|
Jerzy Sikorski
Jerzy Sikorski (born July 25, 1935) is a Polish historian, Copernicologist, medievalist, museologist, author, publisher, journalist, and encyclopedist, who writes and publishes primarily in Polish. He is a resident of Olsztyn, Poland. Life Early life Jerzy Sikorski was born on July 25, 1935, in Vilnius (Polish: Wilno), to Anna Wołk-Lewanowicz (1914–1995) and Feliks Sikorski (1889–1980). Five years later (1940) Sikorski's sister Maria Danuta was born. In October 1944, during World War II, Sikorski's mother Anna was arrested by the People's Commissariat for State Security along with 40 other people, when she was exposed as a courier between Vilnius' "Kedyw" and the general staff of the Polish Home Army. Early in January 1945 Sikorski's father Feliks was also arrested because he was a soldier of the 1st Polish Corps under the Polish general Józef Dowbor-Muśnicki in the ''Polish-Soviet War,'', but he was released after three months. Upon his release, Feliks made efforts to ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copernicus
Nicolaus Copernicus (; pl, Mikołaj Kopernik; gml, Niklas Koppernigk, german: Nikolaus Kopernikus; 19 February 1473 – 24 May 1543) was a Renaissance polymath, active as a mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic canon, who formulated a model of the universe that placed the Sun rather than Earth at its center. In all likelihood, Copernicus developed his model independently of Aristarchus of Samos, an ancient Greek astronomer who had formulated such a model some eighteen centuries earlier. The publication of Copernicus's model in his book ' (''On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres''), just before his death in 1543, was a major event in the history of science, triggering the Copernican Revolution and making a pioneering contribution to the Scientific Revolution. Copernicus was born and died in Royal Prussia, a region that had been part of the Kingdom of Poland since 1466. A polyglot and polymath, he obtained a doctorate in canon law and was a mathematician, astro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warmia
Warmia ( pl, Warmia; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian: ''Warńija''; lt, Varmė; Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia. Its historic capitals were Frombork and Lidzbark Warmiński and the largest city is Olsztyn. Warmia is currently the core of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (province). The region covers an area of around and has approximately 350,000 inhabitants. Important landmarks include the Cathedral Hill in Frombork, the bishops' castles at Olsztyn and Lidzbark, the medieval town of Reszel and the sanctuary in Gietrzwałd, a site of Marian apparitions. Geographically, it is an area of many lakes and lies at the upper Łyna river and on the right bank of Pasłęka, stretching in the northwest to the Vistula Bay. Warmia has a number of architectural monuments ranging from Gothic, Renaissance and Baroque to Classicism, Historicism and Art Nouveau. Warmia is part of a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Dantiscus
Johannes Dantiscus, (german: Johann(es) von Höfen-Flachsbinder; pl, Jan Dantyszek; 1 November 1485 – 27 October 1548) was prince-bishop of Warmia and Bishop of Chełmno (Culm). In recognition of his diplomatic services for Polish kings, the bishop and poet is also known as the "Father of Polish Diplomacy." Johannes Dantiscus' personal seal, a depiction located at Stanford University Libraries, identifies him as ''Ioannes De Curiis, Pruss. Varmien'' with St. Katherine, St. Jacob and St. Peter crests. Biography Dantiscus was born in Danzig (Gdańsk), in the Kingdom of Poland. His family's name was ''von Höfen'', while ''Flachsbinder'' was an occupational name derived from his grandfather's ropemaking trade (literally ''flax binder''). Johannes took on the nickname Dantiscus in order to show that he was a burgher of Danzig ( la, Dantiscum) where his father was a brewer and merchant. He finished his elementary studies at a parish school in Grudziądz (Graudenz), and studied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauritius Ferber
Mauritius Ferber ( pl, Maurycy Ferber; 1471 – 1 July 1537) was a member of the patrician Ferber family. As Roman Catholic Prince-Bishop of Warmia (Ermland), he prevented most towns in his diocese from converting to Protestantism while the surrounding hitherto Catholic State of the Teutonic Order was transformed into the Duchy of Prussia and became the first state to adopt Lutheranism. Life The Ferber family had immigrated in 1415 from Kalkar to Danzig (Gdańsk). During four centuries, several members of the family served as mayor of Danzig, of which four served simultaneously. Johann Ferber was (nicknamed ''iron'') mayor from 1479 until his death in 1501, his son Eberhard Ferber (1463–1529) served from 1510 until 1526, and Eberhard's son Konstantin Ferber (1520–1588) from 1555 until his death in 1588, with others of the name Constantin Ferber holding the office later on. Mauritius Ferber was born in Danzig, in the Kingdom of Poland. He had stayed in England in 1497 before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an emergency decree transferring powers of the Prussian government to German Chancellor Franz von Papen in 1932 and ''de jure'' by an Allied decree in 1947. For centuries, the House of Hohenzollern ruled Prussia, expanding its size with the Prussian Army. Prussia, with its capital at Königsberg and then, when it became the Kingdom of Prussia in 1701, Berlin, decisively shaped the history of Germany. In 1871, Prussian Minister-President Otto von Bismarck united most German principalities into the German Empire under his leadership, although this was considered to be a "Lesser Germany" because Austria and Switzerland were not included. In November 1918, the monarchies were abolished and the nobility lost its political power during the Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mazury
Masuria (, german: Masuren, Masurian: ''Mazurÿ'') is a ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship (administrative area/province). Its biggest city, often regarded as its capital, is Ełk (Elk). The region covers a territory of some 10,000 km2 which is inhabited by approximately 500,000 people. History East Germanic tribes The first known people in today's Mazuria were East Germanic tribes, such as the Sciri. Ptolemy mentioned Galindians (Koine Greek: Galindoi – Γαλίνδοι) in the 2nd century AD. From the 6th/7th century until the 17th century the former central part of the Galindian tribe continued to exist as the Old Prussian clan of *Galindis. The language of the Old Prussians in Galindia became extinct by 17th century, mainly because of the 16th centuries influx of Protestants seeking refug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to the German states of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania and Brandenburg, while the eastern part belongs to the West Pomeranian, Pomeranian and Kuyavian-Pomeranian voivodeships of Poland. Its historical border in the west is the Mecklenburg-Western Pomeranian border '' Urstromtal'' which now constitutes the border between the Mecklenburgian and Pomeranian part of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, while it is bounded by the Vistula River in the east. The easternmost part of Pomerania is alternatively known as Pomerelia, consisting of four sub-regions: Kashubia inhabited by ethnic Kashubians, Kociewie, Tuchola Forest and Chełmno Land. Pomerania has a relatively low population density, with its largest cities being Gdańsk and Szczecin. Ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. A marginal sea of the Atlantic, with limited water exchange between the two water bodies, the Baltic Sea drains through the Danish Straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia, the Bay of Bothnia, the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The " Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the west by the Swedish part of the southern Scandinavian Peninsula. The Baltic Sea is connected by artificial waterways to the White Sea via the White Sea–Baltic Canal and to the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
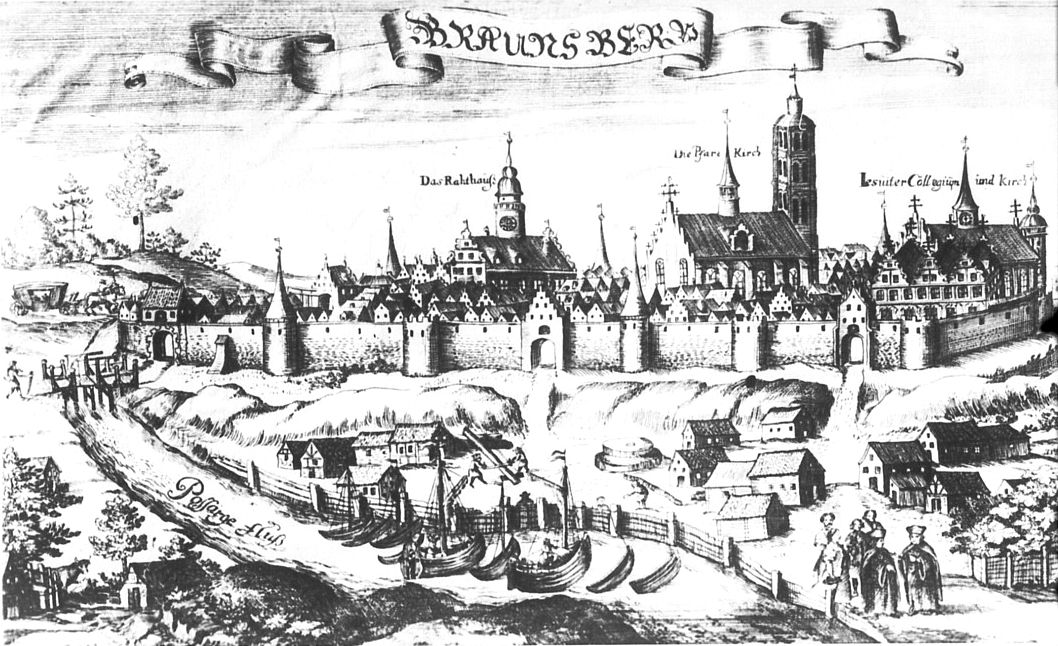
Braniewo
Braniewo () (german: Braunsberg in Ostpreußen, la, Brunsberga, Old Prussian: ''Brus'', lt, Prūsa), is a town in northern Poland, in Warmia, in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, with a population of 16,907 as of June 2021. It is the capital of Braniewo County. Braniewo is the second biggest city of Warmia after Olsztyn and one of the historical centers of the region. Location Braniewo lies on the Pasłęka River about 5 km from the Vistula Lagoon, about 35 km northeast of Elbląg and southwest of Kaliningrad ( pl, Królewiec). The Polish border with Russia's Kaliningrad Oblast lies 6 km north, and may be reached from Braniewo via National road 54. History Middle Ages According to the German geographer Johann Friedrich Goldbeck (1748-1812), the town originally was named Brunsberg after Bruno von Schauenburg (1205–1281), bishop of Olomouc in Moravia, who accompanied King Ottokar II of Bohemia in 1254 and 1267 when the latter participated in the crusade of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lidzbark Warmiński Castle
The Lidzbark Castle ( pl, Zamek w Lidzbarku, german: Burg Heilsberg), officially known as Lidzbark Bishops' Castle, is a fortified castle and palace from the 14th century located in the town of Lidzbark Warmiński, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It is one of the most precious Gothic structures in the country and a popular destination for holidaymakers. Description The palatial stronghold in Lidzbark Warmiński, which for centuries was the largest town in Warmia, is located by the estuary of the river Symsarna with the river Łyna. The stronghold is encircled by a defensive moat. An additional "dry moat" encircled the local living quarters located close to the stronghold - all of the defensive structures survive except the northern-moat, where the castle's windmill was once located. The castle was built on a plan of a square formation, with 48,5 metre long walls. A fourteen level tower is located in the north-east wing of the castle. The lower part of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucas Watzenrode
Lucas Watzenrode the Younger (sometimes ''Watzelrode'' and ''Waisselrod''; german: Lucas Watzenrode der Jüngere; pl, Łukasz Watzenrode; 30 October 1447 – 29 March 1512) was Prince-Bishop of Warmia (Ermland) and patron to his nephew, astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus. Early life The family and its name stemmed from the Silesian village of Weizenrodau, now Pszenno. Watzenrode was born in Toruń, Thorn (Toruń), son of the merchant Lucas Watzenrode the Elder (1400–62). He studied at Jagiellonian University, and at the universities of University of Cologne, Cologne and University of Bologna, Bologna. After his sister Barbara and her husband Niklas Koppernigk died circa 1483, Lucas cared for their four children, Katharina, Barbara, Andreas and Nicolaus, the last of whom would become known as astronomer Nicolaus Copernicus. Historic background The Bishopric of Warmia, previously part of the Monastic State of the Teutonic Knights, had, with the Second Peace of Thorn (1466), com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
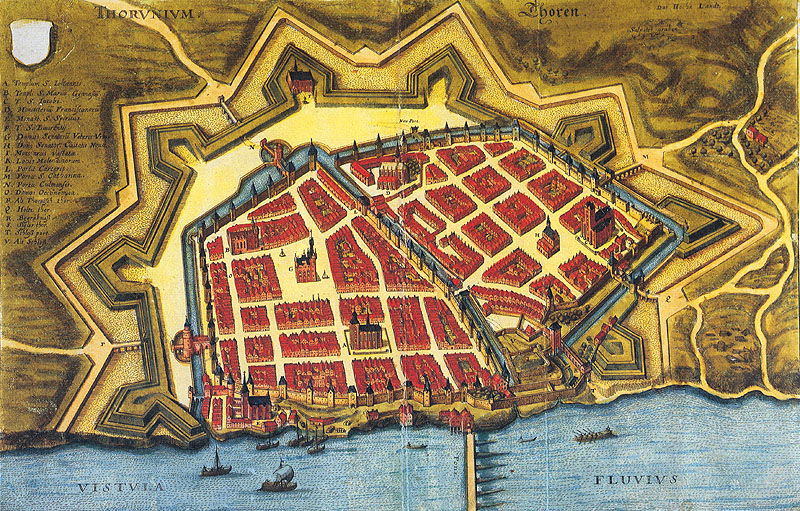
Nicolaus Copernicus University In Toruń
Nicolaus Copernicus University in Toruń or NCU ( pl, Uniwersytet Mikołaja Kopernika w Toruniu, UMK) is located in Toruń, Poland. It is named after Nicolaus Copernicus, who was born in Toruń in 1473. History 
The beginnings of higher education in Toruń The first institution of higher education in Torun, the Toruń Academic Gymnasium was founded in 1568 on Piekary street. It was one of the first universities in northern Poland. The Academic Gymnasium was the precursor to scientific and cultural life (includi ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |