|
Jean-Louis De Cordemoy
The Abbé Jean-Louis de Cordemoy (1655–1714) was a French architectural historian, prior of St-Nicolas at La-Ferté-sous-Jouarre (Seine-et-Marne), and a canon at St-Jean-des-Vignes, Soissons (Aisne). His ''Nouveau Traité de toute l’architecture'' was amongst the first studies of ecclesiastical architecture, wherein he praised the Gothic style for its clear expression of structure. Influenced by Michel de Frémin and Claude Perrault his ideas of ''ordonnance'', ''disposition'' and ''bienséance'' as expressions of integrity to nature and structure were early precursors of the modern concepts of functionalism and truth to materials.History of Architectural Theory, Hanno-Walter Kruft, 1994, p.141. He had a considerable influence on 18th-century architectural theory, especially Antoine Desgodetz, Marc-Antoine Laugier, de la Hire and Boffrand. He also participated in an acrimonious debate with the engineer Amédée-François Frézier regarding sacred architecture in the Jes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Ferté-sous-Jouarre
La Ferté-sous-Jouarre () is a Communes of France, commune in the Seine-et-Marne Departments of France, département in the Île-de-France Regions of France, region in north-central France. It is located at a crossing point over the river Marne (river), Marne between Meaux and Château-Thierry. History This area of France has frequently been a site of warfare. In 1819, British naval officer, Norwich Duff (1792–1862), Edinburgh born, recorded a note on La Ferté. The Bourbon Restoration in France, Bourbon Restoration had apparently dampened the Napoleonic road building boom, as evidenced by unused milestones. Construction projects had rebuilt some facilities destroyed in the wars with Britain and other Powers. La Ferté is famous for millstones used for milling flour. Some have even been found in England. Among notable residents, the artist Émile Bayard was born in this town (1837). The Irish avant-garde writer, dramatist, poet and nobel prize winner Samuel Beckett lived i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American public intellectual: a linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky is also a major figure in analytic philosophy and one of the founders of the field of cognitive science. He is a Laureate Professor of Linguistics at the University of Arizona and an Institute Professor Emeritus at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), and is the author of more than 150 books on topics such as linguistics, war, politics, and mass media. Ideologically, he aligns with anarcho-syndicalism and libertarian socialism. Born to Ashkenazi Jewish immigrants in Philadelphia, Chomsky developed an early interest in anarchism from alternative bookstores in New York City. He studied at the University of Pennsylvania. During his postgraduate work in the Harvard Society of Fellows, Chomsky developed the theory of transformati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edict Of Nantes
The Edict of Nantes () was signed in April 1598 by King Henry IV and granted the Calvinist Protestants of France, also known as Huguenots, substantial rights in the nation, which was in essence completely Catholic. In the edict, Henry aimed primarily to promote civil unity. The edict separated civil from religious unity, treated some Protestants for the first time as more than mere schismatics and heretics and opened a path for secularism and tolerance. In offering a general freedom of conscience to individuals, the edict offered many specific concessions to the Protestants, such as amnesty and the reinstatement of their civil rights, including the right to work in any field, even for the state, and to bring grievances directly to the king. It marked the end of the French Wars of Religion, which had afflicted France during the second half of the 16th century. The Edict of St. Germain, promulgated 36 years earlier by Catherine de Médici, had granted limited tolerance to Hugu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
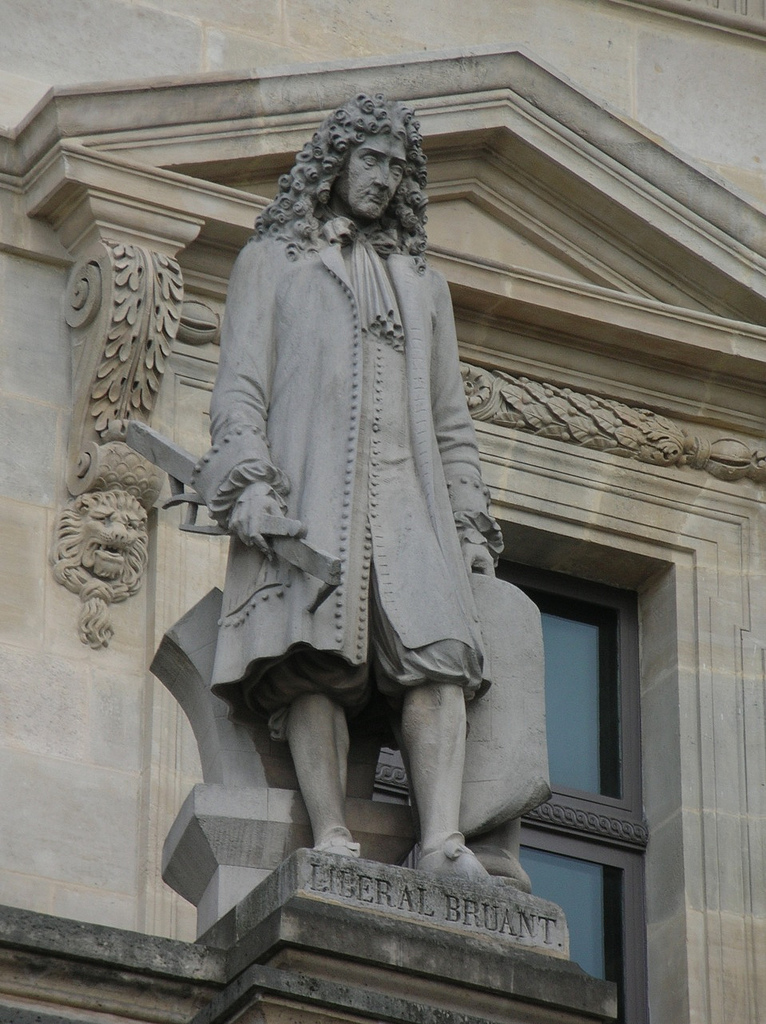
Libéral Bruant
Libéral Bruant (''ca'' 1635 – Paris, 22 November 1697), was a French architect best known as the designer of the Hôtel des Invalides, Paris, which is now dominated by the dome erected by Jules Hardouin Mansart, his collaborator in earlier stages of the construction. A comparison of Bruant's central entrance to the Invalides, under an arched cornice packed with military trophies with Mansart's ''Église du Dome'', gives a clear idea of the difference between Bruant's High Baroque and Hardouin-Mansart's restrained and somewhat academic Late Baroque. Bruant was the most notable in a family that produced a long series of architects active from the 16th to the 18th century. In 1660, Bryuant was the architect chosen for rehabilitations to Louis XIII's old arsenal (the ''Salpêtrière''), which was being converted into what would become the world's largest hospice. It is now the Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital. In the Marais district of Paris, the ''hôtel particulier'' Bruant bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turgot Map Of Paris
The Turgot map of Paris (french: link=no, Plan de Turgot) is a highly accurate and detailed map of the city of Paris, France, as it existed in the 1730s. The map was commissioned by Parisian municipality chief Michel-Étienne Turgot, drawn up by surveyor Louis Bretez, and engraved by Claude Lucas. Description The Turgot map was published in 1739 as an atlas of twenty non-overlapping sectional bird's-eye-view maps (at a scale of approximately 1:400) in isometric perspective toward the southeast. Additionally, there is one simplified general map with a four-by-five grid showing the layout of the twenty sectional maps. The atlas covers an area approximately corresponding to the first eleven of the modern-day arrondissements of Paris. Each sectional map consists of double-facing sheets and is wide; the first row is high, while the remaining rows are high. The assembled map is in height and in width. Turgot's map has been described as "the first all-comprising graphical invento ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indre-et-Loire
Indre-et-Loire () is a department in west-central France named after the Indre River and Loire River The Loire (, also ; ; oc, Léger, ; la, Liger) is the longest river in France and the 171st longest in the world. With a length of , it drains , more than a fifth of France's land, while its average discharge is only half that of the Rhôn .... In 2019, it had a population of 610,079.Populations légales 2019: 37 Indre-et-Loire INSEE Sometimes referred to as Touraine, the name of the historic region, it nowadays is part of the Centre-Val de Loire Regions of France, region. Its Prefectures in France, prefecture is Tours and Subprefectures in France, subprefectures are Chinon and Loches. Indre-et-Loire is a touristic destination for its numerous monuments that are part of the Chât ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richelieu, Indre-et-Loire
Richelieu () is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department in central France. It lies south of Chinon and west of Sainte-Maure de Touraine and is surrounded by mostly agricultural land. Its inhabitants are called Richelais, and Richelaises. Because of its design as the "ideal city" of the seventeenth century, the town is the subject of protective measures for its architecture. History In 1343, salt became a state monopoly by order of the Valois king Philip VI, who established the ''gabelle'', the tax on salt. Anjou was part of the "great gabelle" area and encompassed sixteen special tribunals or "salt granaries", including that of Richelieu. The village was a 17th-century model "new town". It was built at the order of Cardinal Richelieu (1585–1642), who had spent his youth there and bought the village of his ancestors; he had the estate raised to a '' duché-pairie'' August 1631. He engaged the architect Jacques Lemercier, who was already responsible for the Sorbonne and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faye-la-Vineuse
Faye-la-Vineuse () is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department in central France. Population See also *Communes of the Indre-et-Loire department The following is a list of the 272 communes of the Indre-et-Loire department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Indre-et-Loire {{IndreLoire-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Séry-lès-Mézières
Séry-lès-Mézières (, literally ''Séry near Mézières'') is a commune in the Aisne department in Hauts-de-France in northern France. Population See also *Communes of the Aisne department The following is a list of the 799 communes in the French department of Aisne. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):Communes of Aisne Aisne communes articles needing translation from French Wikipedia {{SaintQuentin-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiefdom
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal allegiance, services and/or payments. The fees were often lands, land revenue or revenue-producing real property like a watermill, held in feudal land tenure: these are typically known as fiefs or fiefdoms. However, not only land but anything of value could be held in fee, including governmental office, rights of exploitation such as hunting, fishing or felling trees, monopolies in trade, money rents and tax farms. There never did exist one feudal system, nor did there exist one type of fief. Over the ages, depending on the region, there was a broad variety of customs using the same basic legal principles in many variations. Terminology In ancient Rome, a " benefice" (from the Latin noun , meaning "benefit") was a gift of land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
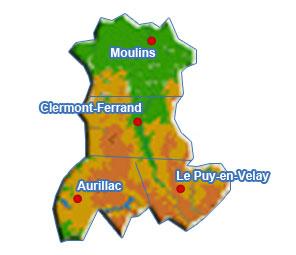
Auvergne (region)
Auvergne (; ; oc, label=Occitan, Auvèrnhe or ) is a former administrative region in central France, comprising the four departments of Allier, Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal and Haute-Loire. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes.. The administrative region of Auvergne is larger than the historical province of Auvergne, one of the seven counties of Occitania, and includes provinces and areas that historically were not part of Auvergne. The Auvergne region is composed of the following old provinces: * Auvergne: departments of Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal, northwest of Haute-Loire, and extreme south of Allier. The province of Auvergne is entirely contained inside the Auvergne region * Bourbonnais: department of Allier. A small part of Bourbonnais lies outside Auvergne, in the neighbouring Centre-Val de Loire region (south of the department of Cher). * Velay: centre and southeast of department of Haute-Loire. Velay is entirely contained inside the Auvergne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |