|
John Campbell (Royal Navy Officer)
Vice-Admiral John Campbell (1720–1790) was born in the parish of Kirkbean in Kirkcudbrightshire, Scotland. Campbell was a British naval officer, navigational expert and colonial governor. Campbell joined the Royal Navy at an early age and sailed around the world in 1740 on ''Centurion''. He later became known as a navigational expert, and was from 1782 to his death Governor and Commander-in-Chief in Newfoundland. Life Early life John Campbell was born in the parish of Kirkbean, Scotland. His father, John Campbell (d. 1733), was minister of Kirkbean and John was at an early age apprenticed to the master of a coasting vessel. That vessel's mate was pressed into the navy, and John is said to have entered the navy by offering himself in exchange for him. He served for three years in ''Blenheim'', ''Torbay'', and ''Russell'' before being appointed in 1740 as a midshipman to ''Centurion''. On ''Centurions ensuing circumnavigation of the world as the flagship of Commodore G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkbean
Kirkbean ( gd, Cille Bheathain) is a Scottish village and civil parish on the Solway Firth, in the historic county of Kirkcudbrightshire and council area of Dumfries and Galloway. In the 2001 census, the four small villages making up the parish of Kirkbean had a total population of 643. It includes the hamlet of Loaningfoot. History The parish was the departure point for thousands of Scots seeking a better life in the American and Australian colonies during the late 18th and early 19th centuries. Convicts were also transported to Australia from here. This has made Kirkbean a rich source of genealogical history. Kirkbean was one of five parishes from Kirkcudbrightshire included in the Nithsdale district of Dumfries and Galloway under the local government reforms of 1975 which abolished Kirkcudbrightshire as an administrative county. The parish has therefore been included in the Dumfries lieutenancy area since 1975. Notable residents In birth order: * John Campbell (1720–1790 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augustus Keppel, 1st Viscount Keppel
Admiral (Royal Navy), Admiral Augustus Keppel, 1st Viscount Keppel, Her Majesty's Most Honourable Privy Council, PC (25 April 17252 October 1786) was a Royal Navy officer and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1755 to 1782. He saw action in command of various ships, including the fourth-rate , during the War of the Austrian Succession. He went on to serve as North America and West Indies Station, Commodore on the North American Station and then Jamaica Station (Royal Navy), Commander-in-Chief, Jamaica Station during the Seven Years' War. After that he served as First Sea Lord, Senior Naval Lord and then Commander-in-Chief of the Channel Fleet. During the American Revolutionary War Keppel came into a notorious dispute with Hugh Palliser, Sir Hugh Palliser over Palliser's conduct as his second-in-command at the inconclusive Battle of Ushant (1778), Battle of Ushant in July 1778; the dispute led to Keppel and Palliser facing courts martial, which acquitted both of them. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenwich
Greenwich ( , ,) is a town in south-east London, England, within the ceremonial county of Greater London. It is situated east-southeast of Charing Cross. Greenwich is notable for its maritime history and for giving its name to the Greenwich Meridian (0° longitude) and Greenwich Mean Time. The town became the site of a royal palace, the Palace of Placentia from the 15th century, and was the birthplace of many Tudors, including Henry VIII and Elizabeth I. The palace fell into disrepair during the English Civil War and was demolished to be replaced by the Royal Naval Hospital for Sailors, designed by Sir Christopher Wren and his assistant Nicholas Hawksmoor. These buildings became the Royal Naval College in 1873, and they remained a military education establishment until 1998 when they passed into the hands of the Greenwich Foundation. The historic rooms within these buildings remain open to the public; other buildings are used by University of Greenwich and Trinity Laban C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Bradley
James Bradley (1692–1762) was an English astronomer and priest who served as the third Astronomer Royal from 1742. He is best known for two fundamental discoveries in astronomy, the aberration of light (1725–1728), and the nutation of the Earth's axis (1728–1748). These two discoveries were called "the most brilliant and useful of the century" by Jean Baptiste Joseph Delambre, historian of astronomy, mathematical astronomer and director of the Paris Observatory. In his ''History of astronomy in the 18th century'' (1821), Delambre stated:"It is to these two discoveries by Bradley that we owe the exactness of modern astronomy. ... This double service assures to their discoverer the most distinguished place (after Hipparchus and Kepler) above the greatest astronomers of all ages and all countries." Biography Bradley was born at Sherborne, near Cheltenham in Gloucestershire, to William Bradley and Jane Pound in September 1692. His nephew John was also an astronomer. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomer Royal
Astronomer Royal is a senior post in the Royal Households of the United Kingdom. There are two officers, the senior being the Astronomer Royal dating from 22 June 1675; the junior is the Astronomer Royal for Scotland dating from 1834. The post was created by King Charles II in 1675, at the same time as he founded the Royal Observatory Greenwich. He appointed John Flamsteed, instructing him "." The Astronomer Royal was director of the Royal Observatory Greenwich from the establishment of the post in 1675 until 1972. The Astronomer Royal became an honorary title in 1972 without executive responsibilities and a separate post of Director of the Royal Greenwich Observatory was created to manage the institution. The Astronomer Royal today receives a stipend of 100 GBP per year and is a member of the Royal Household, under the general authority of the Lord Chamberlain. After the separation of the two offices, the position of Astronomer Royal has been largely honorary, though the ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
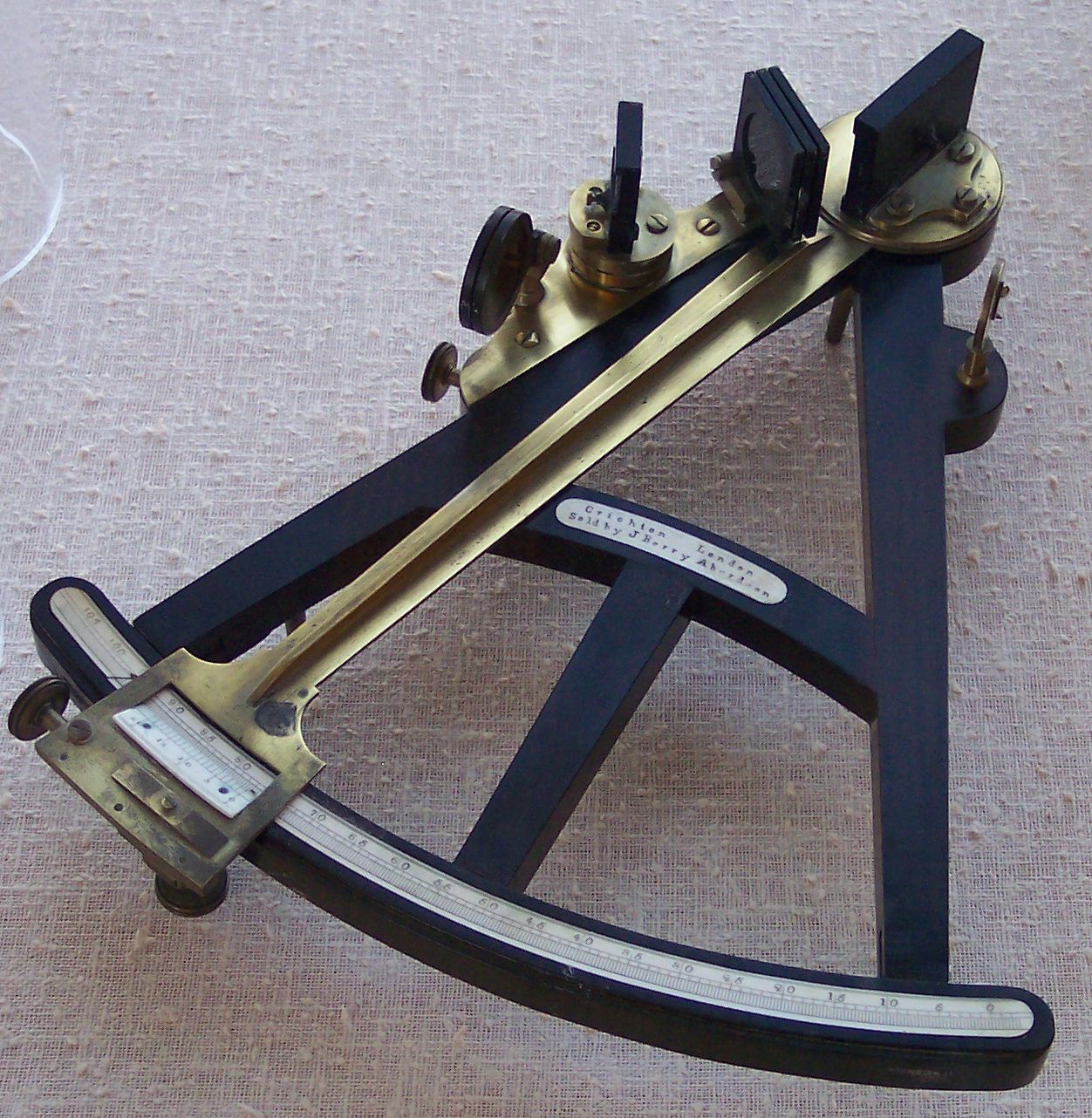
Octant (instrument)
The octant, also called a reflecting quadrant (instrument), quadrant, is a reflecting instrument used in navigation. Etymology The name ''octant'' derives from the Latin ''octans'' meaning ''eighth part of a circle'', because the instrument's arc is one eighth of a circle. ''Reflecting quadrant'' derives from the instrument using mirrors to reflect the path of light to the observer and, in doing so, doubles the angle measured. This allows the instrument to use a one-eighth of a Turn (geometry), turn to measure a quarter-Turn (geometry), turn or Circular sector, quadrant. Origin of the octant Newton's reflecting quadrant Isaac Newton's reflecting quadrant was invented around 1699. A detailed description of the instrument was given to Edmond Halley, but the description was not published until after Halley's death in 1742. It is not known why Halley did not publish the information during his life, as this prevented Newton from getting the credit for the invention that is gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North East Passage
The Northern Sea Route (NSR) (russian: Се́верный морско́й путь, ''Severnyy morskoy put'', shortened to Севморпуть, ''Sevmorput'') is a shipping route officially defined by Russian legislation as lying east of Novaya Zemlya and specifically running along the Russian Arctic coast from the Kara Sea, along Siberia, to the Bering Strait. To be more precise, The Northern Sea Route crosses the seas of the Arctic Ocean (Kara Sea, Laptev Sea, East Siberian Sea, and Chukchi Sea). Administratively, in the west the NSR is bounded by the western entrances to the Novaya Zemlya straits and by the meridian running north from Cape Zhelaniya, and in the east, in the Bering Strait, it is bounded by the parallel of 66 ° N and the meridian of 168 ° 58′37 ″ W. The entire route lies in Arctic waters and within Russia's exclusive economic zone (EEZ). Parts are free of ice for only two months per year. The overall route on Russia's side of the Arctic between No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North West Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arctic coasts of Norway and Siberia is accordingly called the Northeast Passage (NEP). The various islands of the archipelago are separated from one another and from Mainland Canada by a series of Arctic waterways collectively known as the Northwest Passages, Northwestern Passages or the Canadian Internal Waters. For centuries, European explorers, beginning with Christopher Columbus in 1492, sought a navigable passage as a possible trade route to Asia, but were blocked by North, Central, and South America, by ice, or by rough waters (e.g. Tierra del Fuego). An ice-bound northern route was discovered in 1850 by the Irish explorer Robert McClure. Scotsman John Rae explored a more southerly area in 1854 through which Norwegian Roald Amundsen f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Raven (1745)
Fourteen ships and a shore establishment of the Royal Navy have borne the name ''Raven'', after birds of the genus ''Corvus'', particularly the common raven: Ships * was a 36-gun ship captured in 1652, and captured by the Dutch in 1654. * was a 6-gun vessel, possibly a French ship, previously named ''St Cornelius''. She was captured in 1656 and listed until 1659. * was a 14-gun sloop launched in 1745 and sold in 1763. *HMS ''Raven'' was a sloop, previously the 8-gun fireship launched in 1771. She was renamed ''Raven'' later that year and was sold in 1780. * HMS ''Raven'' was an 18-gun sloop, launched in 1777 as ''Ceres'' that the French captured in 1778. The British recaptured her in 1782 and renamed her ''Raven'', only to have the French recapture her again early in 1783. She served in the French Navy until sold at Brest in 1791. * was a 14-gun sloop launched in 1796 and wrecked in 1798. * HMS ''Raven'' was an 18-gun brig-sloop, previously the French ''Aréthuse''. She was capt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Porcupine
Nine vessels of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy have been named HMS ''Porcupine'', after the porcupine, a rodent belonging to the families Erethizontidae or Hystricidae. * was a 16-gun sloop launched in 1743, purchased in 1746, and sold in 1763. She became the mercantile ''Minerva'', which in 1768 traded between London and Africa.''Lloyd's Register'(1768), Seq.No.M295./ref> * was a 24-gun post ship launched in 1777 and broken up in 1805. *HMS ''Porcupine'' was a 16-gun sloop purchased in Jamaica in 1777 and sold in 1788. * was a 22-gun post ship launched in 1807 and sold in 1816. *HMS ''Porcupine'' was to have been a 28-gun sixth rate; ordered in 1819, she was canceled in 1832. * was a wooden paddle wheel surveying vessel built at Deptford and sold in 1883. * was a launched by Palmers in 1895 that served in home waters and was sold in 1920. * was a P-class destroyer launched in 1941 and torpedoed by in the Mediterranean Sea The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Bellona (1747)
''Bellone'', was a French privateer. ''Bellone'' was involved in a naval battle in Loch nan Uamh during the Jacobite rising. She was captured in 1747. She was taken into Royal Navy service as HMS ''Bellona'' and was sold in 1749. French service Following the Jacobite defeat at the Battle of Culloden on 16 April 1746, ''Bellone'' and ''Mars'' anchored at Loch nan Uamh on 30 April 1746.McKerracher, Mairead. (2012). Jacobite Dictionary'. (no page numbers). Neil Wilson Publishing. Upon the approach of the Royal Navy vessels , , and , Captain Claude Lory of ''La Bellone'' set sail; Captain Antoine Rouillé of ''Le Mars'' decided to stay at anchor. After ''Greyhound'' attacked ''Le Mars'', ''La Bellone'' engaged ''HMS Greyhound'' and ''Bellone'' suffered a broken mast after a broadside. ''HMS Greyhound'' attempted to board ''LA Bellone'', however after firing two broadsides into ''HMS Greyhound'', ''La Bellone'' then disabled ''HMS Terror'' with a volley. ''La Bellone'' led ''Le Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frigate
A frigate () is a type of warship. In different eras, the roles and capabilities of ships classified as frigates have varied somewhat. The name frigate in the 17th to early 18th centuries was given to any full-rigged ship built for speed and maneuverability, intended to be used in scouting, escort and patrol roles. The term was applied loosely to ships varying greatly in design. In the second quarter of the 18th century, the 'true frigate' was developed in France. This type of vessel was characterised by possessing only one armed deck, with an unarmed deck below it used for berthing the crew. Late in the 19th century (British and French prototypes were constructed in 1858), armoured frigates were developed as powerful ironclad warships, the term frigate was used because of their single gun deck. Later developments in ironclad ships rendered the frigate designation obsolete and the term fell out of favour. During the Second World War the name 'frigate' was reintroduced to des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)