|
Jewett Car Company
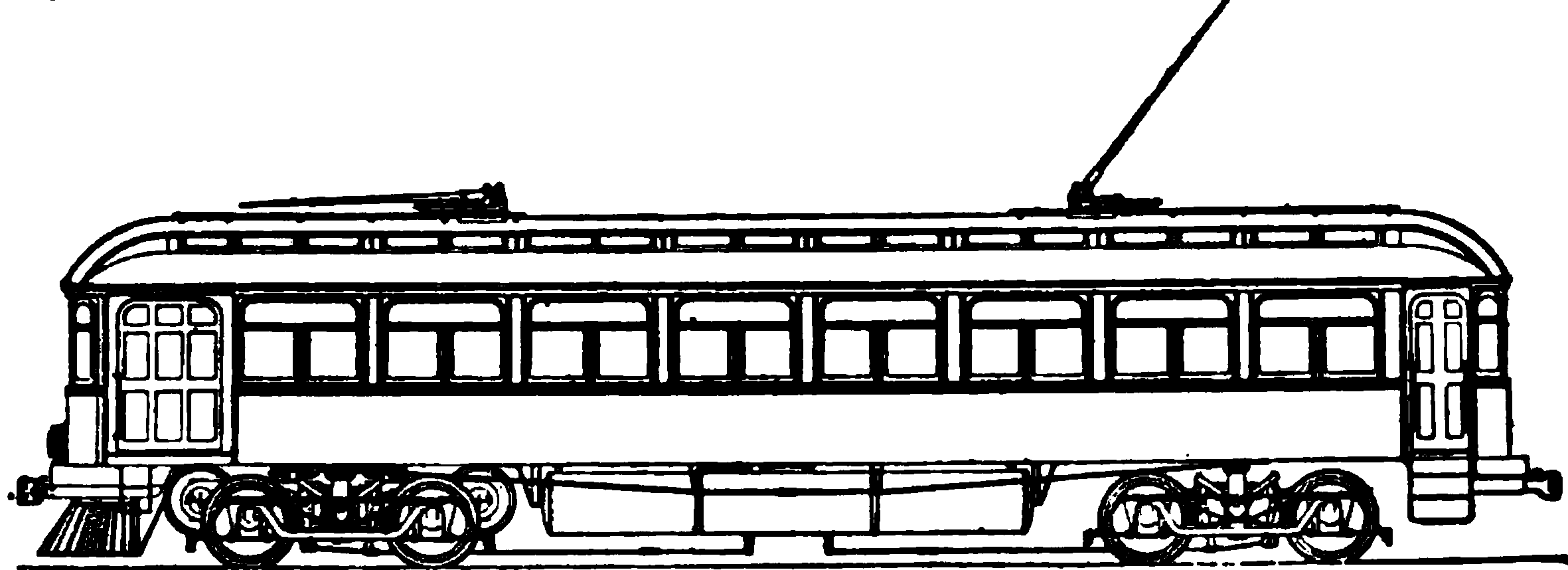
The Jewett Car Company was an early 20th-century American industrial company that manufactured streetcars and interurban cars. History The company was founded in 1893 in Jewett, Ohio, where its first factory was located. In 1904, the company relocated from Jewett to a site along South Williams Street in Newark, Ohio, retaining the original name. The facility soon expanded to become one of Newark's largest employers. Among its customers was the city of San Francisco, California, which purchased several street cars from Jewett. The company produced more than 2,000 wood-and-steel street cars, shipping them to 26 states and Canada. The Jewett Car Company went out of business in 1919 when the automobile began replacing mass transit. The most notable Jewett-built cars that are still running today are: * Brooklyn Rapid Transit streetcar 4547, built in 1906, sees regular operation at the Seashore Trolley Museum in Kennebunkport, Maine. * Chicago Aurora and Elgin interurban car 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewett, Ohio
Jewett is a village in Harrison County, Ohio, United States. The population was 692 at the 2010 census. History Jewett was originally called Fairview, and under the latter name was platted in 1851. The present name is for T. M. Jewett, a railroad official. Jewett was the original home of the Jewett Car Company, a street car manufacturer, from 1894 until 1904. The street cars produced by this factory were shipped throughout the United States. The Jewett Car Company relocated to Newark, Ohio in 1904, and ceased operations in 1919. Geography Jewett is located at (40.368020, -81.003026). According to the United States Census Bureau, the village has a total area of , all land. Jewett is the endpoint of the Conotton Creek Trail, an long multi-use rails-to-trails A rail trail is a shared-use path on railway right of way. Rail trails are typically constructed after a railway has been abandoned and the track has been removed, but may also share the right of way with active railw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seashore Trolley Museum
Seashore Trolley Museum, located in Kennebunkport, Maine, United States, is the world's first and largest museum of mass transit vehicles. While the main focus of the collection is trolley cars (trams), it also includes rapid transit trains, Interurban cars, trolley buses, and motor buses. The Seashore Trolley Museum is owned and operated by the New England Electric Railway Historical Society (NEERHS).Young, Andrew D. (1997). ''Veteran & Vintage Transit'', pp. 43–48. St. Louis: Archway Publishing. . Of the museum's collection of more than 350 vehicles, ten trolley, and railroad cars that historically operated in Maine were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980, as Maine Trolley Cars. History Theodore F. Santarelli de Brasch and Osmond Richard Cummings were two of the founders of the museum, which was initially operated as the Seashore Electric Railway. Santarelli graduated from Harvard University and led the museum until he died in 1987; Cummings, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halton County Radial Railway
The Halton County Radial Railway is a working museum of electric streetcars, other railway vehicles, buses and trolleybuses. It is operated by the Ontario Electric Railway Historical Association (OERHA). It is focused primarily on the history of the Toronto Transit Commission (TTC) and its predecessor, the Toronto Transportation Commission, Its collection includes PCC, Peter Witt, CLRV and ALRV, and earlier cars from the Toronto streetcar system as well as G-series and M-series Toronto subway cars. The museum is open to the public, with rides on many of its vehicles. It is located between the villages of Rockwood and Campbellville in Milton, Ontario, Canada, along part of the Toronto Suburban Railway's former right-of-way. The tracks conform to the TTC's track gauge of , which is wider than . Vehicles from other systems must be altered to accommodate the tracks, and cars intended for third-rail power must be reconfigured for use with overhead wire. In 1889, electric railway s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London And Port Stanley Railway
The London and Port Stanley Railway (L&PS or L&PSR) was a Canadian railway located in southwestern Ontario. It linked the city of London with Port Stanley on the northern shore of Lake Erie, a distance of approximately . History The L&PS was one of the first railways to be built in Ontario, with construction starting in 1856. It provided connections between London, St. Thomas and Port Stanley. It was built primarily to facilitate trade with the United States, particularly of wood and coal. As a result of its rail connection, a substantial investment was made in the port facilities of Port Stanley, which in turn attracted American and Canadian shipping. Until 1932, coal from Conneaut, Ohio was transported via railway car ferries to Port Stanley. The railway also proved popular with local residents, particularly in the summer when many commuters utilized the system to travel to Port Stanley's beach and resort facilities. However, the railway's service was not always impeccable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F Market & Wharves
The F Market & Wharves line is one of several light rail lines in San Francisco, California. Unlike most other lines in the system, the F line runs as a heritage streetcar service, almost exclusively using historic equipment both from San Francisco's retired fleet as well as from cities around the world (although buses are added during peak commute hours). While the F line is operated by the San Francisco Municipal Railway (Muni), its operation is supported by Market Street Railway, a nonprofit organization of streetcar enthusiasts which raises funds and helps to restore vintage streetcars. Introduced as the F Market in 1983, in the first San Francisco Historic Trolley Festival, the service originally operated between the Castro District and the Transbay Terminal, continuing to do so after being launched as a full-time, year-round service in 1995. In March 2000, it was extended at its eastern end to the Embarcadero and northwards along that street to Fisherman's Wharf, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Haven, Connecticut
East Haven is a town in New Haven County, Connecticut, in the United States. As of the 2020 census, the town population was 27,923. Located east of New Haven, it is part of the Greater New Haven area. East Haven is from Hartford, from New York City, from Providence, Rhode Island, and from Boston. History The Connecticut Colony granted the town petition for Township in May 1707 and colonists changed the name from Iron Works Village to East Haven. Some outstanding land issues with New Haven and a minor feud with Governor Gurdon Saltonstall resulted in the rescinding of the township status; the area was made a parish of New Haven. New Haven and neighboring towns such as East Haven have been destinations for a new wave of immigrants since the late 20th century, the majority of whom in East Haven are Latinos from Ecuador. In the 2010 census, Hispanics and Latinos made up more than 10% of the town's population. On August 9, 2013, a Rockwell International Turbo Commander 690 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shore Line Trolley Museum
The Shore Line Trolley Museum is a trolley museum located in East Haven, Connecticut. Incorporated in 1945, it is the oldest continuously operating trolley museum in the United States. The museum includes exhibits on trolley history in the visitors' center and offers rides on restored trolleys along its track as the Branford Electric Railway. In addition to trolleys, the museum also operates a small number of both trolleybuses and conventional buses. The museum encompasses the Branford Electric Railway Historic District, which was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places in 1983. History The museum was incorporated in August 1945 as the Branford Electric Railway Association (BERA), a non-profit historical and educational institution. The Connecticut Company (or ConnCo), which operated most of the streetcar lines in the state of Connecticut, had been making plans since the early 1930s to abandon its "F" route, cutting it back in stages from its long-time terminus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connecticut Company
The Connecticut Company was the primary electric street railway company in the U.S. state of Connecticut, operating both city and rural trolleys and freight service. It was controlled by the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad (New Haven), which also controlled most steam railroads in the state. After 1936, when one of its major leases was dissolved, it continued operating streetcars and, increasingly, buses in certain Connecticut cities until 1976, when its assets were purchased by the state government. History Formation and expansion In 1895, after it acquired control of the New York and New England Railroad, the New Haven controlled almost 90% of the steam railroad mileage in Connecticut. That same year, it gained control of its first street railway, the Stamford Street Railroad, on about April 1. That company, which operated local lines in the city of Stamford, was in bad shape financially, and the owners of a majority of its stocks and bonds, wishing to get rid of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union, Illinois
Union is a village in McHenry County, Illinois, United States. The population was 580 at the 2010 census, up from 576 in 2000. History A post office called Union has been in operation since 1852. The village was named for the federal union of the United States. Geography Union is located at (42.235237, -88.542379). According to the 2010 census, Union has a total area of , all land. Demographics At the 2000 census there were 576 people, 204 households, and 158 families living in the village. The population density was . There were 208 housing units at an average density of . The racial makeup of the village was 98.09% White, 0.35% Native American, 0.87% from other races, and 0.69% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 3.99%. Of the 204 households 37.7% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 63.7% were married couples living together, 9.3% had a female householder with no husband present, and 22.5% were non-families. 15.7% of households were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois Railway Museum
The Illinois Railway Museum (IRM, reporting mark IRMX) is the largest railroad museum in the United States. It is located in the Chicago metropolitan area at 7000 Olson Road in Union, Illinois, northwest of downtown Chicago. Overview History The museum was founded in 1953 by ten people who joined to purchase Indiana Railroad interurban car 65. Originally called the Illinois Electric Railway Museum, the museum was located on the grounds of the Chicago Hardware Foundry in North Chicago. In 1961, it was renamed to the Illinois Railway Museum to reflect its expanding scope. In 1964, the museum moved to Union, Illinois along the former right-of-way of the Elgin and Belvidere Electric Company. In 1968 the first steam locomotive was operated at the museum. The first storage barn was erected in 1972. In 1981, a streetcar loop was constructed. The right-of-way the museum was constructed next to still had back taxes into the 1980s. To gain full use of the track, the museum paid the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chicago North Shore And Milwaukee
The Chicago North Shore and Milwaukee Railroad (reporting mark CNSM), also known as the North Shore Line, was an interurban railroad that operated passenger and freight service over an route between the Chicago Loop and downtown Milwaukee, as well as an branch line between the villages of Lake Bluff and Mundelein, Illinois. The North Shore Line also provided streetcar, city bus and motor coach services along its interurban route. Extensively improved under the one time ownership of Samuel Insull, the North Shore Line was notable for its high operating speeds and substantial physical plant, as well as innovative services such as its pioneering " ferry truck" operations and its streamlined Electroliner trainsets. Author and railroad historian William D. Middleton described the North Shore Line as a "super interurban" and opined that its cessation of rail service marked the end of the "interurban era" in the United States. Since 1964 the Yellow Line of the Chicago Transit Autho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Pleasant, Iowa
Mount Pleasant is a city in and the county seat of Henry County, Iowa. The population was 9,274 in the 2020 census, an increase from 8,668 in the 2010 census. It was founded in 1835 by pioneer Presley Saunders. History The first permanent settlement at Mount Pleasant was made in 1833. Mount Pleasant was incorporated as a town in 1842, and again in 1851. In 1869, Mount Pleasant was the site of a solar eclipse expedition, under the command of James Craig Watson and sponsored by ''National Almanac.'' The total solar eclipse occurred on August 7, 1869. In the Union Block building in 1869, Arabella A. Mansfield became the first woman in the United States to be awarded a license to practice law. She had passed the bar exam with high scores and won a court case for entry to the bar. The legislature changed its statute. The third floor of the Union Block housed the Opera House or Union Hall, a gathering place for the community. It attracted national speakers on tour, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

.jpg)