|
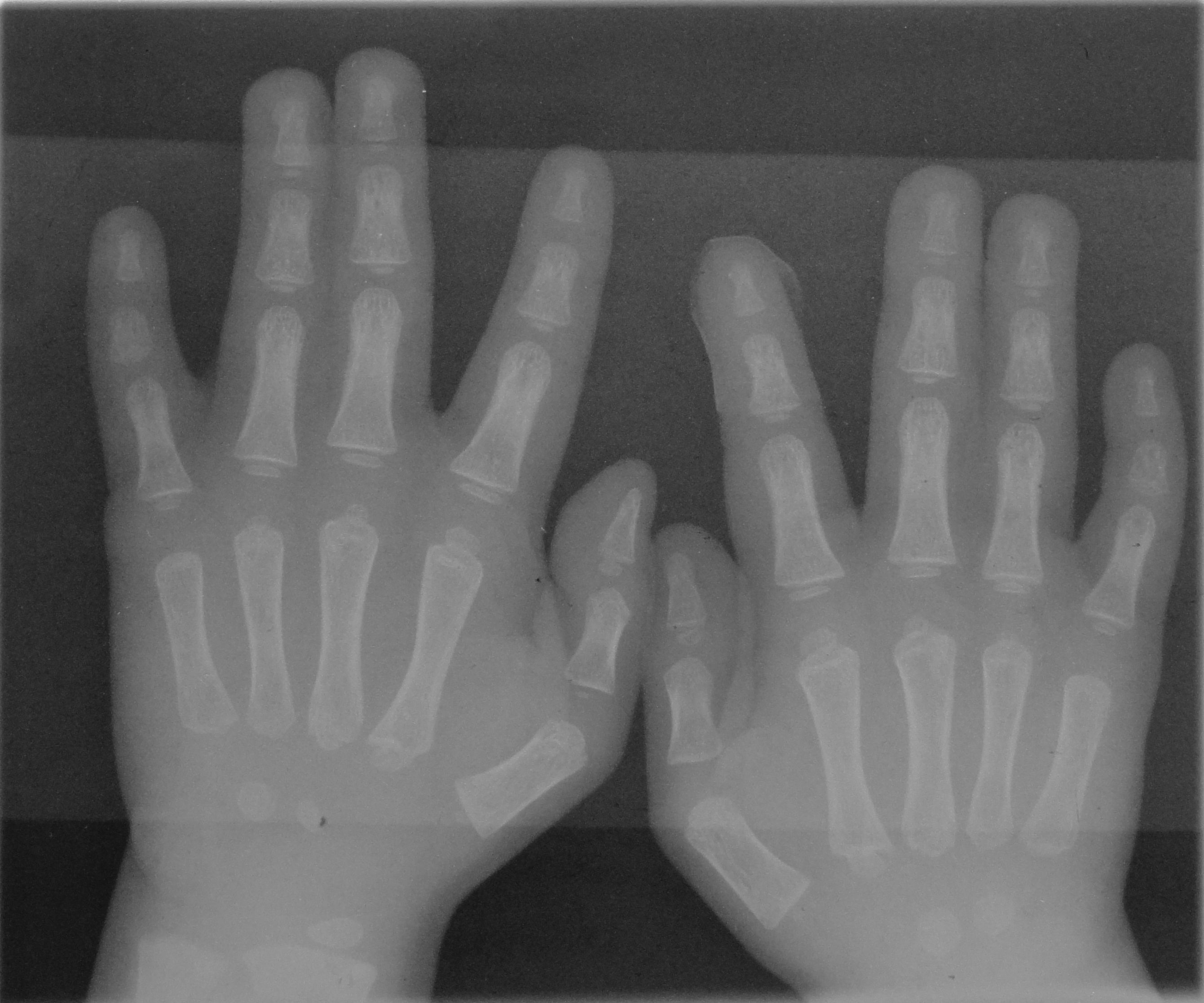
Jersey Finger
Jersey finger, also known as rugby finger, is a finger-related tendon injury that is common in sport and can result in permanent loss of flexion of the end of the finger if not surgically repaired. The injury is common when one player grabs another's jersey with the tips of one or more fingers while that player is pulling or running away. It is the most common closed flexor tendon injury and occurs in the ring finger in 75% of cases. Signs and symptoms * A pop or rip felt in the finger at the time of the injury * Pain when moving the injured finger and the inability to bend the DIPjoint * Tenderness, swelling. and warmth of the injured finger * Bruising after 48 hours * Occasionally a lump felt in the palm of the finger Cause A Jersey finger is a traumatic rupture of the flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) tendon at its point of attachment to the distal phalanx. This injury often occurs in American football when a player grabs another player's jersey with the tips of one or more fing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finger
A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers ( Pentadactyly). Chambers 1998 p. 603 Oxford Illustrated pp. 311, 380 Land vertebrate fingers The five-rayed anterior limbs of terrestrial vertebrates can be derived phylogenetically from the pectoral fins of fish. Within the taxa of the terrestrial vertebrates, the basic pentadactyl plan, and thus also the fingers and phalanges, undergo many variations. Morphologically the different fingers of terrestrial vertebrates are homolog. The wings of birds and those of bats are not homologous, they are analogue flight organs. However, the phalanges within them are homologous. Chimpanzees have lower limbs that are specialized for manipulation, and (arguably) have fingers on their lower limbs as well. In the case of Primates in general, the digits of the hand a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proximal Phalanges
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones. Structure The phalanges are the bones that make up the fingers of the hand and the toes of the foot. There are 56 phalanges in the human body, with fourteen on each hand and foot. Three phalanges are present on each finger and toe, with the exception of the thumb and large toe, which possess only two. The middle and far phalanges of the fifth toes are often fused together (symphalangism). The phalanges of the hand are commonly known as the finger bones. The phalanges of the foot differ from the hand in that they are often shorter and more compressed, especially in the proximal phalanges, those closest to the torso. A phalanx is named according to whether it is proximal, middle, or distal and its associated finger or toe. The proximal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deformity
A deformity, dysmorphism, or dysmorphic feature is a major abnormality of an organism that makes a part of the body appear or function differently than how it is supposed to. Causes Deformity can be caused by a variety of factors: *Arthritis and other rheumatoid disorders *Chronic application of external forces, e.g. artificial cranial deformation *Chronic paresis, paralysis or muscle imbalance, especially in children, e.g. due to poliomyelitis or cerebral palsy *Complications at birth *Damage to the fetus or uterus *Fractured bones left to heal without being properly set (malunion) *Genetic mutation *Growth or hormone disorders *Infection *Reconstructive surgery following a severe injury, e.g. burn injury Deformity can occur in all organisms: * Frogs can be mutated due to Ribeiroia (Trematoda) infection. * Plants can undergo irreversible cell deformation * Insects, such as honeybees, can be affected by deformed wing virus * Fish can be found with scoliosis due to environment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Journal Of Sport Medicine
The ''Clinical Journal of Sport Medicine'' (''CJSM'') is a peer-reviewed medical journal in the sports medicine field. It is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. It was established in 1990 by the Canadian Academy of Sport and Exercise Medicine with Gordon Matheson as the founding editor. It is also the official journal of the Australasian College of Sport and Exercise Physicians, the American Medical Society for Sports Medicine (AMSSM) and American Osteopathic Academy of Sports Medicine. It is the pre-eminent non-surgical sports medicine journal of North America. In North America (USA and Canada), sports medicine is a subspecialty field of medicine with an even split between surgical and non-surgical subspecialties. The surgical branch of sports medicine is a subspecialty field of orthopedics, whereas the non-surgical branch draws from specialties including family practice, physiatry, pediatrics, internal medicine and emergency medicine. The journal editor-in-chief is Chri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carpal Tunnel
In the human body, the carpal tunnel or carpal canal is the passageway on the palmar side of the wrist that connects the forearm to the hand. The tunnel is bounded by the bones of the wrist and flexor retinaculum from connective tissue. Normally several tendons from the flexor group of forearm muscles and the median nerve pass through it. There are described cases of variable median artery occurrence. When any of the nine long flexor tendons passing through the narrow carpal canal swell or degenerate, the narrowing of the canal may result in the median nerve becoming entrapped or compressed, a common medical condition known as carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Structure The carpal bones that make up the wrist form an arch which is convex on the dorsal side of the hand and concave on the palmar side. The groove on the palmar side, the ''sulcus carpi'', is covered by the flexor retinaculum, a sheath of tough connective tissue, thus forming the carpal tunnel. On the side of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Digitorum Profundus Muscle
The flexor digitorum profundus is a muscle in the forearm of humans that flexes the fingers (also known as digits). It is considered an extrinsic hand muscle because it acts on the hand while its muscle belly is located in the forearm. Together the flexor pollicis longus, pronator quadratus, and flexor digitorum profundus form the deep layer of ventral forearm muscles.Platzer 2004, p 162 The muscle is named . Structure Flexor digitorum profundus originates in the upper 3/4 of the anterior and medial surfaces of the ulna, interosseous membrane and deep fascia of the forearm. The muscle fans out into four tendons (one to each of the second to fifth fingers) to the palmar base of the distal phalanx. Along with the flexor digitorum superficialis, it has long tendons that run down the arm and through the carpal tunnel and attach to the palmar side of the phalanges of the fingers. Flexor digitorum profundus lies deep to the superficialis, but it attaches more distally. Therefore, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexor Muscle
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability to withstand significant amounts of tension. Tendons are similar to ligaments; both are made of collagen. Ligaments connect one bone to another, while tendons connect muscle to bone. Structure Histologically, tendons consist of dense regular connective tissue. The main cellular component of tendons are specialized fibroblasts called tendon cells (tenocytes). Tenocytes synthesize the extracellular matrix of tendons, abundant in densely packed collagen fibers. The collagen fibers are parallel to each other and organized into tendon fascicles. Individual fascicles are bound by the endotendineum, which is a delicate loose connective tissue containing thin collagen fibrils and elastic fibres. Groups of fascicles are bounded by the epitenon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
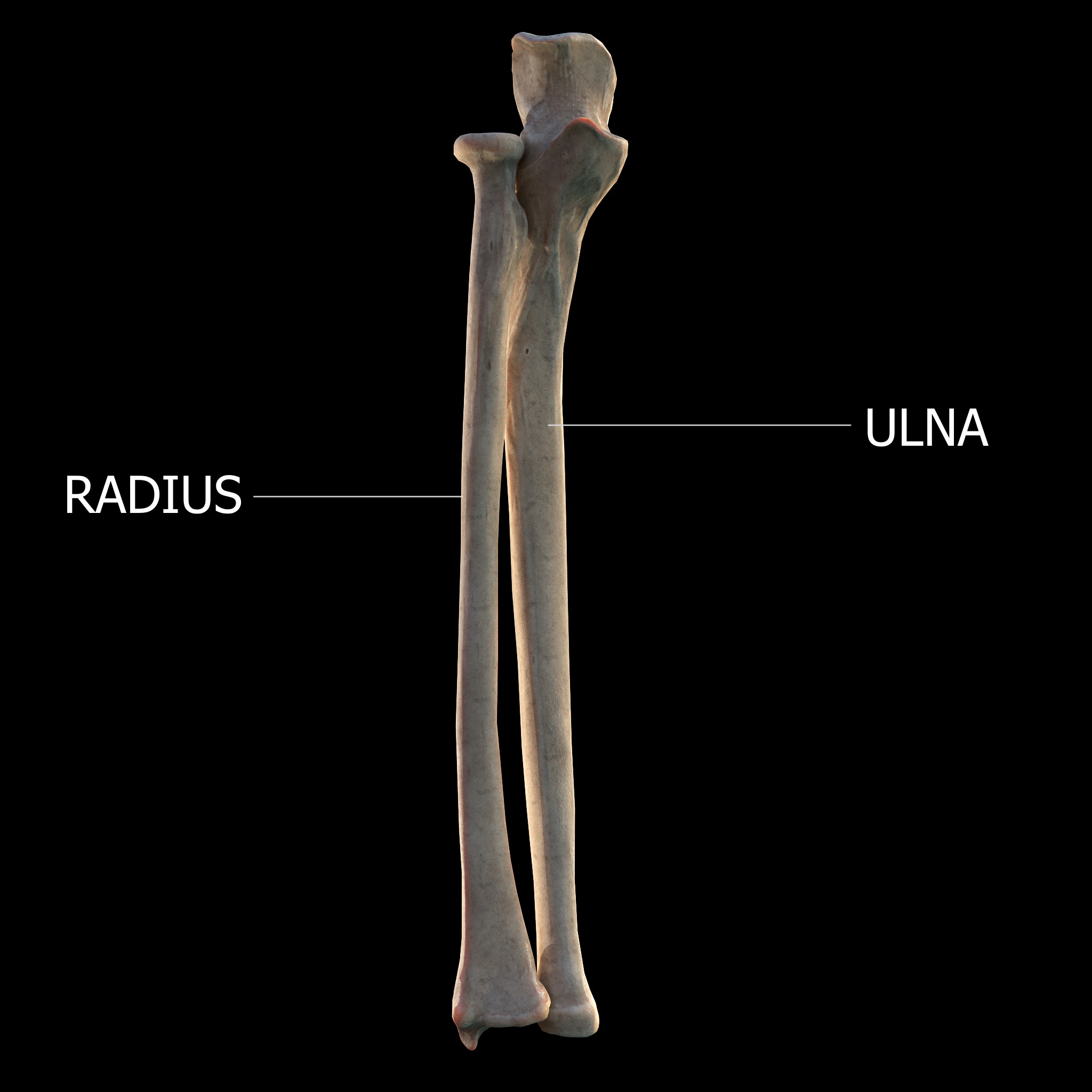
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is most often used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow (brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interphalangeal Articulations Of Hand
The interphalangeal joints of the hand are the hinge joints between the phalanges of the fingers that provide flexion towards the palm of the hand. There are two sets in each finger (except in the thumb, which has only one joint): * "proximal interphalangeal joints" (PIJ or PIP), those between the first (also called proximal) and second (intermediate) phalanges * "distal interphalangeal joints" (DIJ or DIP), those between the second (intermediate) and third (distal) phalanges Anatomically, the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints are very similar. There are some minor differences in how the palmar plates are attached proximally and in the segmentation of the flexor tendon sheath, but the major differences are the smaller dimension and reduced mobility of the distal joint. Joint structure The PIP joint exhibits great lateral stability. Its transverse diameter is greater than its antero-posterior diameter and its thick collateral ligaments are tight in all positions duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |