|
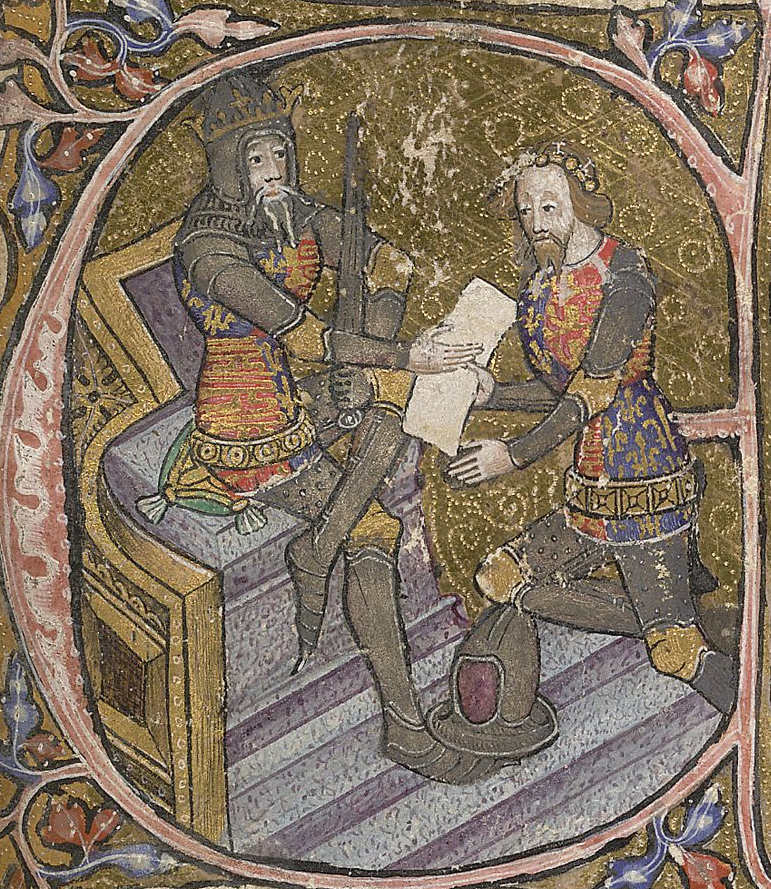
John Colton (archbishop)
John Colton ( 1320 – 1404) was a leading English-born academic, statesman and cleric of the fourteenth century. He was the first Master of Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge. He spent much of his career in Ireland, where he held the offices of Treasurer of Ireland, Lord Chancellor of Ireland and Archbishop of Armagh. He is chiefly remembered today for his book ''The Visitation of Derry'' (1397), which he either wrote or commissioned. Early career Little is known of his parents, or of his early years. He was born at Terrington St Clement in Norfolk.O'Flanagan J. Roderick ''The Lives of the Lord Chancellors of Ireland'' London 1870 He was in the service of William Bateman, who was Bishop of Norwich 1344–1355. He took a degree in divinity at the University of Cambridge in 1348 and the following year became the first Master of the new Gonville Hall, Cambridge, now Gonville and Caius College. The founder of the college, Edmund Gonville, had been a neighbour of Colton's in T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
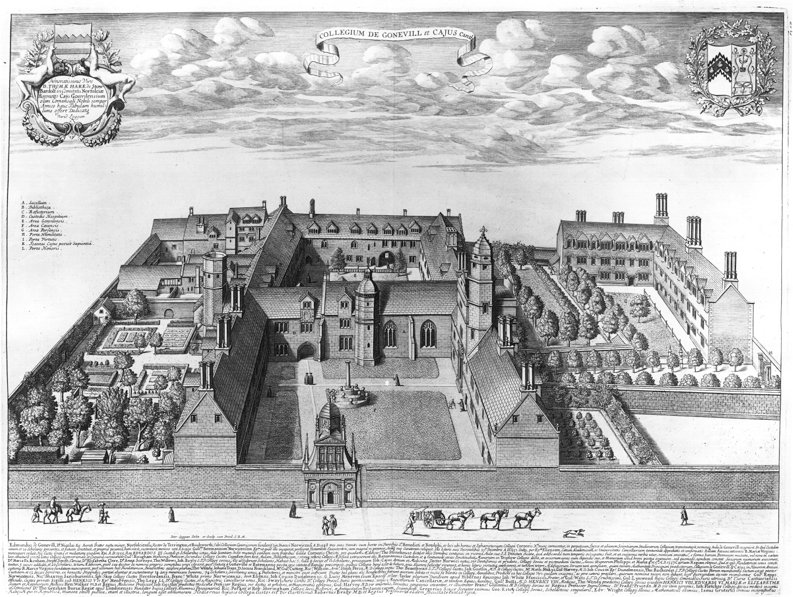
Gonville And Caius College, Cambridge
Gonville and Caius College, often referred to simply as Caius ( ), is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1348, it is the fourth-oldest of the University of Cambridge's 31 colleges and one of the wealthiest. The college has been attended by many students who have gone on to significant accomplishment, including fifteen Nobel Prize winners, the second-highest of any Oxbridge college after Trinity College, Cambridge. The college has long historical associations with the teaching of medicine, especially due to its prominent alumni in the medical profession. It also has globally-recognized and prestigious academic programmes in law, economics, English literature, and history. Famous Gonville and Caius alumni include physicians John Caius (who gave the college the caduceus in its insignia) and William Harvey. Other alumni in the sciences include Francis Crick (joint discoverer of the structure of DNA with James Watson), James Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal Court
The papal household or pontifical household (usually not capitalized in the media and other nonofficial use, ), called until 1968 the Papal Court (''Aula Pontificia''), consists of dignitaries who assist the pope in carrying out particular ceremonies of either a religious or a civil character. It is organised into two bodies: the Papal Chapel (''Cappella Pontificia''), which assists the pope in his functions as the spiritual head of the church, especially in religious ceremonies; and the Papal Family or Household (''Familia Pontificia''), which assists him as head of a juridical body with civil functions. Modern organisation Papal Chapel The Papal Chapel consists of ecclesiastics who participate in religious ceremonies wearing their liturgical vestments or the dress proper to their rank and office.''Annuario Pontificio'' 2013 (Libreria Editrice Vaticana 2013 ), p. 1850 Historically, chanted divine service was held daily in the papal palace, with the Pope in person celebrating or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Dublin
"Action to match our speech" , image_map = Island_of_Ireland_location_map_Dublin.svg , map_alt = map showing County Dublin as a small area of darker green on the east coast within the lighter green background of the Republic of Ireland, with Northern Ireland in pink , map_caption = County Dublin shown darker on the green of the Ireland, with Northern Ireland in pink , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Ireland , subdivision_type2 = Province , subdivision_name2 = Leinster , subdivision_type3 = Region , subdivision_name3 = Eastern and Midland , leader_title2 = Dáil constituencies , leader_name2 = , leader_title3 = EP constituency , leader_name3 = Dublin , seat_type = County town , seat = Dublin , area_total_km2 = 922 , area_rank = 30th , population_as_of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carrickmines
Carrickmines () is an outer suburb of Dublin in Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown, Ireland. The area, still semi-rural, was historically on the border of English control and featured a defensive construction, Carrickmines Castle, which became the subject of national controversy during the building of a late stage of Dublin's M50 orbital motorway. Character Previously a rural area, and today a semi-rural suburban region, Carrickmines is now divided northeast–southwest by the M50 motorway, with, to the northeast, more established residential areas, and to the southwest, including along Glenamuck Road, new retail parks, office buildings, housing schemes and apartments. Geography Carrickmines developed as a settlement in the more than 6 km long valley of the same name, which contains the modest Carrickmines River and its tributaries. The Ballyogan, Glenamuck and Golf Streams all merge in the vicinity. Downstream at Brennanstown, the river merges with St. Bride's Stream, from Foxrock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athy
Athy ( ; ) is a market town at the meeting of the River Barrow and the Grand Canal in south-west County Kildare, Ireland, 72 kilometres southwest of Dublin. A population of 9,677 (as of the 2016 census) makes it the sixth largest town in Kildare and the 50th largest in the Republic of Ireland, with a growth rate of approximately 60 per cent since the 2002 census. Name Athy or ''Baile Átha Í'' is named after a 2nd-century Celtic chieftain, Ae, who is said to have been killed on the river crossing, thus giving the town its name "the town of Ae's ford". The ''Letters of the Ordnance Survey'' (1837) note that "The town is now called by the few old people who speak Irish there and in the Queen's County Laois">/nowiki>Laois.html" ;"title="Laois.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Laois">/nowiki>Laois">Laois.html" ;"title="/nowiki>Laois">/nowiki>Laois/nowiki>, ''"baile átha Aoi"'', pronounced Blahéé", where ''éé'' stands for English 'ee' [i:] as clarified by a note written in pencil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard II
Richard II (6 January 1367 – ), also known as Richard of Bordeaux, was King of England from 1377 until he was deposed in 1399. He was the son of Edward the Black Prince, Prince of Wales, and Joan, Countess of Kent. Richard's father died in 1376, leaving Richard as heir apparent to his grandfather, King Edward III; upon the latter's death, the 10-year-old Richard succeeded to the throne. During Richard's first years as king, government was in the hands of a series of regency councils, influenced by Richard's uncles John of Gaunt and Thomas of Woodstock. England then faced various problems, most notably the Hundred Years' War. A major challenge of the reign was the Peasants' Revolt in 1381, and the young king played a central part in the successful suppression of this crisis. Less warlike than either his father or grandfather, he sought to bring an end to the Hundred Years' War. A firm believer in the royal prerogative, Richard restrained the power of the aristocracy and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cork (city)
Cork ( , from , meaning 'marsh') is the second largest city in Ireland and third largest city by population on the island of Ireland. It is located in the south-west of Ireland, in the province of Munster. Following an extension to the city's boundary in 2019, its population is over 222,000. The city centre is an island positioned between two channels of the River Lee which meet downstream at the eastern end of the city centre, where the quays and docks along the river lead outwards towards Lough Mahon and Cork Harbour, one of the largest natural harbours in the world. Originally a monastic settlement, Cork was expanded by Viking invaders around 915. Its charter was granted by Prince John in 1185. Cork city was once fully walled, and the remnants of the old medieval town centre can be found around South and North Main streets. The city's cognomen of "the rebel city" originates in its support for the Yorkist cause in the Wars of the Roses. Corkonians sometimes refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Mortimer, 3rd Earl Of March
Edmund de Mortimer, 3rd Earl of March and ''jure uxoris'' Earl of Ulster (1 February 135227 December 1381) was the son of Roger Mortimer, 2nd Earl of March, by his wife Philippa, daughter of William Montagu, 1st Earl of Salisbury and Catherine Grandison. Early life An infant at the death of his father, Edmund, as a ward of the crown, was placed by Edward III of England under the care of William of Wykeham and Richard FitzAlan, 10th Earl of Arundel. The position of the young earl, powerful on account of his possessions and hereditary influence in the Welsh marches, was rendered still more important by his marriage on 24 August 1369 at the age of 17 to the 14-year-old Philippa, the only child of the late Lionel of Antwerp, Duke of Clarence, the second son of Edward III. Lionel's late wife, Elizabeth, had been daughter and heiress of William Donn de Burgh, 3rd Earl of Ulster, and Lionel had himself been created Earl of Ulster before his marriage. Edmund inherited the title Earl of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justiciar Of Ireland
The chief governor was the senior official in the Dublin Castle administration, which maintained English and British rule in Ireland from the 1170s to 1922. The chief governor was the viceroy of the English monarch (and later the British monarch) and presided over the Privy Council of Ireland. In some periods he was in effective charge of the administration, subject only to the monarch in England; in others he was a figurehead and power was wielded by others. Nomenclature "Chief governor" is an umbrella term favoured by eighteenth-century historians Walter Harris and John Lodge and subsequently used by many historians and statutes. It was occasionally used before then. Chief governors were appointed under various titles, the most common of which were: * (Chief) justiciar (13th–14th centuries) * (King's) lieutenant (14th–16th century) * Lord Deputy (15th–17th centuries) * Lord Lieutenant (1660–1922) more formally Lieutenant General and General Governor or Lieutenant-Gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard FitzRalph
Richard FitzRalph (also Fitz Ralph; c. 1300 – 16 December 1360) was a scholastic philosopher, theologian, and Norman Irish Archbishop of Armagh during the 14th century. His thought exerted a significant influence on John Wycliffe's. Life FitzRalph was born into a well-off burgess family of Anglo-Norman/Hiberno-Norman descent in Dundalk, Ireland. He is noted as an ex-fellow and teacher of Balliol College, at the University of Oxford in 1325 (which is the earliest known record of him). By 1331, he was a Regent master in Theology, and soon after was made Vice-Chancellor of the university; this was an almost unparalleled achievement for someone still in his early thirties, let alone an Irishman (although Prince, in his "Worthies of Devon" makes the case for him being a Devonian). As Vice-Chancellor, FitzRalph was faced with the crisis caused by the famous secession of masters and students to found a university at Stamford in Lincolnshire, and it is thought that this issue may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
York Minster
The Cathedral and Metropolitical Church of Saint Peter in York, commonly known as York Minster, is the cathedral of York, North Yorkshire, England, and is one of the largest of its kind in Northern Europe. The minster is the seat of the Archbishop of York, the third-highest office of the Church of England (after the monarch as Supreme Governor and the Archbishop of Canterbury), and is the mother church for the Diocese of York and the Province of York. It is run by a dean and chapter, under the Dean of York. The title " minster" is attributed to churches established in the Anglo-Saxon period as missionary teaching churches, and serves now as an honorific title; the word ''Metropolitical'' in the formal name refers to the Archbishop of York's role as the Metropolitan bishop of the Province of York. Services in the minster are sometimes regarded as on the High Church or Anglo-Catholic end of the Anglican continuum. The minster was completed in 1472 after several centuries of buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


