|
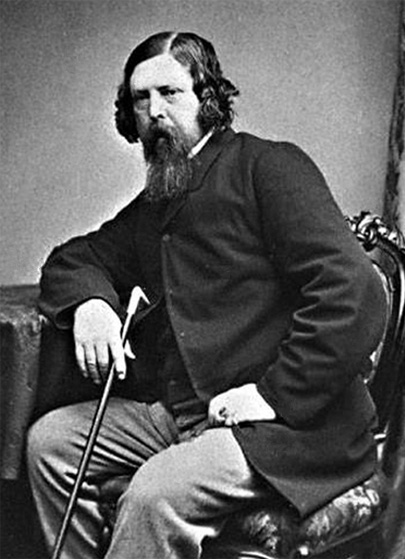
John Batty Tuke
Sir John Batty Tuke PRCPE FRSE LLD (9 January 1835 – 13 October 1913) was one of the most influential psychiatrists in Scotland in the late nineteenth century, and a Unionist Member of Parliament (MP) from 1900 to 1910. Tuke's career in Edinburgh from 1863 to 1910 spanned a period of significant social and political changes in asylum governance and care in Scotland. Tuke's professional success in public and private practice and his powerful role in several prominent medical societies allowed him to influence his colleagues toward a more physiological understanding of mental illness and its treatment. Biography Batty Tuke (as he is most often referenced) was born in Beverley, England on 9 January 1835, the son of John Batty Tuke."Obituary: Sir John Batty Tuke", The British Medical Journal (13 October 1913):1045. Articles about Batty Tuke link him to the famous Tuke family that founded the York Retreat. In 1845 Tuke was sent to Edinburgh where he began attending Edinburgh Aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beverley, England
Beverley is a market and minster town and a civil parish in the East Riding of Yorkshire, England, of which it is the county town. The town centre is located south-east of York's centre and north-west of City of Hull. The town is known for Beverley Minster, Beverley Westwood, North Bar (a 15th-century gate) and Beverley Racecourse. It inspired the naming of the city of Beverly, Massachusetts, which in turn was the impetus for Beverly Hills, California.Marc Wanamaker, ''Early Beverly Hills'', Mount Pleasant, South Carolina: Arcadia Publishing, 2005, pp. 17–1/ref> The town was listed in the 2018 ''Sunday Times'' report on Best Places to Live in northern England. The town was originally known as ''Inderawuda'' and was founded around 700 AD by Saint John of Beverley during the time of the Anglian kingdom of Northumbria. After a period of Viking control, it passed to the Cerdic dynasty, a period during which it gained prominence in terms of religious importance in Grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Skae
David Skae MD, FRCSEd (5 July 1814 – 18 April 1873) was a Scottish physician who specialised in psychological medicine. He has been described as the founder of the Edinburgh School of Psychiatry and several of his assistants and pupils went on to become leading psychiatrists throughout the British Isles. Life David Skae was born at 5 Elder Street in Edinburgh the son of David Skae, an architect and builder, and his wife, Helen Lothian. Both parents died whilst David was a child, and he was educated by his maternal uncle, the Rev. William Lothian, at St Andrews. At the age of fourteen Skae began his university career, studying liberal arts at the University of St Andrews. At sixteen years of age he left St Andrews to take up a post as a clerk in a lawyer's office in Edinburgh. Shortly thereafter he enrolled as a medical student and in 1835 he qualified as a Licentiate of the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh (LRCSEd). In the following year he was awarded Fellowship of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Tennant Gairdner
Sir William Tennant Gairdner (8 November 1824 – 28 June 1907) was a Scottish Professor of Medicine in the University of Glasgow. Early life William Tennant Gardiner was born in Edinburgh, the son of physician John Gairdner and his wife, Susanna Tennant.''Scotland, Select Births and Baptisms, 1564-1950'' He was the elder brother of the historian James Gairdner. He was educated at the Edinburgh Institution and then in his father's profession at the University of Edinburgh, graduating as M.D. in 1845. Immediately after his graduation he went to Rome for six months. He was taught surgery by Prof Monro and Dr Robert Halliday Gunning. Medical career In 1850 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh; and a year or two later was appointed physician and pathologist to the Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh (RIE). During his time at the RIE he was a lecturer at the Edinburgh Extramural School of Medicine. In 1862 he accepted an invitation to take the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commissioners In Lunacy For Scotland
The Commissioners in Lunacy for Scotland or Lunacy Commission for Scotland were a public body established by the Lunacy (Scotland) Act 1857 to oversee asylums and the welfare of mentally ill people in Scotland. Previous bodies The Madhouses (Scotland) Act 1815 established the right of Scottish Sheriffs to order the inspection of madhouses. Establishment The Board of Commissioners in Lunacy for Scotland was established in 1857 by the Lunacy (Scotland) Act 1857. There were two Commissioners of Lunacy each paid £1,200 a year and two Deputy Commissioners each paid £600 a year. Chairmen of the board were as follows: * 1857-1859 William Elliot-Murray-Kynynmound, 3rd Earl of Minto * 1859-1863 William Forbes Mackenzie * 1863-1894 Sir John Don-Wauchope * 1894-1897 Sir Thomas Gibson-Carmichael * 1897-1909 Walter George Hepburne-Scott, 9th Lord Polwarth * 1909-1913 Sir Thomas Mason The Commissioners themselves were physicians. Mainly based at 51 Queen Street in Edinburgh. These includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Smith (physician)
Dr John C. Douglas Smith FRSE PRCPE (c.1800–4 February 1879) was a 19th-century Scottish physician specialising in treating the insane, who served as President of the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh from 1865 to 1867. Life He was born in Edinburgh around 1800 and educated at George Heriot's School. He was apprenticed to George Wood surgeon at 28 Queen Street. He then studied medicine at the University of Edinburgh gaining his doctorate (MD) in 1822. He worked variously at the Saughton Hall Asylum for the Insane (created in 1824), the Edinburgh Charity Workhouse and the Bedlam Asylum on Forest Road. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh in 1833. In 1834 Smith was elected a member of the Harveian Society of Edinburgh and served as President in 1850. In 1838 he was elected a member of the Aesculapian Club. In 1865 he was elected President of the Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh in succession to Dr John Moir. At this t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honoris Causa
An honorary degree is an academic degree for which a university (or other degree-awarding institution) has waived all of the usual requirements. It is also known by the Latin phrases ''honoris causa'' ("for the sake of the honour") or ''ad honorem '' ("to the honour"). The degree is typically a doctorate or, less commonly, a master's degree, and may be awarded to someone who has no prior connection with the academic institution or no previous postsecondary education. An example of identifying a recipient of this award is as follows: Doctorate in Business Administration (''Hon. Causa''). The degree is often conferred as a way of honouring a distinguished visitor's contributions to a specific field or to society in general. It is sometimes recommended that such degrees be listed in one's curriculum vitae (CV) as an award, and not in the education section. With regard to the use of this honorific, the policies of institutions of higher education generally ask that recipients ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warriston Cemetery
Warriston Cemetery is a cemetery in Edinburgh. It lies in Warriston, one of the northern suburbs of Edinburgh, Scotland. It was built by the then newly-formed Edinburgh Cemetery Company, and occupies around of land on a slightly sloping site. It contains many tens of thousands of graves, including notable Victorian and Edwardian figures, the most eminent being the physician Sir James Young Simpson. It is located on the north side of the Water of Leith, and has an impressive landscape; partly planned, partly unplanned due to recent neglect. It lies in the Inverleith Conservation Area and is also a designated Local Nature Conservation Site. The cemetery is protected as a Category A listed building. In July 2013 the Friends of Warriston Cemetery was inaugurated to reveal the heritage and to encourage appropriate biodiversity. The address of the cemetery is 40C Warriston Gardens, Edinburgh EH3 5NE. History Designed in 1842 by Edinburgh architect David Cousin, the cemet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
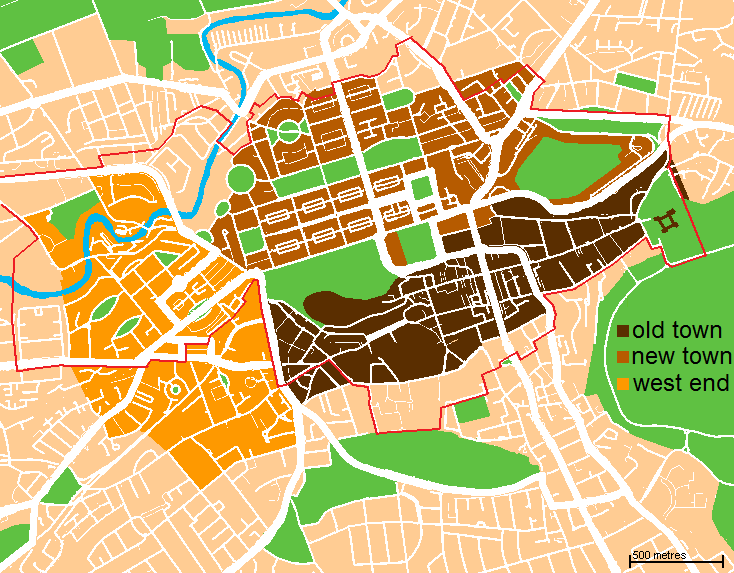
New Town, Edinburgh
The New Town is a central area of Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It was built in stages between 1767 and around 1850, and retains much of its original neo-classical and Georgian period architecture. Its best known street is Princes Street, facing Edinburgh Castle and the Old Town across the geological depression of the former Nor Loch. Together with the West End, the New Town was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site alongside the Old Town in 1995. The area is also famed for the New Town Gardens, a heritage designation since March 2001. Proposal and planning The idea of a New Town was first suggested in the late 17th century when the Duke of Albany and York (later King James VII and II), when resident Royal Commissioner at Holyrood Palace, encouraged the idea of having an extended regality to the north of the city and a North Bridge. He gave the city a grant:That, when they should have occasion to enlarge their city by purchasing ground without the town, or to build ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlotte Square
300px, Robert Adam's palace-fronted north side Charlotte Square is a garden square in Edinburgh, Scotland, part of the New Town, designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The square is located at the west end of George Street and was intended to mirror St. Andrew Square in the east. The gardens, one of the collection of New Town Gardens, are private and not publicly accessible. History Initially named St. George's Square in James Craig's original plan, it was renamed in 1786 after King George III's Queen and first daughter, to avoid confusion with George Square to the south of the Old Town. Charlotte Square was the last part of the initial phase of the New Town to be "completed" in 1820 (note- the north-west section at Glenfinlas Street was not completed until 1990 due to a long-running boundary dispute). Much of it was to the 1791 design of Robert Adam, who died in 1792, just as building began. In 1939 a very sizable air-raid shelter was created under the south side of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edinburgh And St Andrews Universities (UK Parliament Constituency)
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian on the southern shore of the Firth of Forth. Edinburgh is Scotland's List of towns and cities in Scotland by population, second-most populous city, after Glasgow, and the List of cities in the United Kingdom, seventh-most populous city in the United Kingdom. Recognised as the capital of Scotland since at least the 15th century, Edinburgh is the seat of the Scottish Government, the Scottish Parliament and the Courts of Scotland, highest courts in Scotland. The city's Holyrood Palace, Palace of Holyroodhouse is the official residence of the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, British monarchy in Scotland. The city has long been a centre of education, particularly in the fields of medicine, Scots law, Scottish law, literature, philosophy, the sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Member Of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members often have a different title. The terms congressman/congresswoman or deputy are equivalent terms used in other jurisdictions. The term parliamentarian is also sometimes used for members of parliament, but this may also be used to refer to unelected government officials with specific roles in a parliament and other expert advisers on parliamentary procedure such as the Senate Parliamentarian in the United States. The term is also used to the characteristic of performing the duties of a member of a legislature, for example: "The two party leaders often disagreed on issues, but both were excellent parliamentarians and cooperated to get many good things done." Members of parliament typically form parliamentary groups, sometimes called caucuse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sir John Batty Tuke - Bust
''Sir'' is a formal honorific address in English language, English for men, derived from Sire in the High Middle Ages. Both are derived from the old French "Sieur" (Lord), brought to England by the French-speaking Normans, and which now exist in French only as part of "Monsieur", with the equivalent "My Lord" in English. Traditionally, as governed by law and custom, Sir is used for men titled as knights, often as members of Order of chivalry, orders of chivalry, as well as later applied to baronets and other offices. As the female equivalent for knighthood is damehood, the female equivalent term is typically Dame. The wife of a knight or baronet tends to be addressed as Lady, although a few exceptions and interchanges of these uses exist. Additionally, since the late modern period, Sir has been used as a respectful way to address a man of superior social status or military rank. Equivalent terms of address for women are Madam (shortened to Ma'am), in addition to social honorifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |