niagara Peninsula on the Twelve Mile Creek. Merritt attended school in Ancaster and Niagara, studying mathematics and field surveying. Afterwards, he b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twelve Mile Creek (Ontario)
Twelve Mile Creek is a waterway located on the Niagara Peninsula in the Regional Municipality of Niagara in Southern Ontario, Canada. Its headwaters are located in the town of Pelham, encompassing some of the most unspoiled and natural areas of Niagara area. The creek's lower reaches flow through urban areas of Thorold and St. Catharines and has been heavily altered by human activity for almost two centuries. The creek was first known as "Ashquasing" by the Mississaugas Indigenous people, the name meaning "that which lies at the end" in the Anishinaabe language. Watershed description Twelve Mile Creek is named because its outlet to Lake Ontario is located approximately from the Niagara River. It drains a watershed of approximately . This may be grouped into six sub-watersheds: * Upper Twelve Mile Creek * Lake Gibson System * Richardson Creek * Francis Creek * Dicks Creek * Lower Twelve Mile Creek Of these, only the Upper Twelve Mile Creek can truly be considered to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)