|
Jean De Noircarmes
Jean de Noircarmes (died 1585), lord of Selles, was a royalist soldier and diplomat, loyal to Philip II of Spain, during the Dutch Revolt. His most important mission was to attempt to negotiate a return of the Habsburg Netherlands to loyalty after the Pacification of Ghent, with the only two royal demands being the maintenance of Catholicism and the recognition of Philip II's sovereignty. In December 1577 he was sent from Madrid with royal letters to this effect, arriving in Brussels in January 1578.Émile de Borchgrave, "Noircarmes (Jean de)", ''Biographie Nationale de Belgique''vol. 15(Brussels, 1899), 780-784. His negotiations with the States General proved fruitless, but he was able to conclude the Treaty of Arras (1579) with the provinces that had formed the Union of Arras. Jacques Bernard, ''Recueil des traitez de paix, de trêve, de neutralité, de suspension d'armes, de confédération, d'alliance, de commerce, de garantie, et d'autres actes publics'' (The Hague, 1700), p. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip II Of Spain
Philip II) in Spain, while in Portugal and his Italian kingdoms he ruled as Philip I ( pt, Filipe I). (21 May 152713 September 1598), also known as Philip the Prudent ( es, Felipe el Prudente), was King of Spain from 1556, King of Portugal from 1580, and King of Naples and Sicily from 1554 until his death in 1598. He was '' jure uxoris'' King of England and Ireland from his marriage to Queen Mary I in 1554 until her death in 1558. He was also Duke of Milan from 1540. From 1555, he was Lord of the Seventeen Provinces of the Netherlands. The son of Emperor Charles V and Isabella of Portugal, Philip inherited his father's Spanish Empire in 1556 and succeeded to the Portuguese throne in 1580 following a dynastic crisis. The Spanish conquests of the Inca Empire and of the Philippines, named in his honor by Ruy López de Villalobos, were completed during his reign. Under Philip II, Spain reached the height of its influence and power, sometimes called the Spanish Golden Age, and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Revolt
The Eighty Years' War or Dutch Revolt ( nl, Nederlandse Opstand) (Historiography of the Eighty Years' War#Name and periodisation, c.1566/1568–1648) was an armed conflict in the Habsburg Netherlands between disparate groups of rebels and the Spanish Empire, Spanish government. The Origins of the Eighty Years' War, causes of the war included the Reformation, centralisation, taxation, and the rights and privileges of the nobility and cities. After Eighty Years' War, 1566–1572, the initial stages, Philip II of Spain, the sovereign of the Netherlands, deployed Army of Flanders, his armies and Eighty Years' War, 1572–1576, regained control over most of the rebel-held territories. However, Spanish Fury, widespread mutinies in the Spanish army caused a general uprising. Under the leadership of the exiled William the Silent, the Catholic- and Protestant-dominated provinces sought to establish religious peace while jointly opposing the king's regime with the Pacification of Ghent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
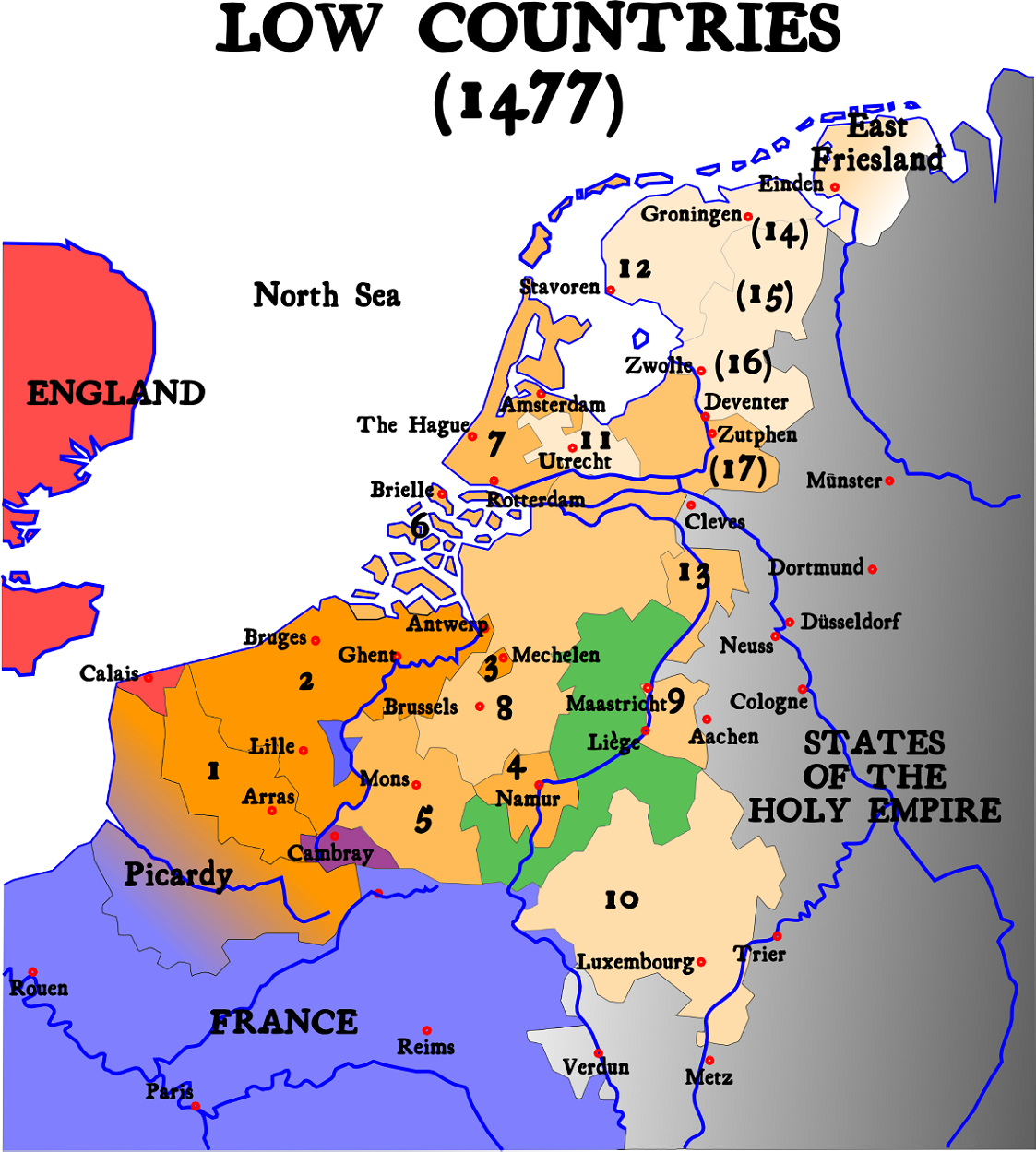
Habsburg Netherlands
Habsburg Netherlands was the Renaissance period fiefs in the Low Countries held by the Holy Roman Empire's House of Habsburg. The rule began in 1482, when the last House of Valois-Burgundy, Valois-Burgundy ruler of the Netherlands, Mary of Burgundy, Mary, wife of Maximilian I of Austria, died. Their grandson, Emperor Charles V, was born in the Habsburg Netherlands and made Brussels one of his capitals. Becoming known as the Seventeen Provinces in 1549, they were held by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs from 1556, known as the Spanish Netherlands from that time on. In 1581, in the midst of the Dutch Revolt, the Seven United Provinces seceded from the rest of this territory to form the Dutch Republic. The remaining Spanish Southern Netherlands became the Austrian Netherlands in 1714, after Austrian acquisition under the Treaty of Rastatt. De facto Habsburg rule ended with the annexation by the revolutionary French First Republic in 1795. Austria, however, did not relinquish its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacification Of Ghent
The Pacification of Ghent, signed on 8 November 1576, was an alliance between the provinces of the Habsburg Netherlands. The main objectives were to remove Habsburg Spain, Spanish mercenaries who had made themselves hated by all sides due to their plundering, and to promote a formal peace with the rebellious provinces of Holland and Zeeland. Background In 1566, the Habsburg Netherlands experienced considerable political upheaval and civil unrest, which culminated in the Beeldenstorm, iconoclastic fury of that year. Its ruler, Philip II of Spain, responded by appointing Fernando Álvarez de Toledo, 3rd Duke of Alba as List of governors of the Habsburg Netherlands, Governor-general, and in 1567 he arrived there to restore order, accompanied by an army of mercenaries. Philip soon replaced the most important advisors to former regent Margaret of Parma, either by summarily executing those such as the counts of Lamoral, Count of Egmont, Egmont and Philip de Montmorency, Count of Hoorn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Émile De Borchgrave
Baron Émile Jacques Yvon Marie de Borchgrave (1837–1917) was a Belgian historian and diplomat. Life Borchgrave was born in Ghent on 27 December 1837. He was educated at the College of St Barbara in Ghent and spent one year studying philosophy at the University of Paris before obtaining a doctorate in law from Ghent University.Jacques Willequet, "Borchgrave (Émile Jacques Yvon Marie de)", ''Biographie Nationale de Belgique''vol. 40(Brussels, 1977), 73-75. At the age of 25 he entered the Belgian foreign service. He was posted to The Hague in 1863, to Frankfurt in 1866, and then to Bern. Borchgrave returned to Brussels to work at the ministry in 1869, and in 1872 became a member of the Royal Academy of Science, Letters and Fine Arts of Belgium. He was secretary to the 1874 Brussels Peace Conference, and a delegate at the 1876 Brussels Geographic Conference. In 1875 he was appointed to the Belgian legation in Berlin, in 1879 chargé d'affaires in Serbia, in 1885 ambassador to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biographie Nationale De Belgique
The ''Biographie nationale de Belgique'' ( French; "National Biography of Belgium") is a biographical dictionary of Belgium. It was published by the Royal Academy of Belgium in 44 volumes between 1866 and 1986. A continuation series, entitled the ''Nouvelle Biographie Nationale'' ("New National Biography"), has been published by the Royal Academy of Science, Letters and Fine Arts of Belgium since 1988. Both the ''Biographie nationale'' and ''Nouvelle biographie nationale'' were digitised by the Fonds InBev-Baillet Latour and can be freely consulted at the Academy's website. A parallel biographical dictionary has been produced in Dutch since 1964, entitled the ''Nationaal Biografisch Woordenboek'' ("National Biographical Dictionary"). It places more emphasis on figures important to the history and culture of Flanders and is published by the Royal Flemish Academy of Belgium for Science and the Arts (with the co-operation of the Royal Academy of Dutch language and literature and the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)