|
Jean-Henri Hassenfratz
Jean Henri Hassenfratz (20 December 1755 – 26 February 1827) was a French chemist, physics professor, mine inspector, and participant in the French Revolution. In 1794, Hassenfratz took part (with Monge) in the creation of the École Polytechnique (first known as ''École centrale des travaux publics''). Hassenfratz became its first professor of physics, a position he held until 1815, when he was succeeded by Alexis Petit (a former child prodigy and Polytechnique alumni who would soon discover the Dulong–Petit law, in 1819). External links * Hassenfratz's (1802"Sur les Ombres colorées,"''Journal de l'Ecole polytechnique, ou Bulletin du travail fait à cette école, ser. 1, vol. 4,'' p. 272 - 283 - digital facsimile from the Linda Hall Library The Linda Hall Library is a privately endowed American library of science, engineering and technology located in Kansas City, Missouri, sitting "majestically on a urban arboretum." It is the "largest independently funded publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Henri Hassenfratz
Jean Henri Hassenfratz (20 December 1755 – 26 February 1827) was a French chemist, physics professor, mine inspector, and participant in the French Revolution. In 1794, Hassenfratz took part (with Monge) in the creation of the École Polytechnique (first known as ''École centrale des travaux publics''). Hassenfratz became its first professor of physics, a position he held until 1815, when he was succeeded by Alexis Petit (a former child prodigy and Polytechnique alumni who would soon discover the Dulong–Petit law, in 1819). External links * Hassenfratz's (1802"Sur les Ombres colorées,"''Journal de l'Ecole polytechnique, ou Bulletin du travail fait à cette école, ser. 1, vol. 4,'' p. 272 - 283 - digital facsimile from the Linda Hall Library The Linda Hall Library is a privately endowed American library of science, engineering and technology located in Kansas City, Missouri, sitting "majestically on a urban arboretum." It is the "largest independently funded publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaspard Monge
Gaspard Monge, Comte de Péluse (9 May 1746 – 28 July 1818) was a French mathematician, commonly presented as the inventor of descriptive geometry, (the mathematical basis of) technical drawing, and the father of differential geometry. During the French Revolution he served as the Minister of the Marine, and was involved in the reform of the French educational system, helping to found the École Polytechnique. Biography Early life Monge was born at Beaune, Côte-d'Or, the son of a merchant. He was educated at the college of the Oratorians at Beaune. In 1762 he went to the Collège de la Trinité at Lyon, where, one year after he had begun studying, he was made a teacher of physics at the age of just seventeen. After finishing his education in 1764 he returned to Beaune, where he made a large-scale plan of the town, inventing the methods of observation and constructing the necessary instruments; the plan was presented to the town, and is still preserved in their library. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
École Polytechnique , a Japanese video-games developer/publisher
{{disambiguation, geo ...
École may refer to: * an elementary school in the French educational stages normally followed by secondary education establishments (collège and lycée) * École (river), a tributary of the Seine flowing in région Île-de-France * École, Savoie, a French commune * École-Valentin, a French commune in the Doubs département * Grandes écoles, higher education establishments in France * The École, a French-American bilingual school in New York City Ecole may refer to: * Ecole Software This is a list of Notability, notable video game companies that have made games for either computers (like PC or Mac), video game consoles, handheld or mobile devices, and includes companies that currently exist as well as now-defunct companies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexis Thérèse Petit
Alexis Thérèse Petit (; 2 October 1791, Vesoul, Haute-Saône – 21 June 1820, Paris) was a French physicist. Petit is known for his work on the efficiencies of air- and steam-engines, published in 1818 (''Mémoire sur l’emploi du principe des forces vives dans le calcul des machines''). His well-known discussions with the French physicist Sadi Carnot, founder of thermodynamics, may have stimulated Carnot in his reflexions on heat engines and thermodynamic efficiency. The Dulong–Petit law (1819) is named after him and his collaborator Pierre Louis Dulong. Biography Petit was born in Vesoul, Haute-Saône. At the age of 10, he proved that he was already capable of taking the difficult entrance exam to France's most prestigious scientific school of the time, the École Polytechnique of Paris. He was then placed in a preparatory school where he actually served as a "''répétiteur"'' to help his own classmates digest the course material. He duly entered Polytechnique at the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
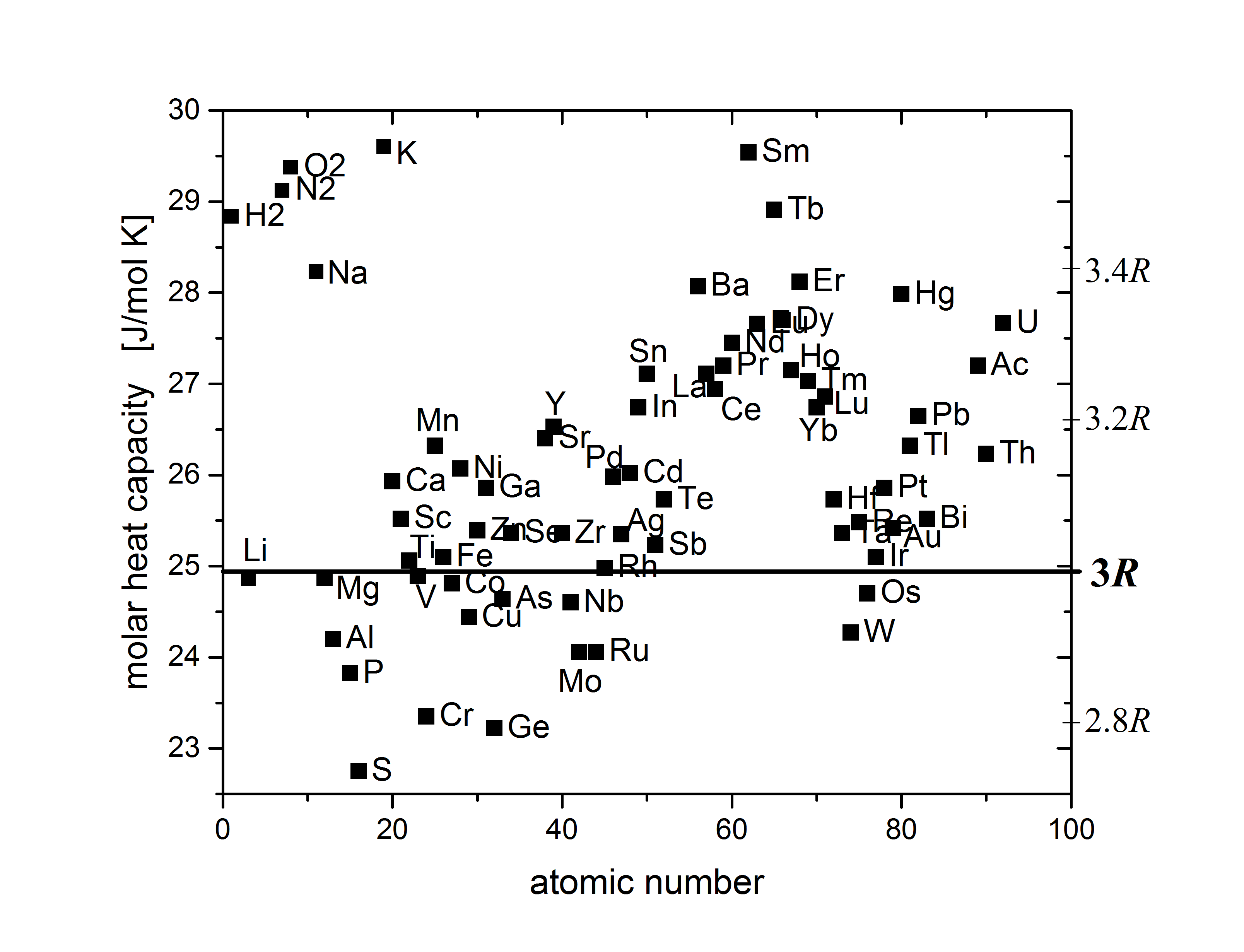
Dulong–Petit Law
The Dulong–Petit law, a thermodynamic law proposed by French physicists Pierre Louis Dulong and Alexis Thérèse Petit, states that the classical expression for the molar specific heat capacity of certain chemical elements is constant for temperatures far from the absolute zero. In modern terms, Dulong and Petit found that the heat capacity of a mole of many solid elements is about 3''R'', where ''R'' is the universal gas constant. The modern theory of the heat capacity of solids states that it is due to lattice vibrations in the solid. History Experimentally Pierre Louis Dulong and Alexis Thérèse Petit had found in 1819 that the heat capacity per weight (the mass-specific heat capacity) for 13 measured elements was close to a constant value, after it had been multiplied by a number representing the presumed relative atomic weight of the element. These atomic weights had shortly before been suggested by John Dalton and modified by Jacob Berzelius. Dulong and Petit were u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linda Hall Library
The Linda Hall Library is a privately endowed American library of science, engineering and technology located in Kansas City, Missouri, sitting "majestically on a urban arboretum." It is the "largest independently funded public library of science, engineering and technology in North America" and "among the largest science libraries in the world." Description Established in 1946 through the philanthropy of Linda (1859–1938) and Herbert F. Hall (1858–1941), of the Hall-Bartlett Grain Co., the library has achieved global recognition and stature. The library is open to the public with individual researchers, academic institutions and companies from Kansas City and around the world using the library’s extensive research-level collection. Though not affiliated with its neighbor, the University of Missouri-Kansas City, many students and faculty from UMKC and other local colleges and universities utilize the library each day. The library's William N. Deramus III Cosmology Theater ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1755 Births
Events January–March * January 23 (O. S. January 12, Tatiana Day, nowadays celebrated on January 25) – Moscow University is established. * February 13 – The kingdom of Mataram on Java is divided in two, creating the sultanate of Yogyakarta and the sunanate of Surakarta. * March 12 – A steam engine is used in the American colonies for the first time as New Jersey copper mine owner Arent Schuyler installs a Newcomen atmospheric engine to pump water out of a mineshaft. * March 22 – Britain's House of Commons votes in favor of £1,000,000 of appropriations to expand the British Army and Royal Navy operations in North America. * March 26 – General Edward Braddock and 1,600 British sailors and soldiers arrive at Alexandria, Virginia on transport ships that have sailed up the Potomac River. Braddock, sent to take command of the British forces against the French in North America, commandeers taverns and private homes to feed and house the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1827 Deaths
Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number), the natural number following 17 and preceding 19 * one of the years 18 BC, AD 18, 1918, 2018 Film, television and entertainment * ''18'' (film), a 1993 Taiwanese experimental film based on the short story ''God's Dice'' * ''Eighteen'' (film), a 2005 Canadian dramatic feature film * 18 (British Board of Film Classification), a film rating in the United Kingdom, also used in Ireland by the Irish Film Classification Office * 18 (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the ''Dragon Ball'' franchise * "Eighteen", a 2006 episode of the animated television series ''12 oz. Mouse'' Music Albums * ''18'' (Moby album), 2002 * ''18'' (Nana Kitade album), 2005 * '' 18...'', 2009 debut album by G.E.M. Songs * "18" (5 Seconds of Summer song), from their 2014 eponymous debut album * "18" (One Direction song), from their 2014 studio album ''Four'' * "18", by Anarbor from their 2013 studio album '' Burnout'' * "I'm Eighteen", by Alice Cooper commonl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th-century French Chemists
The 19th (nineteenth) century began on 1 January 1801 ( MDCCCI), and ended on 31 December 1900 ( MCM). The 19th century was the ninth century of the 2nd millennium. The 19th century was characterized by vast social upheaval. Slavery was abolished in much of Europe and the Americas. The First Industrial Revolution, though it began in the late 18th century, expanding beyond its British homeland for the first time during this century, particularly remaking the economies and societies of the Low Countries, the Rhineland, Northern Italy, and the Northeastern United States. A few decades later, the Second Industrial Revolution led to ever more massive urbanization and much higher levels of productivity, profit, and prosperity, a pattern that continued into the 20th century. The Islamic gunpowder empires fell into decline and European imperialism brought much of South Asia, Southeast Asia, and almost all of Africa under colonial rule. It was also marked by the collapse of the large S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientists From Paris
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences. In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosophical study of nature called natural philosophy, a precursor of natural science. Though Thales (circa 624-545 BC) was arguably the first scientist for describing how cosmic events may be seen as natural, not necessarily caused by gods,Frank N. Magill''The Ancient World: Dictionary of World Biography'', Volume 1 Routledge, 2003 it was not until the 19th century that the term ''scientist'' came into regular use after it was coined by the theologian, philosopher, and historian of science William Whewell in 1833. In modern times, many scientists have advanced degrees in an area of science and pursue careers in various sectors of the economy such as academia, industry, government, and nonprofit environments.'''' History The roles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th-century French Chemists
The 18th century lasted from January 1, 1701 ( MDCCI) to December 31, 1800 ( MDCCC). During the 18th century, elements of Enlightenment thinking culminated in the American, French, and Haitian Revolutions. During the century, slave trading and human trafficking expanded across the shores of the Atlantic, while declining in Russia, China, and Korea. Revolutions began to challenge the legitimacy of monarchical and aristocratic power structures, including the structures and beliefs that supported slavery. The Industrial Revolution began during mid-century, leading to radical changes in human society and the environment. Western historians have occasionally defined the 18th century otherwise for the purposes of their work. For example, the "short" 18th century may be defined as 1715–1789, denoting the period of time between the death of Louis XIV of France and the start of the French Revolution, with an emphasis on directly interconnected events. To historians who expand th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |