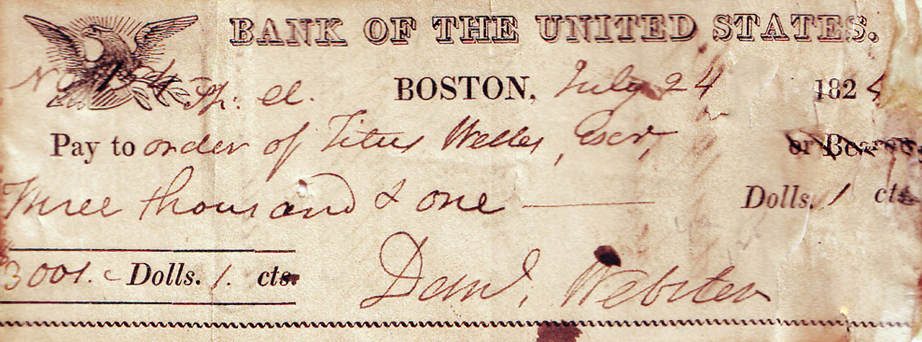|
Job Pierson
Job Pierson (September 23, 1791 – April 9, 1860) was an American lawyer and politician who served two terms as a United States House of Representatives, U.S. Representative from New York (state), New York from 1831 to 1835. Biography Born in East Hampton, New York, Pierson attended the common schools. He graduated from Williams College in 1811. He studied law in Salem and Schaghticoke. He was Admission to the bar in the United States, admitted to the bar in 1815 and commenced practice in Rensselaer County. He served as district attorney from 1824 to 1833. Congress Pierson was elected as a Jacksonian to the 22nd United States Congress, Twenty-second and 23rd United States Congress, Twenty-third Congresses (March 4, 1831 – March 3, 1835). After an unsuccessful campaign for reelection to the 24th United States Congress, Twenty-fourth Congress in 1834, he resumed the practice of law. He served as Surrogate of Rensselaer County from 1835 to 1840 and was a delegate to the Democ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York (state)
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. state by area. With 20.2 million people, it is the fourth-most-populous state in the United States as of 2021, with approximately 44% living in New York City, including 25% of the state's population within Brooklyn and Queens, and another 15% on the remainder of Long Island, the most populous island in the United States. The state is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Vermont to the east; it has a maritime border with Rhode Island, east of Long Island, as well as an international border with the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the north and Ontario to the northwest. New York City (NYC) is the most populous city in the United States, and around two-thirds of the state's popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1856 Democratic National Convention
The 1856 Democratic National Convention was a presidential nominating convention that met from June 2 to June 6 in Cincinnati, Ohio. It was held to nominate the Democratic Party's candidates for president and vice president in the 1856 election. The convention selected former Secretary of State James Buchanan of Pennsylvania for president and former Representative John C. Breckinridge of Kentucky for vice president. Incumbent Democratic President Franklin Pierce's standing with the public had been badly damaged by "Bleeding Kansas," the civil strife in Kansas Territory over slavery. Many dissatisfied Democrats lined up behind Buchanan, who had served as Pierce's ambassador to Britain and thus had avoided the controversy over Bleeding Kansas, while a smaller group of Democrats supported Senator Stephen A. Douglas of Illinois. Buchanan led on the first ballot and slowly grew his support on subsequent ballots, leading Pierce to instruct his delegates to back Douglas. Douglas agr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williams College Alumni
Williams College is a private liberal arts college in Williamstown, Massachusetts, United States. It was established in 1793 with funds from the estate of Ephraim Williams, a colonist from the Province of Massachusetts Bay who was killed in the French and Indian War in 1755. Alumni of the college are listed below. Academia ;A–F * Brooke Ackerly 1988, American political scientist and Professor of Political Science at Vanderbilt University * Peter Adamson 1994, professor of late ancient and Arabic philosophy at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich * Lawrence A. Alexander 1965, Warren Distinguished Professor of constitutional law at University of San Diego * Robert Z. Aliber 1952, professor emeritus of international economics and finance at the University of Chicago * Robert S. Anderson 1974, American geomorphologist at the Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research, Fellow of the American Geophysical Union, and distinguished professor at University of Colorado Bou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1860 Deaths
Year 186 ( CLXXXVI) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Aurelius and Glabrio (or, less frequently, year 939 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 186 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Peasants in Gaul stage an anti-tax uprising under Maternus. * Roman governor Pertinax escapes an assassination attempt, by British usurpers. New Zealand * The Hatepe volcanic eruption extends Lake Taupō and makes skies red across the world. However, recent radiocarbon dating by R. Sparks has put the date at 233 AD ± 13 (95% confidence). Births * Ma Liang, Chinese official of the Shu Han state (d. 222) Deaths * April 21 – Apollonius the Apologist, Christian martyr * Bian Zhang, Chinese official and gener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1791 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – Austrian composer Joseph Haydn arrives in England, to perform a series of concerts. * January 2 – Northwest Indian War: Big Bottom Massacre – The war begins in the Ohio Country, with this massacre. * January 12 – Holy Roman troops reenter Liège, heralding the end of the Liège Revolution, and the restoration of its Prince-Bishops. * January 25 – The British Parliament passes the Constitutional Act 1791, splitting the old province of Quebec into Upper and Lower Canada. * February 8 – The Bank of the United States, based in Philadelphia, is incorporated by the federal government with a 20-year charter and started with $10,000,000 capital.''Harper's Encyclopaedia of United States History from 458 A. D. to 1909'', ed. by Benson John Lossing and, Woodrow Wilson (Harper & Brothers, 1910) p169 * February 21 – The United States opens diplomatic relations with Portugal. * March 2 – Fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tariff Of 1833
The Tariff of 1833 (also known as the Compromise Tariff of 1833, ch. 55, ), enacted on March 2, 1833, was proposed by Henry Clay and John C. Calhoun as a resolution to the Nullification Crisis. Enacted under Andrew Jackson's presidency, it was adopted to gradually reduce the rates following Southerners' objections to the protectionism found in the Tariff of 1832 and the 1828 Tariff of Abominations; the tariffs had prompted South Carolina to threaten secession from the Union. This Act stipulated that import taxes would gradually be cut over the next decade until, by 1842, they matched the levels set in the Tariff of 1816—an average of 20%. The compromise reductions lasted only two months into their final stage before protectionism was reinstated by the Black Tariff of 1842. Background The Tariff of 1828 The Tariff of 1828, enacted on May 19, 1828, was a protective tariff passed by the U.S. Congress. It was the highest tariff in U.S. peacetime history up to that point, enacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Bank Of The United States
The Second Bank of the United States was the second federally authorized Hamiltonian national bank in the United States. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the bank was chartered from February 1816 to January 1836.. The Bank's formal name, according to section 9 of its charter as passed by Congress, was "The President Directors and Company of the Bank of the United States". While other banks in the US were chartered by and only allowed to have branches in a single state, it was authorized to have branches in multiple states and lend money to the US government. A private corporation with public duties, the Bank handled all fiscal transactions for the U.S. Government, and was accountable to Congress and the U.S. Treasury. Twenty percent of its capital was owned by the federal government, the Bank's single largest stockholder.. Four thousand private investors held 80 percent of the Bank's capital, including three thousand Europeans. The bulk of the stocks were held by a few hundr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherokee Nation
The Cherokee Nation (Cherokee: ᏣᎳᎩᎯ ᎠᏰᎵ ''Tsalagihi Ayeli'' or ᏣᎳᎩᏰᎵ ''Tsalagiyehli''), also known as the Cherokee Nation of Oklahoma, is the largest of three Cherokee federally recognized tribes in the United States. It was established in the 20th century and includes people descended from members of the Old Cherokee Nation who relocated, due to increasing pressure, from the Southeast to Indian Territory and Cherokee who were forced to relocate on the Trail of Tears. The tribe also includes descendants of Cherokee Freedmen, Absentee Shawnee, and Natchez Nation. As of 2021, over 400,000 people were enrolled in the Cherokee Nation. Headquartered in Tahlequah, Oklahoma, the Cherokee Nation has a reservation spanning 14 counties in the northeastern corner of Oklahoma. These are Adair, Cherokee, Craig, Delaware, Mayes, McIntosh, Muskogee, Nowata, Ottawa, Rogers, Sequoyah, Tulsa, Wagoner, and Washington counties. History Late 18th century through 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John C
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Webster
Daniel Webster (January 18, 1782 – October 24, 1852) was an American lawyer and statesman who represented New Hampshire and Massachusetts in the U.S. Congress and served as the U.S. Secretary of State under Presidents William Henry Harrison, John Tyler, and Millard Fillmore. Webster was one of the most prominent American lawyers of the 19th century, and argued over 200 cases before the U.S. Supreme Court between 1814 and his death in 1852. During his life, he was a member of the Federalist Party, the National Republican Party, and the Whig Party. Born in New Hampshire in 1782, Webster established a successful legal practice in Portsmouth, New Hampshire, after graduating from Dartmouth College and undergoing a legal apprenticeship. He emerged as a prominent opponent of the War of 1812 and won election to the United States House of Representatives, where he served as a leader of the Federalist Party. Webster left office after two terms and relocated to Boston, Massachusetts. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Clay
Henry Clay Sr. (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American attorney and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives. He was the seventh House speaker as well as the ninth secretary of state, also receiving electoral votes for president in the 1824, 1832, and 1844 presidential elections. He helped found both the National Republican Party and the Whig Party. For his role in defusing sectional crises, he earned the appellation of the "Great Compromiser" and was part of the "Great Triumvirate" of Congressmen, alongside fellow Whig Daniel Webster and John C. Calhoun. Clay was born in Hanover County, Virginia, in 1777, beginning his legal career in Lexington, Kentucky, in 1797. As a member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Clay won election to the Kentucky state legislature in 1803 and to the U.S. House of Representatives in 1810. He was chosen as Speaker of the House in early 1811 and, along with President James Madison, led ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |