|
Johann Otto Uhde
Johann Otto Uhde (born Insterburg 12 May 1725; died Berlin 20 December 1766) was a German composer and violinist. Although he studied violin from age 8 and performed as a soloist in high social circles in Berlin, Uhde became an attorney and practised law in Berlin from 1746 to his death. As an amateur musician he exemplified a movement in the mid-18th century toward amateur music making. He is primarily remembered, however, as a composer, especially of music for amateurs and students. Several of his compositions were published anonymously in Berlin (most likely in anthologies such as the ''Musikalisches Mancherley'' and the ''Musikalischen Nebenstunden''). His manuscripts were acquired by the Harvard University library when it acquired the music collection of Franz Hauser (1794-1870). They include three violin concertos (E-flat, D minor, A minor), two flute concertos, a harpsichord concerto, a trio sonata, and 8 vocal works (cantata A cantata (; ; literally "sung", past p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
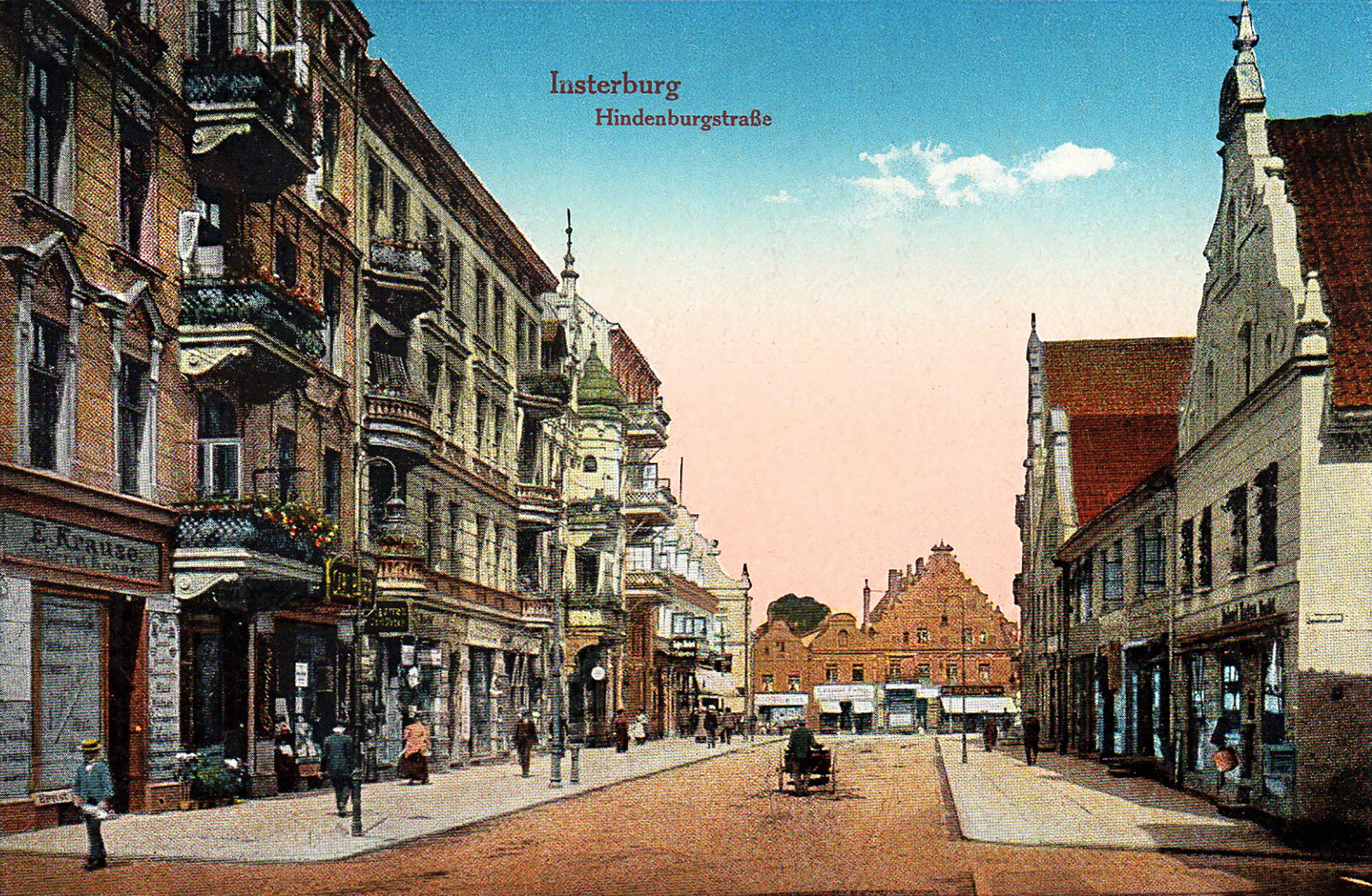
Insterburg
Chernyakhovsk (russian: Черняхо́вск) – known prior to 1946 by its German name of (Old Prussian: Instrāpils, lt, Įsrutis; pl, Wystruć) – is a town in the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia, where it is the administrative center of Chernyakhovsky District. Located at the confluence of the Instruch and Angrapa rivers, which unite to become the Pregolya river below Chernyakhovsk, the town had a population in 2017 of 36,423. History Chernyakhovsk was founded in 1336 by the Teutonic Knights on the site of a former Old Prussian fortification when Dietrich von Altenburg, the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, built a castle called ''Insterburg'' following the Prussian Crusade. During the Teutonic Knights' Northern Crusades campaign against the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the town was devastated in 1376. The castle had been rebuilt as the seat of a Procurator and a settlement also named ''Insterburg'' grew up to serve it. In 1454, Polish King Casimir IV Jagiellon incorpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constituent states, Berlin is surrounded by the State of Brandenburg and contiguous with Potsdam, Brandenburg's capital. Berlin's urban area, which has a population of around 4.5 million, is the second most populous urban area in Germany after the Ruhr. The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's third-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr and Rhine-Main regions. Berlin straddles the banks of the Spree, which flows into the Havel (a tributary of the Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the city's main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel and Dahme, the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee. Due to its l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Hauser
Franz Xaver Hauser (12 January 1794, Krasovice – 14 August 1870 in Freiburg im Breisgau) was a singer, voice teacher, and music manuscript collector. Life Franz Hauser was born in Krasowitz (today Krasovice, part of Kondrac Czech Republic). At his father's insistence, he first studied medicine, but he then studied singing with Václav Tomášek and composition with oboist Josef Triebensee. He made his stage debut in 1817 in Prague as Sarastro in Mozart's ''Magic Flute''. He found great success at the opera theaters in Vienna, Leipzig, and Berlin. He retired from the stage in 1838 and taught singing in Vienna. In 1846 he was appointed as director of the newly established conservatory in Munich (now the Hochschule für Musik und Theater München), serving as its director until 1864. He retired in 1865 to Karlsruhe and two years later to Freiburg im Breisgau. Contemporary critics considered Hauser cold as an actor but approved of his pure voice. He was known for his interpretat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Violin Concerto
A violin concerto is a concerto for solo violin (occasionally, two or more violins) and instrumental ensemble (customarily orchestra). Such works have been written since the Baroque period, when the solo concerto form was first developed, up through the present day. Many major composers have contributed to the violin concerto repertoire, with the best known works including those by Bach, Bartók, Beethoven, Brahms, Bruch, Dvořák, Khachaturian, Mendelssohn, Mozart, Paganini, Prokofiev, Sarasate, Shostakovich, Sibelius, Tchaikovsky, and Vivaldi. Traditionally a three-movement work, the violin concerto has been structured in four movements by a number of modern composers, including Dmitri Shostakovich, Igor Stravinsky, and Alban Berg. In some violin concertos, especially from the Baroque and modern eras, the violin (or group of violins) is accompanied by a chamber ensemble rather than an orchestra—for instance, in Vivaldi's ''L'estro armonico'', originally scored for four vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flute Concerto
A flute concerto is a concerto for solo flute and instrumental ensemble, customarily the orchestra. Such works have been written from the Baroque period, when the solo concerto form was first developed, up through the present day. Some major composers have contributed to the flute concerto repertoire, with the best known works including those by Mozart and Vivaldi. Traditionally a three- movement work, the modern-day flute concerto has occasionally been structured in four or more movements. In some flute concertos, especially from the Baroque and modern eras, the flute is accompanied by a chamber ensemble rather than an orchestra. Selected repertoire Baroque Michel Blavet *Concerto in A minor Jean-Marie Leclair *Concerto in C major, Op. 7, No. 3 (also for violin or oboe solo) Giovanni Battista Pergolesi *Flute Concerto in G major Johann Joachim Quantz (1697–1773) – author of over 300 concertos for the flute. *Concerto in G major *Concerto in C minor Georg Philipp Telemann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpsichord Concerto
A harpsichord concerto is a piece of music for an orchestra with the harpsichord in a solo role (though for another sense, see below). Sometimes these works are played on the modern piano (see ''piano concerto''). For a period in the late 18th century, Joseph Haydn and Thomas Arne wrote concertos that could be played interchangeably on harpsichord, fortepiano, and (in some cases) pipe organ. The Baroque harpsichord concerto The harpsichord was a common instrument in the 1730s, but never as popular as string instrument, string or wind instruments in the concerto role in the orchestra, probably due to its relative lack of volume in an orchestral setting. In this context, harpsichords were more usually employed as a Figured bass, continuo instrument, playing a harmonised bass part in nearly all orchestral music, the player often also directing the orchestra. Bach's Brandenburg Concerto No.5 in D major, BWV 1050, may be the first work in which the harpsichord appears as a concerto so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trio Sonata
The trio sonata is a genre, typically consisting of several movements, with two melody instruments and basso continuo. Originating in the early 17th century, the trio sonata was a favorite chamber ensemble combination in the Baroque era. Basic structure The trio sonata typically consisted of three parts, two violins and (basso) continuo. However, the two violins could be substituted with pairs of flutes, recorders, oboes, or violin and viola da gamba. The third part, the continuo, has two components. First, it includes the bass line, which commonly was played by a bass viol, violone, violoncello, or bassoon. Second, it includes a harmony-producing instrument, such as a small organ, a harpsichord, or a theorbo. The continuo could be performed by two or more performers; a cellist to play the bass line and a harpsichordist or organist to focus on the harmonies. Because there normally are two people playing the continuo part, there are usually four players in all. This accounts for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantata
A cantata (; ; literally "sung", past participle feminine singular of the Italian verb ''cantare'', "to sing") is a vocal composition with an instrumental accompaniment, typically in several movements, often involving a choir. The meaning of the term changed over time, from the simple single-voice madrigal of the early 17th century, to the multi-voice "cantata da camera" and the "cantata da chiesa" of the later part of that century, from the more substantial dramatic forms of the 18th century to the usually sacred-texted 19th-century cantata, which was effectively a type of short oratorio. Cantatas for use in the liturgy of church services are called church cantata or sacred cantata; other cantatas can be indicated as secular cantatas. Several cantatas were, and still are, written for special occasions, such as Christmas cantatas. Christoph Graupner, Georg Philipp Telemann and Johann Sebastian Bach composed cycles of church cantatas for the occasions of the liturgical year. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aria
In music, an aria (Italian: ; plural: ''arie'' , or ''arias'' in common usage, diminutive form arietta , plural ariette, or in English simply air) is a self-contained piece for one voice, with or without instrumental or orchestral accompaniment, normally part of a larger work. The typical context for arias is opera, but vocal arias also feature in oratorios and cantatas, or they can be stand-alone concert arias. The term was originally used to refer to any expressive melody, usually, but not always, performed by a singer. Etymology The Italian term ''aria'', which derives from the Greek ἀήρ and Latin ''aer'' (air), first appeared in relation to music in the 14th century when it simply signified a manner or style of singing or playing. By the end of the 16th century, the term 'aria' refers to an instrumental form (cf. Santino Garsi da Parma lute works, 'Aria del Gran Duca'). By the early 16th century it was in common use as meaning a simple setting of strophic poetry; me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1725 Births
Seventeen or 17 may refer to: *17 (number), the natural number following 16 and preceding 18 * one of the years 17 BC, AD 17, 1917, 2017 Literature Magazines * ''Seventeen'' (American magazine), an American magazine * ''Seventeen'' (Japanese magazine), a Japanese magazine Novels * ''Seventeen'' (Tarkington novel), a 1916 novel by Booth Tarkington *''Seventeen'' (''Sebuntiin''), a 1961 novel by Kenzaburō Ōe * ''Seventeen'' (Serafin novel), a 2004 novel by Shan Serafin Stage and screen Film * ''Seventeen'' (1916 film), an American silent comedy film *''Number Seventeen'', a 1932 film directed by Alfred Hitchcock * ''Seventeen'' (1940 film), an American comedy film *''Eric Soya's '17''' (Danish: ''Sytten''), a 1965 Danish comedy film * ''Seventeen'' (1985 film), a documentary film * ''17 Again'' (film), a 2009 film whose working title was ''17'' * ''Seventeen'' (2019 film), a Spanish drama film Television * ''Seventeen'' (TV drama), a 1994 UK dramatic short starring Christ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1766 Deaths
Events January–March * January 1 – Charles Edward Stuart ("Bonnie Prince Charlie") becomes the new Stuart claimant to the throne of Great Britain, as King Charles III, and figurehead for Jacobitism. * January 14 – Christian VII becomes King of Denmark. * January 20 – Outside of the walls of the Thailand capital of Ayutthaya, tens of thousands of invaders from Burma (under the command of General Ne Myo Thihapate and General Maha Nawatra) are confronted by Thai defenders led by General Phya Taksin. The defenders are overwhelmed and the survivors take refuge inside Ayutthaya. The siege continues for 15 months before the Burmese attackers collapse the walls by digging tunnels and setting fire to debris. The city falls on April 9, 1767, and King Ekkathat is killed. * February 5 – An observer in Wilmington, North Carolina reports to the Edinburgh newspaper ''Caledonian Mercury'' that three ships have been seized by British men-of-war, on the char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century German Composers
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |