|
Johann Von Charpentier
Jean de Charpentier or Johann von Charpentier (8 December 1786 – 12 December 1855) was a German-Swiss geologist who studied Swiss glaciers. He was born in Freiberg, Saxony, Germany and died in Bex, Switzerland. Life After following in his father's footsteps as a mining engineer he excelled in his field while working in the copper mines in the Pyrénées and salt mines in western Switzerland. In 1818 a catastrophic event changed his life focus when an ice-dammed lake in the Val de Bagnes above Martigny broke through its barrier, causing many deaths. Afterwards, he made extensive field studies in the Alps. Using evidence of erratic boulders and moraines and drawing on the works of Goethe, he hypothesized that Swiss glaciers had once been much more extensive. These boulders, characteristic of glaciers, were strewn as if they were brought there by glaciers that no longer existed. Even so, he wasn't sure how glaciers first formed, moved, or how they disappeared. His ideas were l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Von Charpentier
Jean de Charpentier or Johann von Charpentier (8 December 1786 – 12 December 1855) was a German-Swiss geologist who studied Swiss glaciers. He was born in Freiberg, Saxony, Germany and died in Bex, Switzerland. Life After following in his father's footsteps as a mining engineer he excelled in his field while working in the copper mines in the Pyrénées and salt mines in western Switzerland. In 1818 a catastrophic event changed his life focus when an ice-dammed lake in the Val de Bagnes above Martigny broke through its barrier, causing many deaths. Afterwards, he made extensive field studies in the Alps. Using evidence of erratic boulders and moraines and drawing on the works of Goethe, he hypothesized that Swiss glaciers had once been much more extensive. These boulders, characteristic of glaciers, were strewn as if they were brought there by glaciers that no longer existed. Even so, he wasn't sure how glaciers first formed, moved, or how they disappeared. His ideas were l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
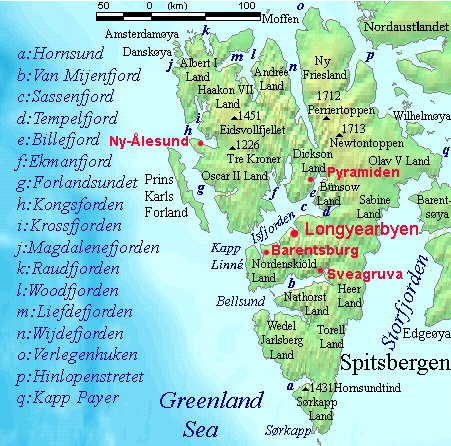
Charpentierbreen
Charpentierbreen is a glacier in Nathorst Land at Spitsbergen, Svalbard. It is named after Swiss geologist Jean de Charpentier Jean de Charpentier or Johann von Charpentier (8 December 1786 – 12 December 1855) was a German-Swiss geologist who studied Swiss glaciers. He was born in Freiberg, Saxony, Germany and died in Bex, Switzerland. Life After following in his f .... The glacier has a length of about four kilometers, and is located within the mountain range of Törnbohmfjella, flowing eastwards from the peak of Såta down to the valley of Davisdalen. The mountain of Venetzhumpen separates Charpentierbreen from Venetzbreen. References Glaciers of Spitsbergen {{spitsbergen-glacier-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1855 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 – Ottawa, Ontario, is incorporated as a city. * January 5 – Ramón Castilla begins his third term as President of Peru. * January 23 ** The first bridge over the Mississippi River opens in modern-day Minneapolis, a predecessor of the Father Louis Hennepin Bridge. ** The 8.2–8.3 Wairarapa earthquake claims between five and nine lives near the Cook Strait area of New Zealand. * January 26 – The Point No Point Treaty is signed in the Washington Territory. * January 27 – The Panama Railway becomes the first railroad to connect the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. * January 29 – Lord Aberdeen resigns as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, over the management of the Crimean War. * February 5 – Lord Palmerston becomes Prime Minister of the United Kingdom. * February 11 – Kassa Hailu is crowned Tewodros II, Emperor of Ethiopia. * February 12 – Michigan State University (the "pioneer" land- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1786 Births
Events January–March * January 3 – The third Treaty of Hopewell is signed, between the United States and the Choctaw. * January 6 – The outward bound East Indiaman '' Halsewell'' is wrecked on the south coast of England in a storm, with only 74 of more than 240 on board surviving. * February 2 – In a speech before The Asiatic Society in Calcutta, Sir William Jones notes the formal resemblances between Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, laying the foundation for comparative linguistics and Indo-European studies. * March 1 – The Ohio Company of Associates is organized by five businessmen at a meeting at the Bunch-of-Grapes Tavern in Boston, to purchase land from the United States government to form settlements in what is now the U.S. state of Ohio. * March 13 – Construction begins in Dublin on the Four Courts Building, with the first stone laid down by the United Kingdom's Viceroy for Ireland, the Duke of Rutland. April–June * Apri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Gordon
Dame Maria Matilda Gordon (née Ogilvie; 30 April 1864 – 24 June 1939), sometimes known as May Ogilvie Gordon or May Gordon, was an eminent Scottish geologist, palaeontologist, and politician. She was the first woman to be awarded a Doctor of Science from University of London and the first woman to be awarded a PhD from the University of Munich.Wachtler, M. and Burek, C.V. 2007Maria Matilda Ogilvie Gordon (1864–1939): a Scottish researcher in the Alps Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 281(1), pp.305-317. She was also a supporter and campaigner for the rights and equality of children and women. Early life and education Ogilvie was born in Monymusk, Aberdeenshire in April 1864, making her the eldest daughter of eight children (five brothers and two sisters, one of who passed away in infanthood). With her parents being Maria Matilda Nichol and Reverend Alexander Ogilvie LL.D.. Her family was overall very well educated and had good connections and friends in va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Alfred Von Zittel
Karl Alfred Ritter von Zittel (25 September 1839 – 5 January 1904) was a German palaeontologist best known for his ''Handbuch der Palaeontologie'' (1876–1880). Biography Karl Alfred von Zittel was born in Bahlingen in the Grand Duchy of Baden. His father, Karl was a leading liberal cleric in Baden. He was educated at the University of Heidelberg, the University of Paris and the University of Vienna. For a short period he served on the Geological Survey of Austria, and as assistant in the mineralogical museum at Vienna. In 1863, he became teacher of geology and mineralogy in the polytechnic at Karlsruhe, and three years later he succeeded Albert Oppel as professor of palaeontology in the University of Munich, with the charge of the state collection of fossils. In 1880, he was appointed to the geological professorship, and eventually to the directorship of the natural history museum of Munich. His earlier work comprised a monograph on the ''Cretaceous bivalve mollusca of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and greenhouse periods, during which there are no glaciers on the planet. Earth is currently in the Quaternary glaciation. Individual pulses of cold climate within an ice age are termed ''glacial periods'' (or, alternatively, ''glacials, glaciations, glacial stages, stadials, stades'', or colloquially, ''ice ages''), and intermittent warm periods within an ice age are called '' interglacials'' or ''interstadials''. In glaciology, ''ice age'' implies the presence of extensive ice sheets in both northern and southern hemispheres. By this definition, Earth is currently in an interglacial period—the Holocene. The amount of anthropogenic greenhouse gases emitted into Earth's oceans and atmosphere is predicted to prevent the next glacial period for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian Polar Institute
The Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI; no, Norsk Polarinstitutt) is Norway's central governmental institution for scientific research, mapping and environmental monitoring in the Arctic and the Antarctic. The NPI is a directorate under Norway's Ministry of Climate and Environment. The institute advises Norwegian authorities on matters concerning polar environmental management and is the official environmental management body for Norwegian activities in Antarctica. Activities The institute's activities are focused on environmental research and management in the polar regions. The NPI's researchers investigate biodiversity, climate and environmental toxins in the Arctic and Antarctic, and in this context the institute equips and organizes large-scale expeditions to both polar regions. The institute contributes to national and international climate work, and is an active contact point for the international scientific community. The institute collects and analyses data on the environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svalbard
Svalbard ( , ), also known as Spitsbergen, or Spitzbergen, is a Norwegian archipelago in the Arctic Ocean. North of mainland Europe, it is about midway between the northern coast of Norway and the North Pole. The islands of the group range from 74° to 81° north latitude, and from 10° to 35° east longitude. The largest island is Spitsbergen, followed by Nordaustlandet and . The largest settlement is Longyearbyen. The islands were first used as a base by the whalers who sailed far north in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which they were abandoned. Coal mining started at the beginning of the 20th century, and several permanent communities were established. The Svalbard Treaty of 1920 recognizes Norwegian sovereignty, and the 1925 Svalbard Act made Svalbard a full part of the Kingdom of Norway. They also established Svalbard as a free economic zone and a demilitarized zone. The Norwegian Store Norske and the Russian remain the only mining companies in place. Res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitsbergen
Spitsbergen (; formerly known as West Spitsbergen; Norwegian: ''Vest Spitsbergen'' or ''Vestspitsbergen'' , also sometimes spelled Spitzbergen) is the largest and the only permanently populated island of the Svalbard archipelago in northern Norway. Constituting the westernmost bulk of the archipelago, it borders the Arctic Ocean, the Norwegian Sea, and the Greenland Sea. Spitsbergen covers an area of , making it the largest island in Norway and the 36th-largest in the world. The administrative centre is Longyearbyen. Other settlements, in addition to research outposts, are the Russian mining community of Barentsburg, the research community of Ny-Ålesund, and the mining outpost of Sveagruva. Spitsbergen was covered in of ice in 1999, which was approximately 58.5% of the island's total area. The island was first used as a whaling base in the 17th and 18th centuries, after which it was abandoned. Coal mining started at the end of the 19th century, and several permanent commun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathorst Land
Nathorst Land is the land area between Van Keulenfjorden and Van Mijenfjorden on Spitsbergen, Svalbard. The area is named after Alfred Gabriel Nathorst Alfred Gabriel Nathorst (7 November 1850 – 20 January 1921) was a Swedish Arctic explorer, geologist, and palaeobotanist. Life He was born in Väderbrunn in Sweden. Nathorst's interest in geology was awoken by Charles Lyell’s ‘’Pr .... The Aspelintoppen mountain is the highest peak in Nathorst Land. References Peninsulas of Spitsbergen {{Spitsbergen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |