|
Johann Jakob Balmer
Johann Jakob Balmer (1 May 1825 – 12 March 1898) was a Swiss mathematician best known for his work in physics, the Balmer series of hydrogen atom. Biography Balmer was born in Lausen, Switzerland, the son of a chief justice also named Johann Jakob Balmer. His mother was Elizabeth Rolle Balmer, and he was the oldest son. During his schooling he excelled in mathematics, and so decided to focus on that field when he attended university. He studied at the University of Karlsruhe and the University of Berlin, then completed his PhD from the University of Basel in 1849 with a dissertation on the cycloid. Johann then spent his entire life in Basel, where he taught at a school for girls. He also lectured at the University of Basel. In 1868 he married Christine Pauline Rinck at the age of 43. The couple had six children. Despite being a mathematician, Balmer is best remembered for his work on spectral series. His major contribution (made at the age of sixty, in 1885) was an empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lausen
Lausen is a municipality in the district of Liestal in the canton of Basel-Country in Switzerland. History Lausen is first mentioned in 1275 as ''in villa et banno Langenso''. In 1305 it became the property of the Bishop of Basel, passing in 1400 to the city of Basel. Geography Lausen has an area, , of . Of this area, or 23.6% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 50.5% is forested. Of the rest of the land, or 25.0% is settled (buildings or roads), or 0.5% is either rivers or lakes and or 0.4% is unproductive land.Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data accessed 25 March 2010 Of the built up area, industrial buildings made up 3.8% of the total area while housing and buildings made up 12.9% and transportation infra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anders Jonas Ångström
Anders Jonas Ångström (; 13 August 181421 June 1874) was a Swedish physicist and one of the founders of the science of spectroscopy.P.Murdin (2000): "Angstrom" chapter in ''Encyclopedia of Astronomy and Astrophysics''. Ångström is also well known for his studies of astrophysics, heat transfer, terrestrial magnetism, and the aurora borealis. In 1852, Ångström formulated in ''Optiska undersökningar'' (Optical investigations), a law of absorption, later modified somewhat and known as Kirchhoff's law of thermal radiation. Biography Anders Jonas Ångström was born in Medelpad to Johan Ångström, and schooled in Härnösand. He moved to Uppsala in 1833 and was educated at Uppsala University, where in 1839 he became docent in physics. In 1842 he went to the Stockholm Observatory to gain experience in practical astronomical work, and the following year he was appointed keeper of the Uppsala Astronomical Observatory. Intrigued by terrestrial magnetism he recorded observations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
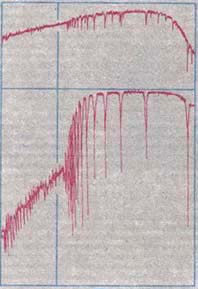
Balmer Jump
The Balmer jump, Balmer discontinuity, or Balmer break is the difference of intensity of the stellar continuum spectrum on either side of the limit of the Balmer series of hydrogen, at approximately 364.5 nm. It is caused by electrons being completely ionized directly from the second energy level of a hydrogen atom (bound-free absorption), which creates a continuum absorption at wavelengths shorter than 364.5 nm. In some cases the Balmer discontinuity can show continuum emission, usually when the Balmer lines themselves are strongly in emission. Other hydrogen spectral series also show bound-free absorption and hence a continuum discontinuity, but the Balmer jump in the near UV has been the most observed. The strength of the continuum absorption, and hence the size of the Balmer jump, depends on temperature and density in the region responsible for the absorption. At cooler stellar temperatures, the density most strongly affects the strength of the discontinuity and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balmer Line
The Balmer series, or Balmer lines in atomic physics, is one of a set of six named series describing the spectral line emissions of the hydrogen atom. The Balmer series is calculated using the Balmer formula, an empirical equation discovered by Johann Balmer in 1885. The visible spectrum of light from hydrogen displays four wavelengths, 410 nm, 434 nm, 486 nm, and 656 nm, that correspond to emissions of photons by electrons in excited states transitioning to the quantum level described by the principal quantum number ''n'' equals 2. There are several prominent ultraviolet Balmer lines with wavelengths shorter than 400 nm. The number of these lines is an infinite continuum as it approaches a limit of 364.5 nm in the ultraviolet. After Balmer's discovery, five other hydrogen spectral series were discovered, corresponding to electrons transitioning to values of ''n'' other than two . Overview The Balmer series is characterized by the electron t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niels Bohr
Niels Henrik David Bohr (; 7 October 1885 – 18 November 1962) was a Danish physicist who made foundational contributions to understanding atomic structure and quantum theory, for which he received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1922. Bohr was also a philosopher and a promoter of scientific research. Bohr developed the Bohr model of the atom, in which he proposed that energy levels of electrons are discrete and that the electrons revolve in stable orbits around the atomic nucleus but can jump from one energy level (or orbit) to another. Although the Bohr model has been supplanted by other models, its underlying principles remain valid. He conceived the principle of complementarity: that items could be separately analysed in terms of contradictory properties, like behaving as a wave or a stream of particles. The notion of complementarity dominated Bohr's thinking in both science and philosophy. Bohr founded the Institute of Theoretical Physics at the University of Cope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohr Model Of The Atom
In atomic physics, the Bohr model or Rutherford–Bohr model, presented by Niels Bohr and Ernest Rutherford in 1913, is a system consisting of a small, dense nucleus surrounded by orbiting electrons—similar to the structure of the Solar System, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces in place of gravity. It came after the solar system Joseph Larmor model (1897), the solar system Jean Perrin model (1901), the cubical model (1902), the Hantaro Nagaoka Saturnian model (1904), the plum pudding model (1904), the quantum Arthur Haas model (1910), the Rutherford model (1911), and the nuclear quantum John William Nicholson model (1912). The improvement over the 1911 Rutherford model mainly concerned the new quantum physical interpretation introduced by Haas and Nicholson, but forsaking any attempt to align with classical physics radiation. The model's key success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rydberg Constant
In spectroscopy, the Rydberg constant, symbol R_\infty for heavy atoms or R_\text for hydrogen, named after the Swedish physicist Johannes Rydberg, is a physical constant relating to the electromagnetic spectra of an atom. The constant first arose as an empirical fitting parameter in the Rydberg formula for the hydrogen spectral series, but Niels Bohr later showed that its value could be calculated from more fundamental constants via his Bohr model. Before the redefinition of the SI base units in , R_\infty and the electron spin ''g''-factor were the most accurately measured physical constants. The constant is expressed for either hydrogen as R_\text, or at the limit of infinite nuclear mass as R_\infty. In either case, the constant is used to express the limiting value of the highest wavenumber (inverse wavelength) of any photon that can be emitted from an atom, or, alternatively, the wavenumber of the lowest-energy photon capable of ionizing an atom from its ground state. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Rydberg
Johannes (Janne) Robert Rydberg (; 8 November 1854 – 28 December 1919) was a Swedish physicist mainly known for devising the Rydberg formula, in 1888, which is used to describe the wavelengths of photons (of visible light and other electromagnetic radiation) emitted by changes in the energy level of an electron in a hydrogen atom. Biography Rydberg was born 8 November 1854 in Halmstad in southern Sweden, the only child of Sven Rydberg and Maria Anderson Rydberg. When he was 4 years old his father died, and the family was forced to live on a small income. In 1873 he graduated from Halmstads elementärläroverk, where he received high grades in maths and physics. Later that year he enrolled in Lund University, and two years later he was awarded his bachelor's degree. In 1879 he was awarded his Doctor of Philosophy with his dissertation "Konstruktioner af kägelsnitt i 3- och 4-punktskontakt". Rydberg began his career as an amanuensis in the institution. He became a docent i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rydberg Formula
In atomic physics, the Rydberg formula calculates the wavelengths of a spectral line in many chemical elements. The formula was primarily presented as a generalization of the Balmer series for all atomic electron transitions of hydrogen. It was first empirically stated in 1888 by the Swedish physicist Johannes Rydberg, then theoretically by Niels Bohr in 1913, who used a primitive form of quantum mechanics. The formula directly generalizes the equations used to calculate the wavelengths of the hydrogen spectral series. History In 1880, Rydberg worked on a formula describing the relation between the wavelengths in spectral lines of alkali metals. He noticed that lines came in series and he found that he could simplify his calculations using the wavenumber (the number of waves occupying the unit length, equal to 1/''λ'', the inverse of the wavelength) as his unit of measurement. He plotted the wavenumbers (''n'') of successive lines in each series against consecutive integers w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Huggins
Sir William Huggins (7 February 1824 – 12 May 1910) was an English astronomer best known for his pioneering work in astronomical spectroscopy together with his wife, Margaret. Biography William Huggins was born at Cornhill, Middlesex, in 1824. In 1875, he married Margaret Lindsay, daughter of John Murray of Dublin, who also had an interest in astronomy and scientific research. She encouraged her husband's photography and helped to put their research on a systematic footing. Huggins built a private observatory at 90 Upper Tulse Hill, London, from where he and his wife carried out extensive observations of the spectral emission lines and absorption lines of various celestial objects. On 29 August 1864, Huggins was the first to take the spectrum of a planetary nebula when he analysed NGC 6543. He was also the first to distinguish between nebulae and galaxies by showing that some (like the Orion Nebula) had pure emission spectra characteristic of gas, while others ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Wilhelm Vogel
Hermann Wilhelm Vogel (26 March 1834 – 17 December 1898) was a German photochemist and photographer who discovered dye sensitization, which is of great importance to photography. Academic career After finishing school in Frankfurt (Oder), he studied at the Royal Industrial Institute of Berlin, earning his Ph.D. with Karl Friedrich August Rammelsberg in 1863. Vogel's thesis, which was published in ''Poggendorffs Annalen'' , had the title: ''Über das Verhalten des Chlorsilbers, Bromsilbers und Iodsilbers im Licht und die Theorie der Photographie'' (Reactions of Silver Chloride, Silver Bromide and Silver Iodide with Light and the Theory of Photography). This marked the beginning of his research into the photographic process. From 1860 until 1865, he was an assistant in the mineralogical museum of the University of Berlin, and from 1884 was director of the photo-technical laboratory of the Technical Institute there. From 1864 he was a professor at Berlin's Technische Hochschu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground State
The ground state of a quantum-mechanical system is its stationary state of lowest energy; the energy of the ground state is known as the zero-point energy of the system. An excited state is any state with energy greater than the ground state. In quantum field theory, the ground state is usually called the vacuum state or the vacuum. If more than one ground state exists, they are said to be degenerate. Many systems have degenerate ground states. Degeneracy occurs whenever there exists a unitary operator that acts non-trivially on a ground state and commutes with the Hamiltonian of the system. According to the third law of thermodynamics, a system at absolute zero temperature exists in its ground state; thus, its entropy is determined by the degeneracy of the ground state. Many systems, such as a perfect crystal lattice, have a unique ground state and therefore have zero entropy at absolute zero. It is also possible for the highest excited state to have absolute zero temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |