|
Jean Swank
Jean Hebb Swank is an astrophysicist who is best known for her studies of black holes and neutron stars. Early life and education Swank graduated with a Bachelor of Arts degree in physics from Bryn Mawr College in 1961. Two of her physics professors at Bryn Mawr were alumni of Caltech. They influenced her decision to attend graduate school at the California Institute of Technology. Under the supervision of Steve Frautschi, she was awarded her PhD in physics in 1967. Her thesis was "Radiative Corrections to Neutrino-Electron Interactions". Teaching career Swank taught physics as an assistant professor at California State University at Los Angeles from 1966 to 1969. After her marriage, Swank moved to Illinois where she taught at Chicago State University from 1969 until 1971. In 1971, Swank and her husband moved to Ankara, Turkey, to join the faculty of the Middle East Technical University as assistant professors. There she met Hakkı Boran Ögelman, a high-energy astrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bachelor Of Arts
Bachelor of arts (BA or AB; from the Latin ', ', or ') is a bachelor's degree awarded for an undergraduate program in the arts, or, in some cases, other disciplines. A Bachelor of Arts degree course is generally completed in three or four years, depending on the country and institution. * Degree attainment typically takes four years in Afghanistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bangladesh, Brazil, Brunei, China, Egypt, Ghana, Greece, Georgia, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Ireland, Japan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Kuwait, Latvia, Lebanon, Lithuania, Mexico, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Netherlands, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines, Qatar, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Scotland, Serbia, South Korea, Spain, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, Ukraine, the United States and Zambia. * Degree attainment typically takes three years in Albania, Australia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Caribbean, Iceland, India, Israel, Italy, New Zealand, Norway, South Africa, Switzerland, the Canadian province of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma-ray Astronomy
Gamma-ray astronomy is the astronomical observation of gamma rays,Astronomical literature generally hyphenates "gamma-ray" when used as an adjective, but uses "gamma ray" without a hyphen for the noun. the most energetic form of electromagnetic radiation, with photon energies above 100 keV. Radiation below 100 keV is classified as X-rays and is the subject of X-ray astronomy. In most known cases, gamma rays from solar flares and Earth's atmosphere are generated in the MeV range, but it is now known that gamma rays in the GeV range can also be generated by solar flares. It had been believed that gamma rays in the GeV range do not originate in the Solar System. As GeV gamma rays are important in the study of extra-solar, and especially extra-galactic, astronomy, new observations may complicate some prior models and findings. The mechanisms emitting gamma rays are diverse, mostly identical with those emitting X-rays but at higher energies, including electron–positro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emeritus
''Emeritus'' (; female: ''emerita'') is an adjective used to designate a retired chair, professor, pastor, bishop, pope, director, president, prime minister, rabbi, emperor, or other person who has been "permitted to retain as an honorary title the rank of the last office held". In some cases, the term is conferred automatically upon all persons who retire at a given rank, but in others, it remains a mark of distinguished service awarded selectively on retirement. It is also used when a person of distinction in a profession retires or hands over the position, enabling their former rank to be retained in their title, e.g., "professor emeritus". The term ''emeritus'' does not necessarily signify that a person has relinquished all the duties of their former position, and they may continue to exercise some of them. In the description of deceased professors emeritus listed at U.S. universities, the title ''emeritus'' is replaced by indicating the years of their appointmentsThe Protoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Distinguished Service Medal
The NASA Distinguished Service Medal is the highest award that can be bestowed by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration of the United States. The medal may be presented to any member of the federal government, including both military astronauts and civilian employees. The NASA Distinguished Service Medal is awarded to those who display distinguished service, ability, or courage, and have personally made a contribution representing substantial progress to the NASA mission. The contribution must be so extraordinary that other forms of recognition would be inadequate. Typical presentations of the NASA Distinguished Service Medal included awards to senior NASA administrators, mission control leaders, and astronauts who have completed several successful space flights. Due to the prestige of the award, the decoration is authorized for wear on active uniforms of the United States military. Another such authorized decoration is the NASA Space Flight Medal. Upon the rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Journal
In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication intended to further the progress of science, usually by reporting new research. Content Articles in scientific journals are mostly written by active scientists such as students, researchers, and professors instead of professional journalists. There are thousands of scientific journals in publication, and many more have been published at various points in the past (see list of scientific journals). Most journals are highly specialized, although some of the oldest journals such as ''Nature'' publish articles and scientific papers across a wide range of scientific fields. Scientific journals contain articles that have been peer reviewed, in an attempt to ensure that articles meet the journal's standards of quality and scientific validity. Although scientific journals are superficially similar to professional magazines, they are actually quite different. Issues of a scientific journal are rarely read casuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Physical Society
The American Physical Society (APS) is a not-for-profit membership organization of professionals in physics and related disciplines, comprising nearly fifty divisions, sections, and other units. Its mission is the advancement and diffusion of knowledge of physics. The society publishes more than a dozen scientific journals, including the prestigious '' Physical Review'' and ''Physical Review Letters'', and organizes more than twenty science meetings each year. APS is a member society of the American Institute of Physics. Since January 2021 the organization has been led by chief executive officer Jonathan Bagger. History The American Physical Society was founded on May 20, 1899, when thirty-six physicists gathered at Columbia University for that purpose. They proclaimed the mission of the new Society to be "to advance and diffuse the knowledge of physics", and in one way or another the APS has been at that task ever since. In the early years, virtually the sole activity of the AP ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity And Extreme Magnetism
Gravity and Extreme Magnetism Small Explorer (GEMS or SMEX-13) mission was a NASA space observatory mission. The main scientific goal of GEMS was to be the first mission to systematically measure the polarization of X-ray sources. GEMS would have provided data to help scientists study the shape of spacetime that has been distorted by a spinning black hole's gravity and the structure and effects of the magnetic fields around neutron stars. It was cancelled by NASA in June 2012 for potential cost overruns due to delays in developing the technology and never moved into the development phase. GEMS was managed by the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC). The project was an astrophysics program reporting to NASA's Science Mission Directorate (SMD) in Washington, D.C. Cancelled missions can be reinstated - for example, NuSTAR was cancelled in 2006, but reinstated a year later and launched in June 2012. However, NuSTAR was not cancelled due to project overruns, but rather due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hale Bradt
Hale may refer to: Places Australia *Hale, Northern Territory, a locality *Hale River, in southeastern Northern Territory Canada *Hale, Ontario, in Algoma District United Kingdom * Hale, Cumbria, a hamlet near Beetham, Cumbria *Hale, Greater Manchester, a village in the Metropolitan Borough of Trafford, Greater Manchester **Hale (Trafford ward), a former electoral ward in the Metropolitan Borough of Trafford, Greater Manchester *Hale, Halton, a village in Halton, Cheshire **Hale, an electoral ward in the Borough of Halton, Cheshire *Hale, Hampshire, a village in the New Forest *Hale, Surrey, a village near Farnham *Great Hale, a village in the North Kesteven district of Lincolnshire *Little Hale, a hamlet in the North Kesteven district of Lincolnshire *Tottenham Hale, a district in the London Borough of Haringey *The Hale, an area of the London Borough of Barnet **Hale, an electoral ward in the London Borough of Barnet *The Hale, Buckinghamshire, a hamlet near Wendover United Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruno Rossi Prize
The Bruno Rossi Prize is awarded annually by the High Energy Astrophysics division of the American Astronomical Society "for a significant contribution to High Energy Astrophysics, with particular emphasis on recent, original work". Named after astrophysicist Bruno Rossi, the prize is awarded with a certificate and a gift of USD $500, and was first awarded in 1985 to William R. Forman and Christine Jones Forman "for pioneering work in the study of X-ray emission from early type galaxies". It has been awarded 32 times. In 2010, the prize was awarded to William B. Atwood, Peter Michelson and the Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope team "for enabling, through the development of the Large Area Telescope, new insights into neutron stars, supernova remnants, cosmic rays, binary systems, active galactic nuclei, and gamma-ray bursts". In 2013, the prize was awarded to Roger W. Romani of Leland Stanford Junior University and Alice Harding of Goddard Space Flight Center for their work in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
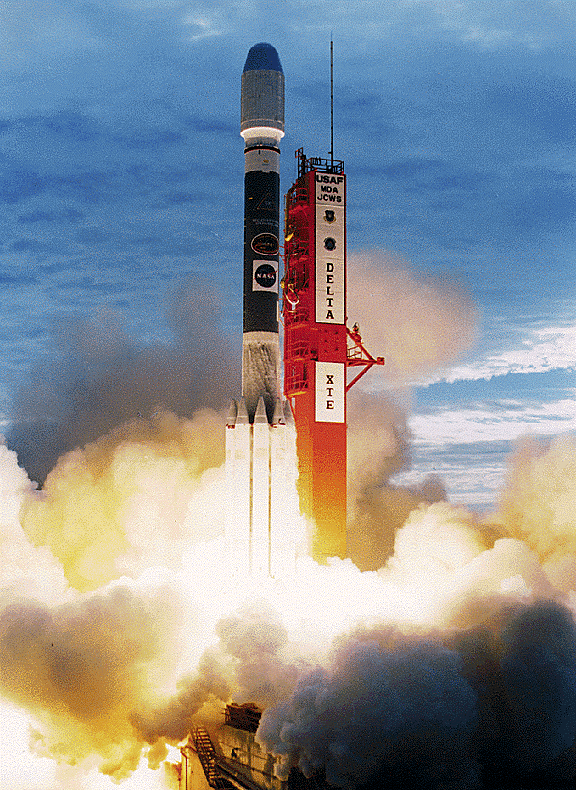
Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer
The Rossi X-ray Timing Explorer (RXTE) was a NASA satellite that observed the time variation of astronomical X-ray sources, named after physicist Bruno Rossi. The RXTE had three instruments — an All Sky Monitor, the High-Energy X-ray Timing Experiment (HEXTE) and the Proportional Counter Array. The RXTE observed X-rays from black holes, neutron stars, X-ray pulsars and X-ray bursts. It was funded as part of the Explorer program, and was also called Explorer 69. RXTE had a mass of and was launched from Cape Canaveral on 30 December 1995, at 13:48:00 UTC, on a Delta II launch vehicle. Its International Designator is 1995-074A. Mission The X-Ray Timing Explorer (XTE) mission has the primary objective to study the temporal and broad-band spectral phenomena associated with stellar and galactic systems containing compact objects in the energy range 2--200 KeV, and in time scales from microseconds to years. The scientific instruments consists of two pointed instruments, the Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principal Investigator
In many countries, the term principal investigator (PI) refers to the holder of an independent grant and the lead researcher for the grant project, usually in the sciences, such as a laboratory study or a clinical trial. The phrase is also often used as a synonym for "head of the laboratory" or "research group leader". While the expression is common in the sciences, it is used widely for the person or persons who make final decisions and supervise funding and expenditures on a given research project. A co-investigator (Co-I) assists the principal investigator in the management and leadership of the research project. There may be a number of co-investigators supporting a PI. Federal funding In the context of United States federal funding from agencies such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH) or the National Science Foundation (NSF), the PI is the person who takes direct responsibility for completion of a funded project, directing the research and reporting directly to the fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States National Research Council
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (also known as NASEM or the National Academies) are the collective scientific national academy of the United States. The name is used interchangeably in two senses: (1) as an umbrella term for its three quasi-independent honorific member organizations the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), the National Academy of Engineering (NAE), and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM); and (2) as the brand for studies and reports issued by the operating arm of the three academies, the National Research Council (NRC). The NRC was first formed in 1916 as an activity of the NAS. Now jointly governed by all three academies, the NRC produces some 200 publications annually which are published by the National Academies Press. The reports produced by the National Academies have been characterized as reflective of scientific consensus. History The US National Academy of Sciences was created by an Act of Incorporation dated March 3, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |