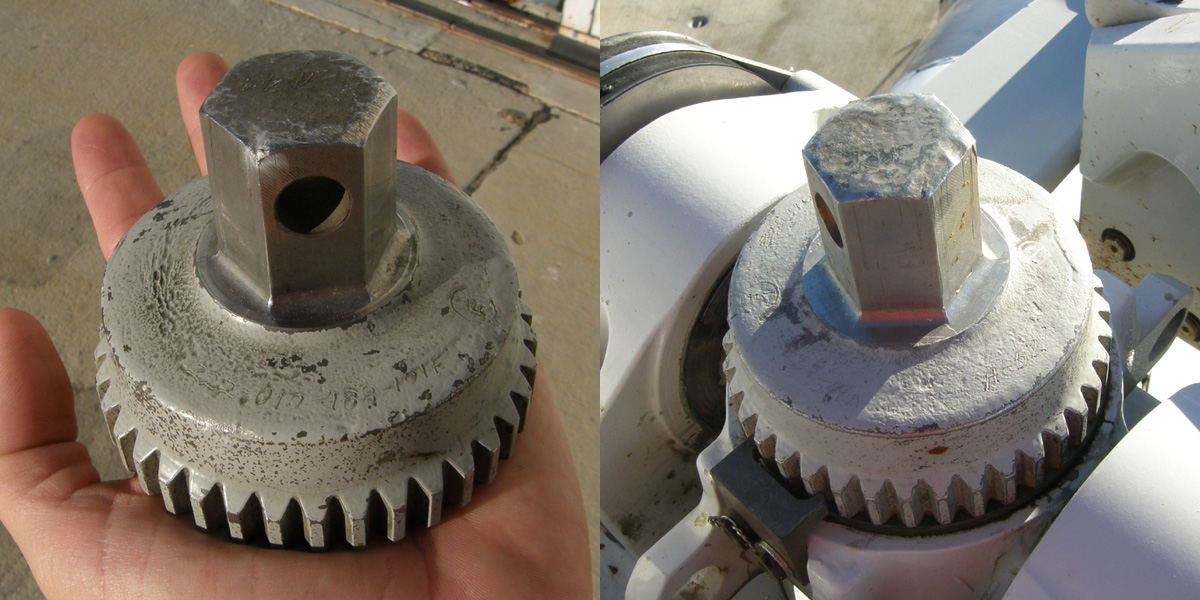
|
Jesus Nut
''Jesus nut'' is a slang term for the main rotor retaining nut or mast nut, which holds the main rotor to the mast of some helicopters. The related slang term Jesus pin refers to the lock pin used to secure the retaining nut. More generally, ''Jesus nut'' (or ''Jesus pin'') has been used to refer to any component that is a single point of failure which results in catastrophic consequences, and the only thing left to do is pray to Jesus, hence the name. Origin of name The term ''Jesus nut'' may have been coined by American soldiers in Vietnam; the Vietnam War was the first war to feature large numbers of soldiers riding in helicopters. The term may also have originated with the PBY Catalina, which had two ''Jesus bolts'' holding the wing onto the fuselage. If the Jesus nut were to fail in flight, the rotor would detach from the helicopter and the only thing left for the crew to do would be to "pray to Jesus." Real examples of the Jesus nut/pin failing are rare. However, the nut/p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesus Nut
''Jesus nut'' is a slang term for the main rotor retaining nut or mast nut, which holds the main rotor to the mast of some helicopters. The related slang term Jesus pin refers to the lock pin used to secure the retaining nut. More generally, ''Jesus nut'' (or ''Jesus pin'') has been used to refer to any component that is a single point of failure which results in catastrophic consequences, and the only thing left to do is, metaphorically speaking, pray to Jesus, hence the name. Origin of name The term ''Jesus nut'' may have been coined by American soldiers in Vietnam; the Vietnam War was the first war to feature large numbers of soldiers riding in helicopters. The term may also have originated with the PBY Catalina, which had two ''Jesus bolts'' holding the wing onto the fuselage. If the Jesus nut were to fail in flight, the rotor would detach from the helicopter and the only thing left for the crew to do would be to "pray to Jesus." The nut/pin must be checked before the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
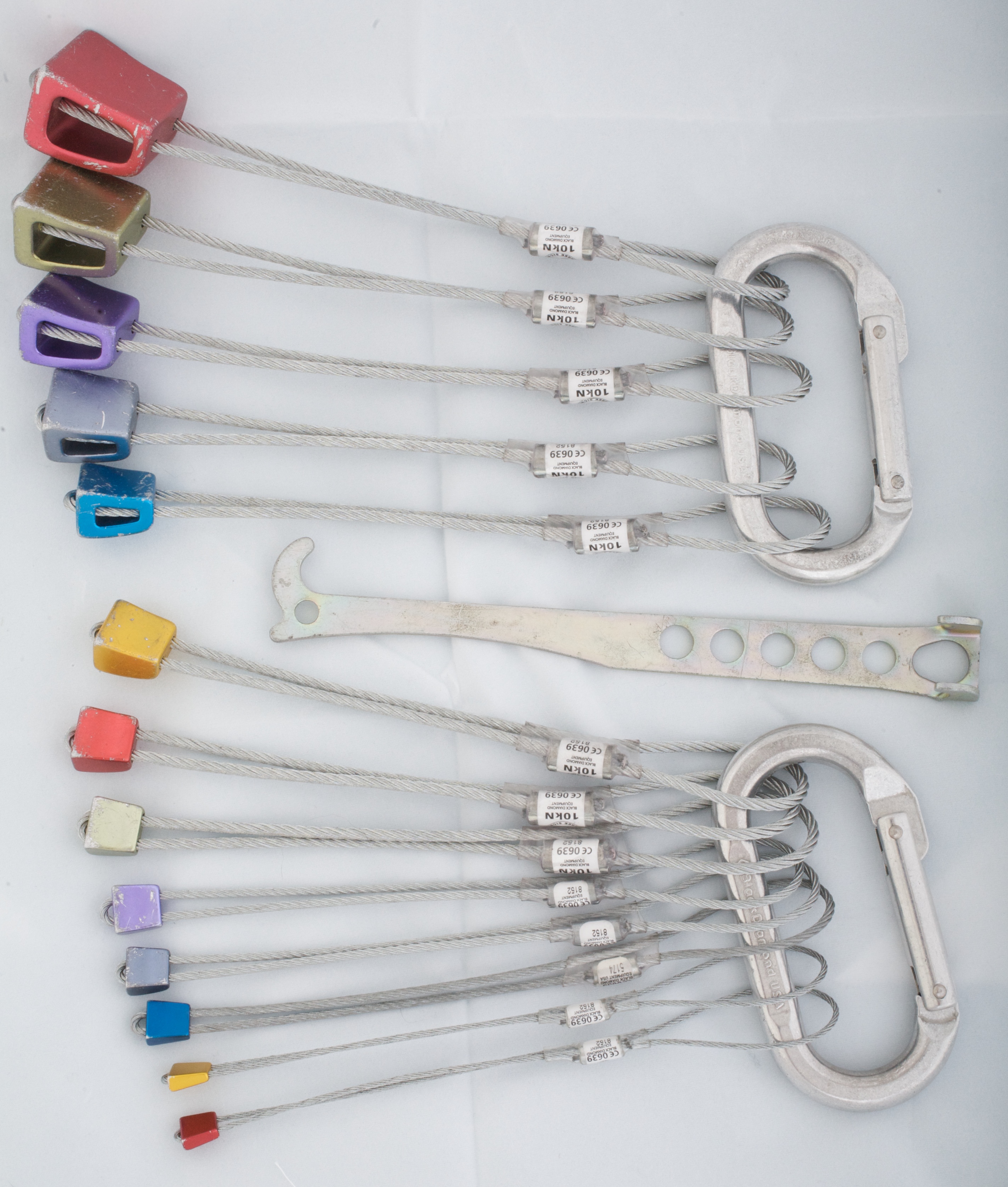
Nut (climbing)
In rock climbing, a nut (or ''chock'' or ''chockstone'') is a metal wedge threaded on a wire that climbers use for protection by wedging it into a crack in the rock. Quickdraws are clipped to the nut wire by the ascending climber and the rope threads through the quickdraw. Nuts come in a variety of sizes and styles, and several different brands are made by competing manufacturers. Most nuts are made of aluminum. Larger nuts may be threaded on Dyneema cord instead of wire, but this has become unusual. The very smallest nuts are known as ''micronuts'' and may be made of brass or other metal, and typically have their wires soldered into them, instead of looped through drilled holes. They are mostly used in aid climbing, and their value as protection, arresting a climber's fall, is marginal because of both their low breaking strength and their tiny surface area (the HB 0 measures about 4 x 7 x 2.5 mm) in contact with the rock, though this can be offset if several are placed at a ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linchpin
A linchpin, also spelled linch pin, lynchpin, or lynch pin, is a fastener used to prevent a wheel or other part from sliding off the axle upon which it is riding. The word is first attested in the late fourteenth century and derives from Middle English elements meaning "axletree pin". Securing implements onto the three-point hitch of a tractor is an example of application. Linchpins may also be used in place of an R-clip for securing hitch pins. Metaphorical use The word "linchpin" is also used figuratively to mean "something r someone R, or r, is the eighteenth letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ar'' (pronounced ), plural ''ars'', or in Irela ...that holds the various elements of a complicated structure together". See also * * * * * * * * References External links Fasteners {{tech-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circlip
A circlip (a portmanteau of "circle" and "clip"), also known as a C-clip, Rotor Clip, snap ring or Jesus clip, is a type of fastener or retaining ring consisting of a semi-flexible metal ring with open ends which can be snapped into place, into a machined groove on a dowel pin or other part to permit rotation but to prevent axial movement. There are two basic types: internal and external, referring to whether they are fitted into a bore or over a shaft. Circlips are often used to secure pinned connections. Details When used to retain piston wrist pins or gudgeon pins, the clips are known as wrist pin clips, wrist pin retainers, or gudgeon pin clips. The most commonly used circlip for this application is a simple spring steel circlip, or plain wire ring. The term "Jesus clip" comes from the propensity of the clip's spring action to launch the clip at a high velocity when removing or installing, leading to remarks such as, "Oh Jesus, where did it go?" E-clip Common examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Mason (writer)
Robert C. Mason (born March 20, 1942) is a Vietnam War veteran and author of several books, including his first, best-selling memoir: '' Chickenhawk'' (1983). Mason piloted Huey "Slicks" in the United States Army as a Warrant Officer 1. He sailed to Vietnam with the 1st Cavalry Division (Airmobile) and served a one-year tour, nine months with the "First Cav", the last three months with the 48th Aviation Company. Mason spent his first month in Vietnam clearing land for his unit's airbase, after which he and his fellow pilots flew many missions to resupply the infantry and pick up wounded. At that time 1st Cavalry Medevac helicopters were not allowed to fly if the landing zone was hot. While serving with the 1st Cavalry, Mason was involved in several battles and other missions, including the Battle of Ia Drang and the Battle of Bong Son. Mason transferred to the 48th Aviation Company (referred to as the 49th in his memoir) in May 1966. He continued to fly helicopters, including a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chickenhawk (book)
''Chickenhawk'' is Robert Mason's narrative of his experiences as a "Huey" UH-1 Iroquois helicopter pilot during the Vietnam War. The book chronicles his enlistment, flight training, deployment to and experiences in Vietnam, and his experiences after returning from the war. Writing, publishing, and reaction Mason was encouraged to write his Vietnam memoir by Knox Burger, the editor of an author-friend of Mason (Bill Smith, better known as Martin Cruz Smith). He began writing ''Chickenhawk'' on May 17, 1979 while living in Florida. The first chapter written became the fifth chapter in the finished book. By February 1980, Mason had a 200-page partial manuscript (about one-third), and an outline of the rest of his memoir. Knox agreed to offer the book to publishers. While waiting to see whether Burger could sell the book, after several rejections (i.e. "it is good but no one wants to read about Vietnam"), Mason was running a paper route each night, 100 miles on back roa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anchor (climbing)
In rock climbing, an anchor can be any device or method for attaching a climber, a rope, or a load above or onto a climbing surfacetypically rock, ice, steep dirt, or a buildingeither permanently or temporarily. The intention of an anchor is case-specific but is usually for fall protection, primarily fall arrest and fall restraint. Climbing anchors are also used for hoisting, holding static loads, or redirecting (also called deviating) a rope. Types of anchors Depending on the surface being climbed, there are many types of protection that can be used to construct an anchor, including natural protection such as boulders and trees, or artificial protection such as cams, nuts, bolts or pitons. Natural anchor A natural anchor is a secure natural feature which can serve as a climbing anchor by attaching a sling, lanyard, or cordelette and a carabiner. Examples of natural anchors include trees, boulders, lodged chockstones, horns, icicles, and protrusions. Artificial anchor An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Factor
In lead climbing using a dynamic rope, the fall factor (''f'') is the ratio of the height (''h'') a climber falls before the climber's rope begins to stretch and the rope length (''L'') available to absorb the energy of the fall, :f = \frac. It is the main factor determining the violence of the forces acting on the climber and the gear. As a numerical example, consider a fall of 20 feet that occurs with 10 feet of rope out (i.e., the climber has placed no protection and falls from 10 feet above the belayer to 10 feet below—a factor 2 fall). This fall produces far more force on the climber and the gear than if a similar 20 foot fall had occurred 100 feet above the belayer. In the latter case (a fall factor of 0.2), the rope acts like a bigger, longer rubber band, and its stretch more effectively cushions the fall. Sizes of fall factors The smallest possible fall factor is zero. This occurs, for example, in top-rope a fall onto a rope with no slack. The rope stretches, so al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belay
Belaying is a variety of techniques climbers use to create friction within a climbing system, particularly on a climbing rope, so that a falling climber does not fall very far. A climbing partner typically applies tension at the other end of the rope whenever the climber is not moving, and removes the tension from the rope whenever the climber needs more rope to continue climbing. The term "belay" also means the place where the belayer is anchored; this is typically the ground or a ledge, but may be a ''hanging belay'', where the belayer themself is suspended from an anchor in the rock. How it works Belaying is a critical part of the climbing system. A correct belaying method lets the belayer hold the entire weight of the climber with relatively little force, and easily arrest even a long fall. In its simplest form, a belay consists of merely a rope that runs from a climber to another person (the belayer) who can stop the climber's fall. In the modern day, most climbers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (vertical Space)
In rock climbing and ice climbing, a pitch is a steep section of a route that requires a rope between two belays, as part of a climbing system. Standard climbing ropes are between 50 and 80 metres long, so a pitch is always shorter, between two convenient ledges if possible; longer routes are multi-pitch, requiring the re-use of the rope each time. In free climbing, pitch refers to classification by climbers of the difficulty of ascent on certain climbing routes. illustrated superimposed on the successful ascent of the Dawn Wall, as photographed on El Capitan in Yosemite. In climbing In advanced climbing or mountaineering, another definition of ''pitch'' is not restricted by the length of the rope. On easier terrain or when moving quickly, ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climbing Protection
Climbing protection is any of a variety of devices employed to reduce risk and protect others while climbing rock and ice. It includes such items as nylon webbing and metal nuts, cams, bolts, and pitons. Different forms of climbing draw on varying forms of protection and the systems that are created from its elements. Types of climbing There are a number of ways to "protect" a climb, varying according to the type of climbing: Lead climbing A lead climber places protection (temporary or permanent anchors) in the rock, snow, or ice establishing a climbing route. The rope is clipped through carabiners (often joined by a short length of webbing into a pair known as a quickdraw) which are in turn connected to the protection. The belayer pays out rope during the ascent, and manually arrests the climber's fall by locking the rope, typically with some form of belay device. Aid climbing Aid climbing involves standing on or pulling oneself up via devices attached to fixed or pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of STOL (Short TakeOff and Landing) or STOVL (Short TakeOff and Vertical Landing) aircraft cannot perform without a runway. In 1942, the Sikorsky R-4 became the first helicopter to reach full-scale production.Munson 1968.Hirschberg, Michael J. and David K. Dailey"Sikorsky". ''US and Russian Helicopter Development in the 20th Century'', American Helicopter Society, International. 7 July 2000. Although most earlier designs used more than one main rotor, the configuration of a single main rotor accompanied by a vertical anti-torque tail rotor (i.e. unicopter, not to be confused with the single-blade monocopter) has become the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |